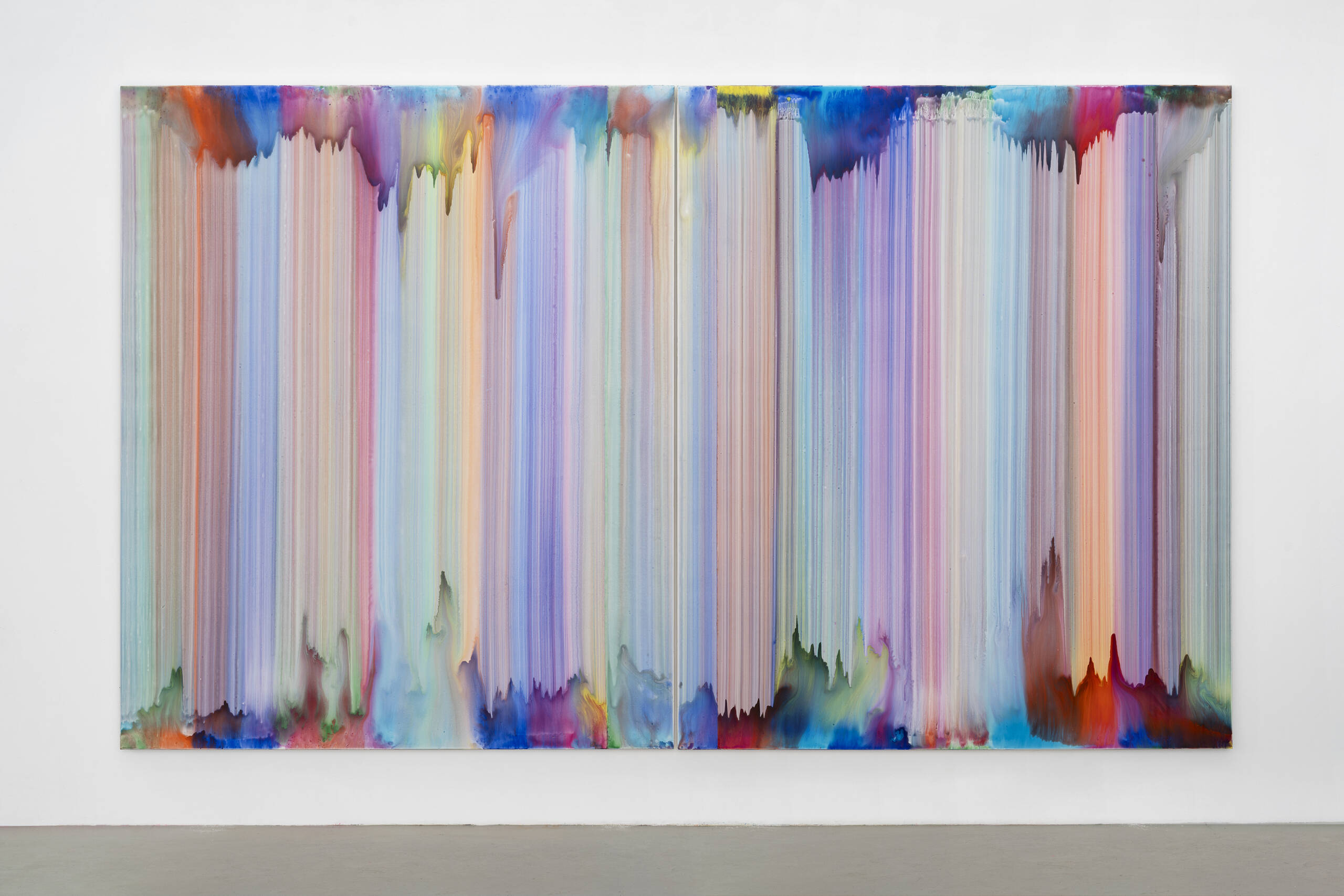
‘Geller’, 2024, on display at Bernard Frize’s upcoming exhibition at the LA branch of Marian Goodman Gallery.
Bernard Frize is an artist who lets the materials decide for him. A French painter who has been developing his uniquely industrial practice over the past 45 years, leading gallery Marian Goodman announced their representation of him in 2024. Ahead of his inaugural solo exhibition at Marian Goodman’s Los Angeles space, Cleo Scott asks him about process, materiality, and the role of the artist
LUX: Your works are centred around the process of creation. Can you take me through your process of creation of ‘Tama’, which will be on display in your upcoming exhibition at Marian Goodman in LA?
Bernard Frize: I’ve always liked the fact that my paintings are multicoloured, in other words that I don’t choose the colours and mix them. These paintings are very simple: large brushstrokes crossing the canvas vertically; there is an overload of paint on both edges because there is no beginning or end – could I say that the edges are in their raw state? In fact, I paint in both directions and I stop the brushstrokes before the end of the canvas. The latency, the veil which covers what has not yet explanation, but shows its potential, this is what I wish to call in these paintings.

Bernard Frize photographed before his work
LUX: Your works ‘Tama’, ‘Kario’, and ‘Voni’ appear to have been made using the same process of creation. What is the relationship between your works, focusing on process and materiality?
BF: I’m always fascinated by the dissolution of the image into its materiality or by the creation of images from their raw components.
It reminds me of the birth of Aphrodite on the shore of Paphos and I like to imagine how to describe a picture, her body emerging from the waves, which could also be interpreted as a plunge into the sea. There is always this temporal ambiguity in the image, between diving and emerging, doing and undoing; each gesture stopped at a moment in its course could have been something different if we had thought of other options. The paint is wet and then dries.
I went to Paphos a long time ago and stared at the beautiful sea; now, the place of Aphrodite’s birth has become a waterpark.
When doing a painting, either there is no goal, no objective, or there are means and processes for doing something. There is no idea without its material inscription. I like processes to embody ways of thinking. There is always a sequence of operations necessary for the organisation of a painting; I like this organisation and its possibility to be the motif of a painting, because after all, the subject of a painting is what makes it exist, not only what it represents, but also how it is represented. The word itself, representation tells us that it is presented two times.
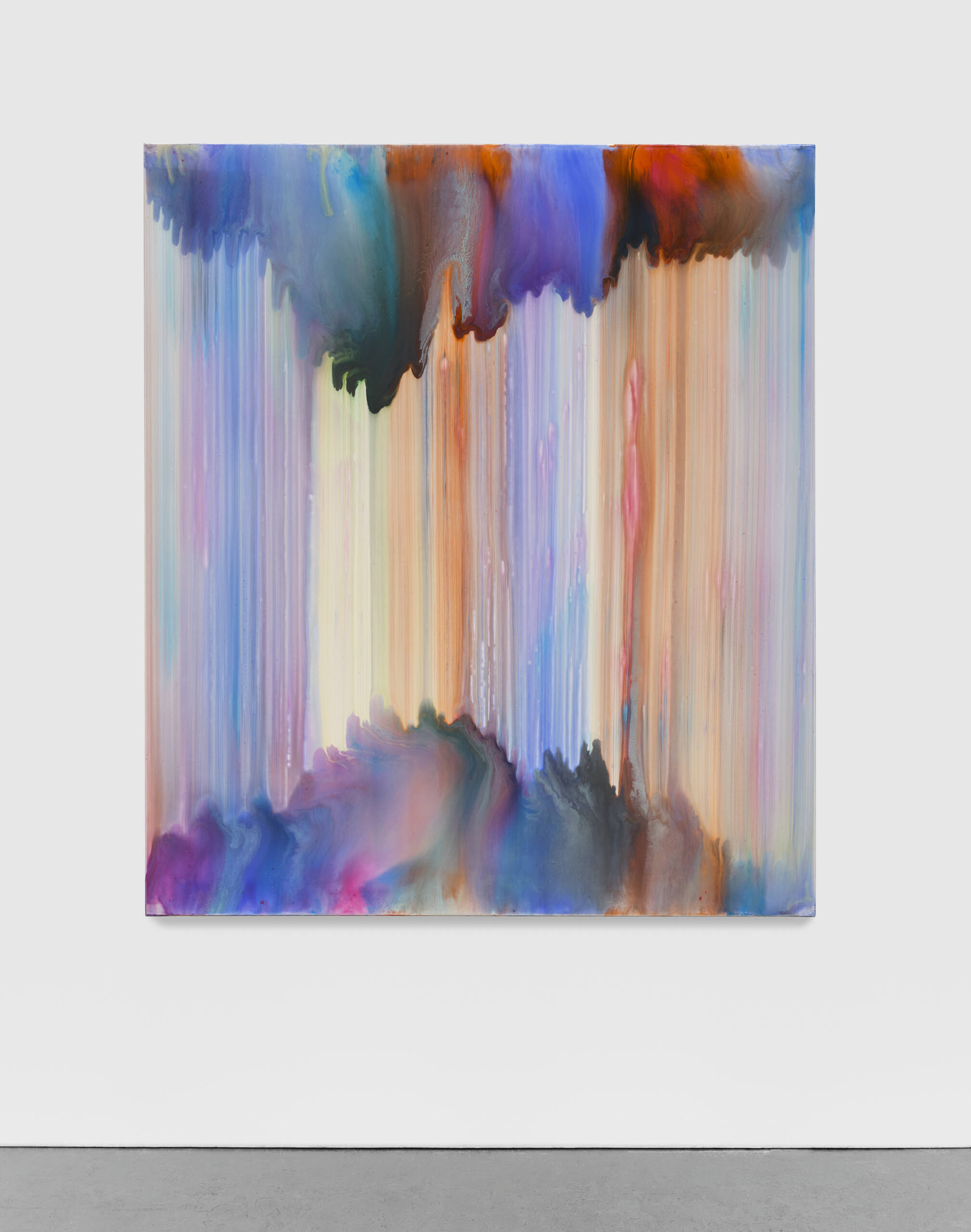

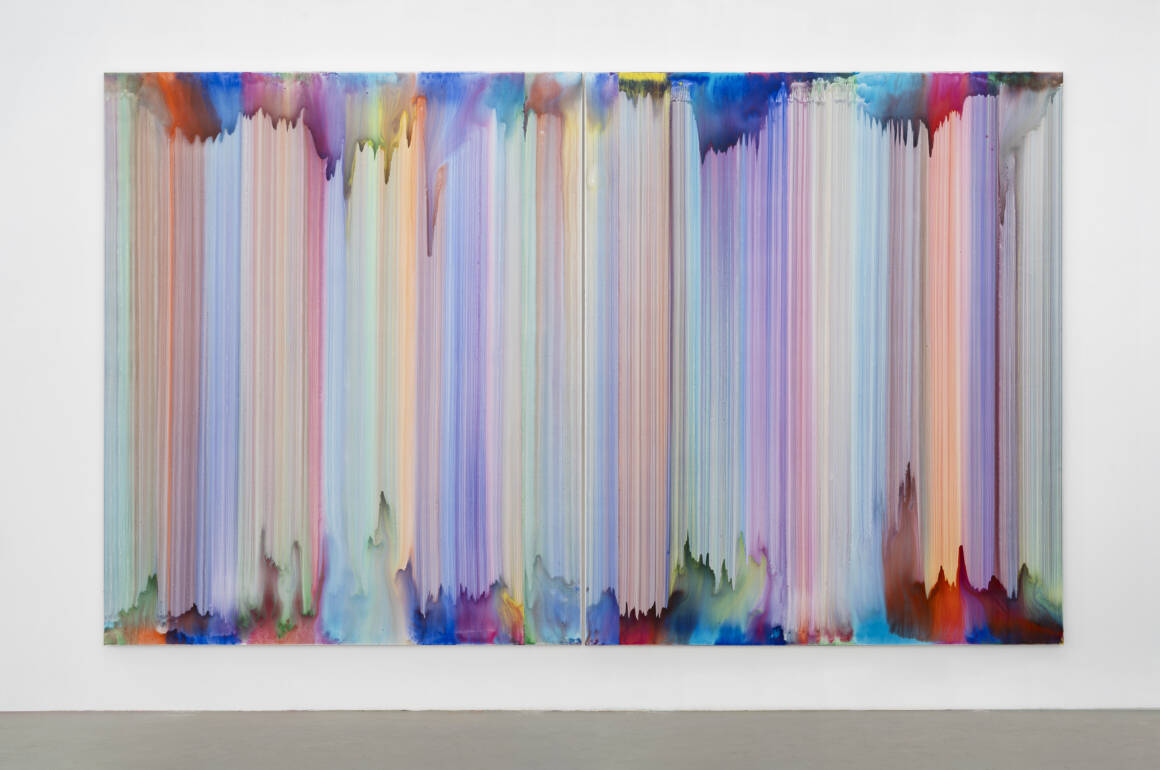
Bernard Frize’s ‘Voni’, which will be on display at his upcoming exhibition at the LA branch at Marian Goodman Gallery.
LUX: You have said ‘the method has disappeared under the conditions of its realisation’ in your work. Does this create a tension between your experience of creation and the viewer’s experience of its realisation?
BF: I will always feel and understand my painting in a different way than a viewer. A painting is not showing a recipe. Its description will, I hope, never exhaust what is in it. Why can we stay long minutes in front a painting in a museum, come back, and find again pleasure to see it? Isn’t it incredible that a canvas could provoke feelings and thoughts? Do we ever think about the painter? We mostly think about ourselves, how we receive the painting and decipher how the elements we look at are stimulating thoughts and feelings.
I always had some warmth enveloping me and a feeling of completeness from my visit in a museum. I am not receptive to all the paintings but looking at those which move me – and this is often changing – give me a feeling of wealth, of exhaustion. I hope my work can do the same; a work of art does not talk, does not say anything and will never be replaced by sentences. We read explanations on plates in the museums, do they satisfy our feelings?
Follow LUX on Instagram: @luxthemagazine
They give, at most, a context for the painting, and most people read them but do not look at the paintings more than the time it takes to read. The viewer and I have different goals; my work is to be as clear as possible to offer satisfying and intellectual pleasure which lasts and could be renewed.

Frize’s acrylic and resin painting ‘Irfan’, 2024, as part of Frize’s inaugural solo show.
LUX: How does the space of the Marian Goodman gallery in LA interact with your works?
BF: I have no idea! I only know the beautiful cardboard model that the French branch of Marian Goodman Gallery offered me. I printed the reproduction of my paintings and hang them into the model. I know that when I will see the real space, I will have another experience and I will hang the paintings.
LUX: Why have you chosen to be represented by Marian Goodman?
BF: I had the chance to meet Philip Kaiser a long time ago when he was working in the Kunsthalle Basel and always appreciated his curatorial vision. I was thrilled when he proposed me to join the gallery; I suppose everyone in the art world pays respect for the achievement of Marian Goodman’s gallery and for the exhibitions of the artists it is working with. There was, for me, no doubt that being represented by the gallery would be a great opportunity.
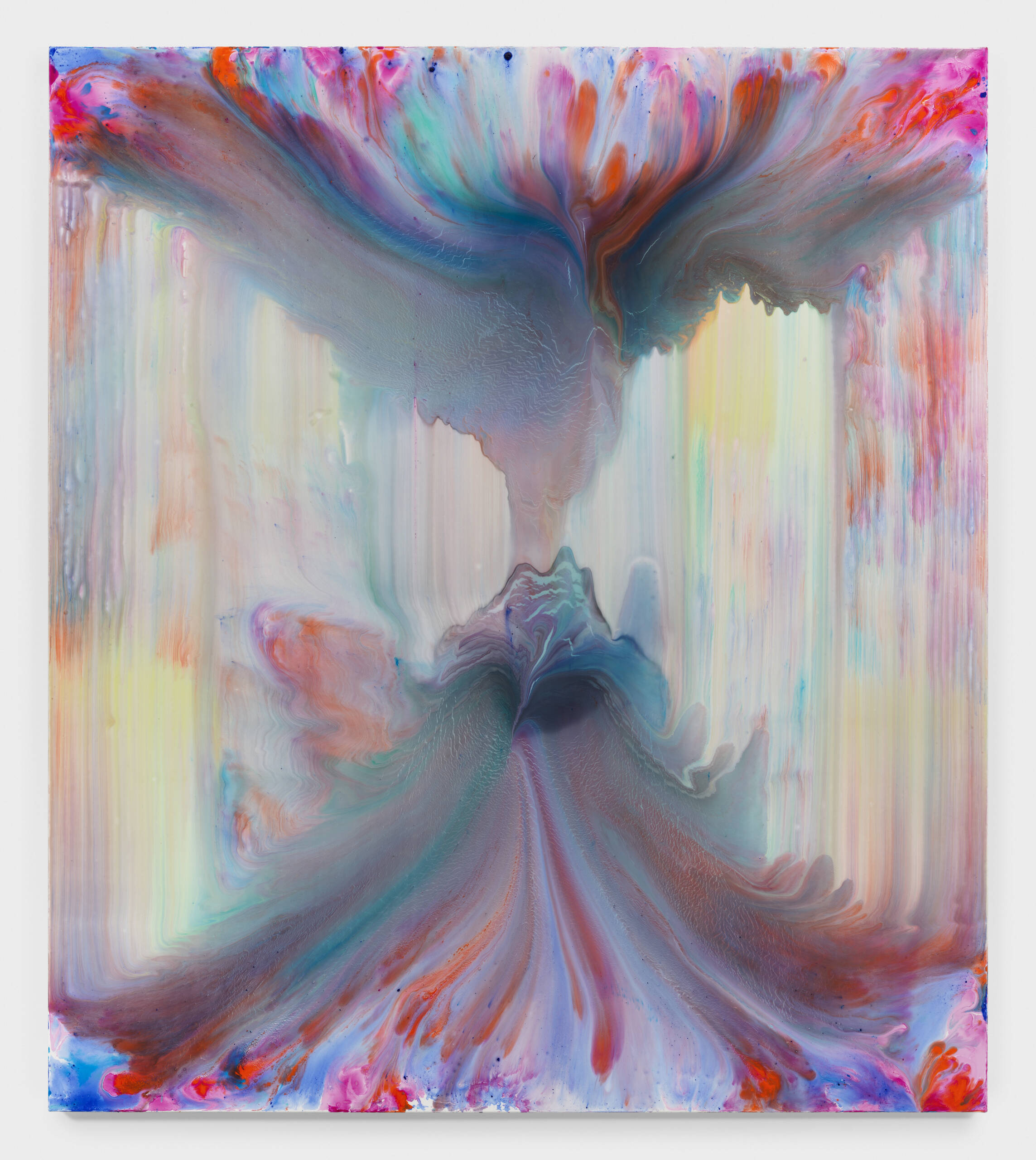

In ‘Yudzon’, the transparency of the layers reveal ‘the creation of images from their raw components’.
LUX: Are there any values – aesthetic or philosophical – that you share with the gallery?
BF: A gallery is a business; painting is a business too. I’ve spent many years, if not the majority of my adult life, without earning much from painting. I believe one continues to do what one likes not for the money but because one is driven. At one point, I had the chance to work with galleries who helped me to live from my work and found ways to distribute my work. There are many good artists at Marian Goodman Gallery who seem difficult to sell. I suppose it is a balance between the artists who sell well and those who don’t very much. The quality of their work is not a question. The aesthetic or philosophical qualities of these artists are not meeting market value, but aesthetic or intellectual ones. Meanwhile, the gallery respect them and decided to support them. Most galleries today would not do this, or would not afford it.
Read more: LUX curates for Richard Mille
I suppose running a gallery is an intellectual journey with companions you admire and you want to give them time to develop. In reverse, many galleries would not exist without the support of artists.
In my understanding, Marian Gallery is “old-fashioned” like one would say there is tradition in quality; there is a deep belief that good art is not always meeting the request of the market and it is important to give time to the time when the art is the main preoccupation.
Bernard Frize will be exhibiting his work at Marian Goodman, Los Angeles, from November 16th.
Markus Müller and Jean-Baptiste Jouffray on resilience and complacency in the green and blue economy

A sustainable blue economy is essential for the world’s future economic growth and environmental preservation
Markus Mueller, global head of ESG in the chief investment office at Deutsche Bank, has clear views on the transformation required to create a sustainable economic system. Meanwhile Jean-Baptiste Jouffray, of Stanford University and previously the Stockholm Resilience Centre, is a leading young thinker around the effects of our era on the oceans. LUX Editor-in-Chief Darius Sanai brings them together for a refreshing and thought-provoking conversation.
What happens when a leading economist with a strong understanding of science and a focus on the oceans, and a brilliant young ocean scientist with an interest in economics, get together? Fireworks, or at least one of the more interesting conversations to be had over Zoom.
I first introduced Markus, a good friend and at that point also a client of ours, and Jean-Baptiste, whose charm and perspective on the oceans and what needs to be done had always intrigued me, a year or so ago, and we decided a free-ranging chat about the economy, oceans, and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) would be compelling for our readers. So we came together again, over Zoom, and it was as engaging as I had hoped.
Markus is a thought-leading economist and also a realist; Jean-Baptiste is a brilliant thinker on the oceans but also knows sustainability is indelibly linked to economic systems. Let the conversation begin.
Follow LUX on instagram: luxthemagazine
Darius Sanai: Let me start with the question of shifting baselines. As I understand it, that means that people of a certain age or coming into awareness at a certain time have a different experience of the world than those who remember things 20, 30 years prior, in a world that’s rapidly changing.
Specifically when it comes to the environment and nature, although that could also include politics, economics, and everything else. As a basic example, a child today could thinks 40 degree summers and green winters in the Alps are “normal”. How important is this? Is it a universal negative? And how do we address it?
Markus Mueller: I think shifting baselines is something which fortunately makes humans and societies resilient. Because they automatically, through the shifting of baselines, adapt to the new reality which they have not seen unfolding.

Deutsche Bank’s Markus Müller says that nature-based solutions are a critical tool in creating a sustainable economic system
DS: Does it also make them complacent?
MM: This is a risk. It makes them complacent at the same time. There is a little bit of ambiguity. So, on the one side, I think it’s an important ingredient for social and economic development in the end because it makes us resilient in regards to changing environmental constitution and impacts on us.
But being not aware of this change makes us too complacent in the sense that we might run into a risk that something will further limit our development.
DS: Jean-Baptiste, can I ask you a variation of the same question? Last week, I watched a repeat of a TV show made in 2010, a murder mystery. The police detectives are standing outside the scene of the crime in the British countryside in summer.
And what struck me was that this frame was full of insects. And right now, 2024, just 14 years later, you wouldn’t see these insects. That’s a shifting baseline because a child born in 2010 would have no idea. That has to be a worry?
Jean-Baptiste Jouffray: Thanks, Darius. I think Markus knows how to trigger a debate because by pointing out how a shifting baseline is making us more resilient, he’s already triggered me. From an academic perspective, the shifting baseline syndrome is really well documented – it’s a whole theory, to explain change’s in the natural environment. And I wouldn’t have started by saying it makes us more resilient.
I would have argued that it makes the loss of resilience. One of the challenges of the shifting baseline is that, as you just pointed out with your example of the loss of biodiversity and insects in the British countryside, as generations come through, they are no longer accustomed to what things used to be.
Read more: Javad Marandi on investing and philanthropy
A very typical example in the coastal environment is fisheries in Florida, where you have historical photos of the catches of competition that takes place every year, about who is able to catch the biggest fish. And it’s a striking legacy of photos because you go back 70 years ago and you see the size of the fish and the first prize is this gigantic fish.
And the fishermen holding the fish and smiling with it. And as the years go by, the first prize goes to smaller and smaller fish. And it is almost an iconic illustration of the shifting baseline. For the people who come into that competition for the first time, that’s their biggest fish and that’s what the ecosystem has. There is no memory of what it used to be.
MM: And this is what I meant! And this is exactly the point why are we in a more biological devastating situation yet are still acting. Because we do not know how it was, we just know it in memory. It’s a nice story. I’m doing now the same with the younger generations.
When I was young, I went into church in April, and it was still snowing. It’s now warm. But I worry because I recognize it. But the new generations who just hear this from me do not worry about the situation in general.
JBJ: And that’s why I would argue that it may lead to inaction.
MM: Exactly. And complacency. It is a slippery slope because it shrinks our possibilities. It limits the room, which is already limited through physics and physical limitations.
DS: Can I now ask with regard to the situation you both outlined, just relating that to the question of effective change on climate and the blue economy? The idea of shifting baselines means, that I think we agree, that people are less incentivized to act because they don’t see change because it happened before they remember. Yet the change has happened.
How important is that emotive aspect in creating meaningful action? Or in fact, is that an irrelevance? Because the economic system and the regulatory system, which are not shaped by emotion, but by capitalism, are set up in a way that cannot enable this change. So is it really something that we shouldn’t be worrying about?
Read more: The future of philanthropy: AVPN South Asia Summit, Mumbai
JBJ: I would argue that it matters a lot and that emotions matter a lot and that it has been one of the battles that ocean conservation has had to face, when it comes to places in the ocean so remote like the deep sea, for instance, which has had to fight that battle for public awareness and public emotions.
How can people relate to a place that is pitch dark, 6,000 meters below the water and that no one has ever seen except a handful of people? More people used to have walked on the moon than actually dived at the very bottom of the Mariana Trench. So that aspect of emotion has been something really important in the context of ocean conservation.
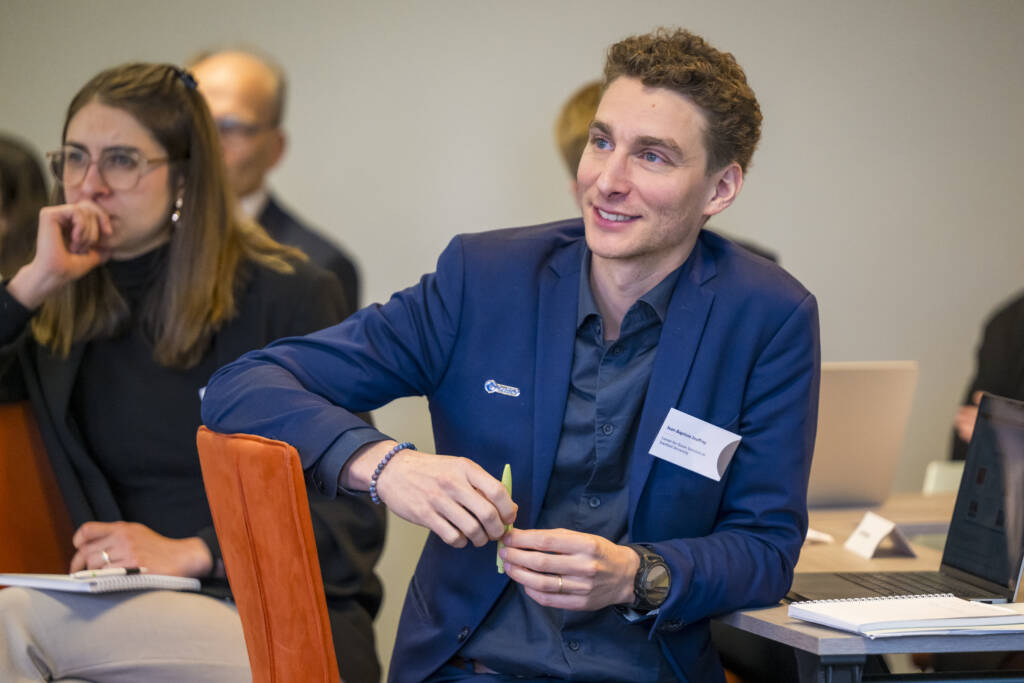

Jean-Baptiste Jouffray says that shifting baselines, where new generations do not have the same perception of what environmental “normality” is, are a real and present issue. Photograph by Pelle T Nilsson/SPA
MM: In terms of economics, put simply we don’t need more money in order to deal with the situation. We just need to make the money flowing in the sustainable and economically viable projects if we factor in all costs. But this is not what we are currently doing. Hence, I fear that we run into situations where suddenly something is not anymore possible. And then we change. So you see this with the energy situation in Europe.
DS: On that note, Markus and Jean-Baptiste, so it’s now nine years since the SDGs were adopted. It’s coming up to four years since the Dasgupta report (which outlined the need for a new economics of biodiversity, to create systemic change in the sustainable future). How would you rate progress?
MM: I think in general, the progress is there. But this progress in the biodiversity and the ocean world has also been piggybacked by the climate change discussion, which is more immediate to us as more and more have to admit that they feel it.
Something which was there, which we didn’t know that it was there, and which then disappears, we don’t miss. This is one problem. The other problem is that it’s so local that it’s maybe not relevant for us in other places.
My last point is that we do not have a systemic discussion. We still have a very separate discussion. And this leads to the following problem. For example around SDG 4, education. Someone said to me recently, why is the SDG 4 so under-invested?
And for me, it’s clear, because if you do not have a labour market in a country which is able to absorb highly skilled people. Why should you invest in education, from a return capital perspective? So we need to think about developing a system which enables us also to generate the returns we need for societal prosperity in the end. It is not just as simple that we say, we stop here and all will be good. We also need to find an answer to what will the people get out of it to feed their families, to pursue their daily life. And if I develop education without having a functioning labour market, I will have a brain drain in the best case. In the worst case, I will have no investments in education.
JBJ: I think Markus made some really interesting points. Starting with how can we care about something we didn’t know existed.
Well, that really brings us back to the shifting baseline syndrome. And it’s interesting because, in a sense, that is one of the issues, right? So I’m glad we finally came to terms with that.
MM: But again, this is a risk. But it’s interesting that we are still able to survive in situations where something is not anymore there, which has been there before, right?
JBJ: Absolutely. No, no. And I’m half teasing you, half being serious here. But one of the embodiments of the shifting baseline syndrome is precisely that lack of caring, which might hinder progress. That’s one aspect.
To answer your question, Darius, yes, there is progress. But what we’re seeing, first and foremost, is progress in the vision rather than the impact. So in other words, we are living in an era of ambitious collective vision, but limited collective impact.

Oceans are at systemic risk from climate change. Photograph by Isabella Fergusson
I think the vision is one thing, and it’s great. That’s where we’ve seen countries coming together. That’s where we’ve seen multiple stakeholders coming together. That’s why there’s an increasing number of multi-stakeholder collaboration and voluntary commitments.
All those are articulating progress in the vision of what one should do. But the impacts do not follow. And I think if we look at metrics, we’re nowhere close to where we should be given the urgency of the situation.
The financial sector is not doing, what it should do. The private sector is not doing, what it should do. It doesn’t have the incentives to do so. And the governments and the regulators certainly are not levelling the playing field and doing what they should do.
We’re now within six years of the 2030 agenda and we are not on track to achieve any of the SDGs. The Kunming Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework may be superseding the SDGs and giving us an outlook for a post-2030 agenda with more ambitious targets.
MM: I would agree. The other thing I wanted to add is that, compared for example to AI, the discussion about ESG is not liked. Sustainability is not liked. It’s seen as a paternalistic activity driven by regulators and governments.
Who wants to tell us how we should live, how economies should act? A regulatory approach for more sustainable development should be supportive, an approach which enables the economy, corporates, individuals to find solutions for their challenges… instead of telling them what they should not do.
Read more: Art collector Andrea Morante talks on artist Sassan Behnam-Bakhtiar
So these are two different sides of the same coin. To forbid something, but at the same time to enable something.
JBJ: I could argue that those two are not exclusive. And so I would tell Markus, maybe, you know, maybe regulators should enable while forbidding.
What I’m trying to get at here, and it’s something we have discussed in the context of the role of financiers in particular, is that I agree with Markus that there is a role for finance and financiers and financial institutions as enablers of sustainable futures and enablers of the blue economy.

The world’s oceans produce more than 2/3 of our oxygen and are essential for regulating our climate and biodiversity. Photograph by Isabella Fergusson
That brings us back to this dominant narrative in the blue economy of an ocean finance gap, right? Because, indeed, SDG 14 (about the oceans) is the least funded goal of all. So there is a gap in terms of ocean conservation.
There’s not enough investment going towards sustainable and equitable projects and into ocean conservation. In that sense, regulators, the public sector, the private sector and the financial institutions really have a role to play as enablers to unlock capital towards those projects.
DS: What needs to happen this year?
JBJ: Gosh, so many things. If I stick to the context of the ocean economy and the blue economy, one of the high-level processes that is ongoing is the ratification of the United Nations Agreement on Biodiversity beyond National Jurisdiction.
That’s often referred to as the High Seas Treaty or the BBNJ Treaty, which has been celebrated as a landmark of multilateralism. Countries have agreed on the treaty, which was a milestone, and now it needs 60 signatories to enter into force.
As of today, there are only four signatories. So if you ask me, by next year, which will also coincide with the 2025 UN Ocean Conference hosted by France and Costa Rica, then my hope would be that, this serves as a milestone for the treaty to enter into force. So what I’m hoping to see and what needs to happen is 56 countries between now and next summer to actually ratify the BBNJ Agreement.
DS: Thank you. And Markus?
MM: At COP 29 (in Baku in November) in a nutshell, collaboration, alignment and trust-building will be crucial ingredients to make progress on all of the aims. To deliver in the end a resilient and sustainable future. I think we have a lot on our plate and we need to work on it.
I think it’s a bad idea to put more on the list instead of working down the pile of things we already have on the list. I think this is a challenge of the COP that it’s not about adding on top all the time. It’s rather about getting the things done we already have on our list instead of putting new things on.

Veronica Colondam champions the field of social entrepreneurship in Indonesia with the establishment of YCAB Foundation in 1999
Veronica Colondam was the youngest ever recipient of the UN-Vienna Civil Society Award, a World Economic Forum Young Global Leader, and received accolades throughout her career including Globe Asia’s Most Powerful Women in Indonesia, Forbes’ one of 10 most inspiring women in Asia and one of Asia’s 48 Philanthropists, and one of UN’s Solution Makers; through YCAB Foundation she helms a social enterprise that aims to improve welfare through education and innovative financing, running programmes that have reached over 5 million underprivileged youth. She speaks with LUX Leaders & Philanthropists Editor, Samantha Welsh about creating a sustainable system that scales change.
LUX: How have your spiritual beliefs informed your leadership values?
Veronica Colondam: I established YCAB Foundation in 1999 when I was 26 years old. Yayasan Cinta Anak Bangsa Foundation (YCAB) means ‘Loving the Nation’s Children Foundation’) and reflected my love for all Indonesia’s children and my aspiration to nurture intelligent and innovative young minds. As a committed Christian, I believe we are called to be the Salt & Light of this world, to be a Good Samaritan, to love our neighbour and to help all those in need. My leadership values foster a culture that prioritises Integrity, Service, Empathy, Resilience, Vibrancy, and Excellence (iSERVE.)
LUX: Was there a catalytic ‘aha’ moment, when the scale of social injustice in Indonesia impelled you to set-up YCAB to drive change?
VC: For me it all started with education injustice. About three years after YCAB was founded, I realized that the school drop-out rate in Indonesia was very high. Millions of students did not complete their primary education. Further, the ASEAN Free Trade agreement 2010 put Indonesians at a competitive disadvantage as our schools did not offer teaching in tech and English. In response, we launched our first Rumah Belajar (Rumah = house, Belajar = learning to improve English and tech literacy. The ‘aha’ moment was when my 12-year-old daughter, Adelle took me as parent chaperone on her school community project and introduced me to the concept of microfinance. This catalysed our YCAB family intervention model.

YCAB Foundation is the founding and flagship organisation in the YCAB social enterprise group which bases its operations on a mutually reinforcing and financially sustainable social change model
LUX: What was the thinking behind that?
VC: We implement a family intervention model that empowers both mothers and children – ‘prosperous mothers smart kids’. We can transform low-income families and lift them sustainably out of poverty. We focus on the mothers because research shows the critical impact of a mother’s prosperity on the household. Economically-empowered earning mothers are in a better position to support their children’s education, reducing high school drop-out rates and lifting the family unit.
Follow LUX on instagram @luxthemagazine
LUX: Why is YCAB’s microfinance model sustainable?
VC: This comes down to the integration of financial support with educational advancement. We deploy capital to fund low-income women entrepreneurs ensuring their children’s education is a precondition for loan access. This dual focus on immediate financial aid and long-term educational goals fosters a cycle of empowerment. Additionally, YCAB’s transition into a self-reliant social enterprise, where profits from its ventures are reinvested into its mission, underpins its sustainability. The model’s success is evidenced by its recognition and supervision by the Indonesian Financial Services Authority, highlighting its impactful and sustainable approach to breaking the cycle of poverty and promoting community welfare

YCAB’s change model has one clear mission which is to improve welfare through education and innovative financing. YCAB aims to vitalize underprivileged youths to become self-reliant through economic empowerment and education, bringing them from mere subsistence to sustainable livelihood
LUX: Twenty five years on, how successful has YCAB been in mobilising resources throughout Asia?
VC: We mobilized more than $120M US to reach over five million low-income young people, together with hundreds of thousands of mothers. This is equivalent to a per capita increase from $2 to the threshold of an aspiring middle class at $8.
LUX: How did YCAB evolve from a not-for-profit to a social enterprise model?
VC: Honestly, I didn’t know anything about the concept of social enterprise back in 1999! In fact, the term “social enterprise” only began gaining recognition in Indonesia about 12-15 years ago. I initially founded YCAB with financial sustainability in mind and after the first year, I started-up a company as the first business unit of the foundation. Over time, we developed several business units to support the foundation’s mission and around 10 years’ later, after my INSEAD program, I realised we were operating under a social enterprise model.
LUX: Where does microfinance fit within social impact entrepreneurship?
VC: Microfinance operates as a business model and enables the poor to access capital. This embodies the essence of social entrepreneurship, where business and social impact are integrated into the model. We leverage our for-profit businesses to support the mission of YCAB, the foundation, so we operate our education program under the YCAB Foundation structure, and the economic empowerment program for mothers (or MFi) under YCAB Ventures, a company licensed by the Indonesian Securities and Exchange Commission (OJK) since 2015. Under the Ventures structure mandated by OJK, we engage in equity-like investments to support SMEs and have expanded into impact investment. This structure allows us to consolidate all our companies that support YCAB’s mission into a portfolio — from our original business units to new impact investments. The Ventures structure provides us with the flexibility to engage in financing (MFi), investments across all business units and new impact ventures, all while advancing our agenda of empowering families out of generational poverty towards a prosperous future.

YCAB believes in the power of education to improve welfare. To date, YCAB has brought impact five millions underprivileged youths and hundreds of thousands of low income families
LUX: YCAB’s partners rank among the world’s leading corporates; what is it about your approach to partnerships over 25 years that secures engagement at this level?
VC: We are commited not only to meet the needs of our beneficiaries but also to align closely with the objectives of our partners, some being the world’s leading corporations. One key aspect of our partnership strategy is our engagement with governments. Sustainable change requires collaboration across sectors, so partnering with governments allows us to leverage their resources, expertise, and influence to optimise our impact. Furthermore, our board members bring their expertise, networks, and insights to the table which enhances the value proposition for our partners, because partnerships are strategic, impactful, and mutually beneficial. Successful partnerships are built on a foundation of trust, collaboration and a shared commitment to driving positive change.
Read more: Zahida Fizza Kabir on why philanthropy needs programmes to achieve systemic change
LUX: Was there any time that you overcame a barrier that, in retrospect, catalysed a systemic solution to a particularly challenging social problem?
VC: The first standout catalytic moment was our shift in focus from preventing youth drug addiction to primary prevention through education and soft skill development, addressing the root causes of youth curiosity toward substance abuse. However, gaining access to schools, the focus of our target audience was a significant challenge. In 2002, in a pivotal moment for YCAB, I and our board member Professor Rofikoh Rockim met the former Minister of Education, Mr. Yahya Muhaimin. He granted us his influential letter of recommendation so we could access schools and campaign with authority. This shows the impact of personal connections, advocacy, and strategic partnerships that sparked transformative change and empowered communities throughout Indonesia.
The second catalytic moment was the covid pandemic. During lockdown, we could only help people who had basic literacy and smartphones to access e-support, including e-donations. We also used a WhatsApp-based chatbot. This revolutionised the financial literacy of mothers, the clients of our MFi program. The pandemic also opened the door to financing social goods using capital market products, such as mutual funds. To coincide with YCAB’s 25th Anniversary in August 2024, we will launch financial products that offer financial returns with social impact. This is gamechanging because with philanthropy in Indonesia, there is generally no tax deduction for donations aside from Islamic zakat giving which is regulated by a national zakat collection body. For non-religious non profits like YCAB, giving is not tax deductible so private corporate CSR donations are taken from EBITDA, contrary to public-listed companies.

YCAB is now exploring ways to implement the last link in its change model, that is, to create a sustainable system whereby students who graduate and become entrepreneurs or employed can pay it forward
LUX: What is impact exactly for a social impact entrepreneur and how can you measure it fully?
VC: At YCAB, we embed impact measurement into all our programs. With our microfinance initiative, for example, we conduct our “welfare survey” with our beneficiaries tracking our impact on their increased earnings, business expansion, and perhaps most significantly, the educational opportunities their children receive as a result of our interventions.
LUX: Finally, how do governments and financial institutions benefit by partnering with SIEs?
VC: We are not sitting behind our desks, we are out there in the heart of communities, listening, learning, and understanding their real needs. These grassroots connections mean our initiatives are genuine and address issues where they make impact, right where people live and breathe. We are always pushing boundaries, finding fresh ways to tackle age-old problems. When governments and financial institutions join forces with us, they are tapping into that spirit of innovation. When we innovate together, that vision becomes more than just a dream – it becomes our shared reality.

SAJIDA Foundation is a value-driven, non-government organisation. It embodies the principle of corporate philanthropy.
From a garage school start-up with 12 children educated for free with two meals a day, fast forward 30 years and SAJIDA’s annual budget is close to US$13 million with a microfinance portfolio of approximately US$300 million and seven independent portfolio companies. CEO Zahida Fizza Kabir speaks with LUX Leaders & Philanthropists Editor, Samantha Welsh, about relieving extreme poverty through systemic interventions in climate change resilience, women’s health and livelihood, mental health, and urban poverty.
LUX: How did SAJIDA come about?
Zahida Kabir: In 1972 my father was MD & Chairman of Pfizer Bangladesh, which in 1991 reincorporated as Renata. Renata is the fourth largest pharma company in Bangladesh. SAJIDA Foundation was the brainchild of my father, who was driven by compassion and a strong sense of duty towards the less fortunate. It started modestly in 1987 as a school for underprivileged children in my parents’ former garage.
In 1993, my father gave 51% of Renata’s shares to SAJIDA as a 25th wedding anniversary gift to my mother. I have been with SAJIDA since the start, shared my father’s vision, and helped it grow to the organisation you see today
LUX: How did you evolve your leadership role?
ZK: I have always believed in empowering women, particularly mothers; SAJIDA recognizes the pivotal role women play within the family, community, and broader social context. At SAJIDA, we advocate for the holistic empowerment of women within the context of their multifaceted roles and contributions. Bangladesh is still a country with about 32 million people living below the poverty line. Women in particular face significant barriers to recover in health and education. SAJIDA is committed to mitigating the gaps by focusing on women’s and mothers’ welfare.
The organisation, founded in 1993, aims to empower communities, catalyse entrepreneurship, build equity and establish enterprises for good with an overarching vision of ensuring health, happiness, and dignity for all.
LUX: What are SAJIDA’s standout impacts?
ZK: Thirty years on, we have representation in 36 districts impacting lives through our Development and Microfinance programmes. Microfinance Programme empowers over 700,000 participants, mostly women, to benefit from our USD 377 million portfolio.
This lifts more than 6 million individuals, or 1.5 million households, annually. At SAJIDA, we see all our work through a gender lens. How is our work benefiting women? Are we investing in the welfare of the mother?
Follow LUX on instagram @luxthemagazine
LUX: How are women’s rights reflected in SAJIDA’s governance?
ZK: SAJIDA is a family of over 6,000 employees, each contributing to drive meaningful change.We advocate strongly for our female employees at all levels when it comes to implementing safeguarding policies at in their workplace. We also advocate for female leadership at all levels.
Since founding, SAJIDA has been led by a woman. Women encounter disproportionate challenges across various domains, yet their invaluable contributions are often overlooked for short-term gains. At SAJIDA we understand that empowering women leads to exponential impact.
LUX: What are the main areas of SAJIDA’s work?

SAJIDA’s operations in Bangladesh have touched over 6 million individuals through its multi-sectoral development programmes which focus on poverty alleviation, community healthcare and climate change.
ZK: SAJIDA interventions are under two main umbrellas – healthcare (which includes Renata Ltd) and financial inclusion. Our development programmes blend both within our main themes: climate change, women’s health and livelihood, mental health and urban poverty. Our Climate Change Programme targets vulnerable communities, utilizing a Locally Led Adaptation approach.
Uttaran Programme focuses on women’s health and livelihood development striving to improve Reproductive, Maternal, Neonatal, Child, and Adolescent Health outcomes. We recognize the unique multiple challenges faced by the urban extreme poor with our SUDIN programme adopting a holistic approach encompassing economic, health, education, community mobilisation together with our Mental Health Program. Indeed, we are dedicated to advancing mental health care in Bangladesh and have one of the country’s largest multidisciplinary mental health care teams.
LUX: How is this work supported at grass roots level?
ZK: We support the health programs in a number of ways. We have a 80-bed hospital equipped with ICU, NICU and dialysis facilities; our Home & Community Care service for the elderly; Inner Circle Private bespoked suite of services for special needs and autistic children; and, most recently, Neuroscience & Psychiatric provides mental health care. My commitment is to prioritize solutions to social challenges over purely profit-driven ventures and we catalyse entrepreneurship to empower communities through our financial inclusion interventions. Our Microfinance Programme fosters economic empowerment. We have also established our Impact Investment Unit to offer investment opportunities to smaller ventures.
LUX: How do you teach women to value entrepreneurship?
ZK: SAJIDA’s Microfinance Programme prioritises women’s economic empowerment by providing collateral-free loans. Our interventions are also at point of inter-generational wealth transfer, as it is important to guide second-generation women and affluent women to make good decisions and use their resources effectively. To extend our entrepreneurial ecosystem, we collaborate with Orange Corners to launch initiatives to support innovative ideas provided the company has at least one female founder. We believe using tech is a driver to women’s effective entrepreneurship and innovation. Digitally-literate women entrepreneurs deliver 35% higher ROI compared to their male counterparts.
Read more: Leading MACAN, Indonesia’s first contemporary art museum
LUX: How is SAJIDA using tech to scale engagement with your programs?
ZK: Our goal is to be a fully-digitised organization so we have launched several mobile and web Apps to offer a range of functions and services to our beneficiaries, stakeholders and SAJIDA employees. Our Microfin360 FO collection App is a digital credit system that synchs all transaction history in real-time with a web application, allowing Field Officers to view essential daily reports such as due reports, unrealised collection reports, and loan settlements. We are developing a Digital Passbook ‘Agrani: Amar Pashbook’ to give our Microfinance Programme clients access to their financial information, facilitate communication, and offer essential services.
Our Field Force Management Platform (FFMP) is an App which automates outdoor workforces and facilitates easy monitoring of field employees in real-time with its instant notification feature. In 2022, we launched our Monitoring Module to streamline our Monitoring and Evaluation processes through a dashboard for our monitoring officers to access data, analyse, share and report on impacts from their laptops. We favour a programmatic approach over projects if we are to maximize lasting impact. And for this we need sustainable, long-term funding.

The foundation enables communities to have agency over their own development, be their own drivers for change and instill a vested interest in their own futures.
LUX: How can microfinance help communities, for example, to become climate resilient?
ZK: Bangladesh is the seventh most extreme disaster risk-prone country in the world. To build climate resilience we have to open up access to water and sanitation infrastructures. Microfinance can facilitate tailored loans and microloans for constructing rainwater harvesting systems, ensuring communities have access to clean water during the dry season, significantly improving community health and resilience. Customized financial products, including savings, credit, and insurance, which are tailored to the local context can be instrumental in supporting smallholder farmers in disaster-prone regions. Microfinance can facilitate investments in climate-resilient practices and the adoption of environment-friendly technologies by designing loans to support MSMEs to purchase environment-friendly technologies and agro-machineries. Weather-indexed insurance and bundle insurance for both crop and livestock can act as a shield against unprecedented climate events.
LUX: Where do you collaborate to scale climate resilience?
ZK: In areas where SAJIDA microfinance branches are not present, we collaborate with other Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) to reach a wider range of climate-vulnerable communities. By providing first-loss guarantees, or credit guarantees, SAJIDA facilitates the provision of zero-interest loans through partner MFIs. This strategy maximizes the impact of our resources, enabling us to extend the benefits of reduced-interest loans to a broader population, acting through intermediaries. It is important to take a collaborative approach with public and private agencies to enhance the effectiveness of microfinance interventions. Remote consultancy and weather advisory services can increase the community members’ capacity to implement resilient practices. Matched savings products where the community members can collectively save and receive matching funds from the programme and rotational savings products to facilitate savings and investment in resilient agricultural practices, can further empower these communities. The programme can also support the green skills enterprise within these communities, which are necessary for implementing and maintaining climate-resilient practices
LUX: What is the role for NGOs?

The foundation covers four thematic areas: catalysing entrepreneurship, fostering equity, community empowerment and enterprises for good.
ZK: As Bangladesh’s journey progressed, and the country graduated from an LDC to an LMIC, we, at SAJIDA also evolved our approaches accordingly. We transitioned from a service delivery mindset to a system-strengthening approach. This evolution involves enhancing existing public systems rather than operating separately. NGOs have a crucial role to play in shaping broader climate financing and sustainable development strategies at the macro level. NGOs also serve as incubators for innovation, testing, and refining models that can be scaled up and replicated across diverse contexts. However, they should engage with the public administration, private entities, and policy-making bodies from the outset so that real-world needs are aligned with broader development goals.
LUX: What is the approach to public private partnerships?
ZK: The start-up and social enterprise ecosystem is at a nascent stage in Bangladesh and many parts of Africa. To support ecosystem development, sector-specific incubation and accelerator programs need to be introduced and the deployment of blended patient capital will be critical. As mentioned, this is why SAJIDA is currently implementing the Orange Corners program, to provide heavy-touch mentorship to budding entrepreneurs to develop effective business models. SAJIDA also implements smart solutions in the areas of WASH, agriculture, and health to empower and uplift communities. I believe an empowered community will be attractive to the private sector and thus paves a pathway for mobilising additional capital.
LUX: Philanthropists talk about taking ‘baby steps’, how would you guide a philanthropist starting on their journey?
My father was a caring, compassionate and empathetic man. From a young age he was deeply troubled by the inequalities in the world around him. He wanted to solve a very complex problem, that of poverty. I believe that behind every desire to make a change is a passion to challenge and to stand up for the most neglected in society. We all have to believe that it is our responsibility to make a contribution to the betterment of our society. The size of the contribution does not matter – no amount is too small. Ask yourself this, what will be my legacy? What kind of a world do I want to see for the next generation? I urge everyone to take that leap. Take that small step to see what you can do.
Philanthropic pioneers across education, conservation, health and culture , on key issues in the rapidly changing world of philanthropy. In association with UBS Optimus Foundation

Patrizia Sandretto Re Rebaudengo is the founder and President of Fondazione Sandretto Re Rebaudengo. After graduating in Economy and Business at Turin university, she approached the world of contemporary art as a collector, in the early 1990s.
The cultural educationist
Who: Patrizia Sandretto Re Rebaudengo
What: Founder and president, Sandretto Re Rebaudengo Foundation
Where: Italy Achievements: Creating one of Italy’s leading contemporary art foundations and cultural education programmes together with the Italian Ministry of Culture; creating a new environmental and cultural centre from the island of San Giacomo, Venice.
LUX: How does educational philanthropy work effectively?
PSRR: In the educational workshops of the Sandretto Re Rebaudengo Foundation – the non-profit contemporary art centre I have led since 1995 – children are involved in activities designed to develop creativity, collaboration and mutual trust.
The challenge is precisely to imagine and then structure, within a contemporary-art museum, a dynamic learning and growth experience for a small group. I think it is very important to think of the museum as an educational agency, capable of promoting an education based on respect, coexistence, plurality. Philanthropy comes later and accordingly.

Works from “Visual Persuasion”, an exhibition by Pauline Olowska at the Sandretto Re Rebaudengo Foundation, Turin, 2023-24
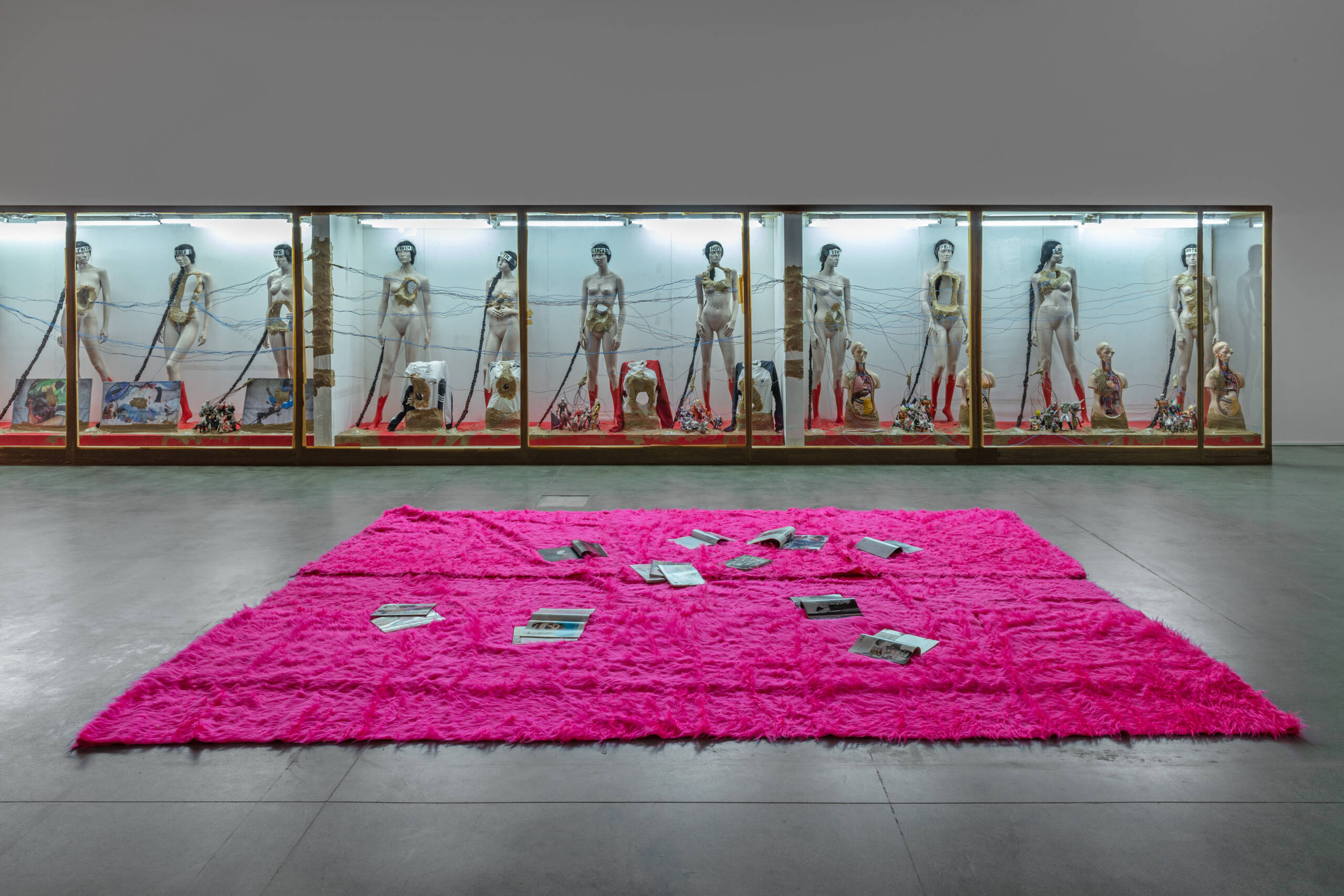

Works from “Visual Persuasion”, an exhibition by Pauline Olowska at the Sandretto Re Rebaudengo Foundation, Turin, 2023-24
Follow LUX on instagram: luxthemagazine
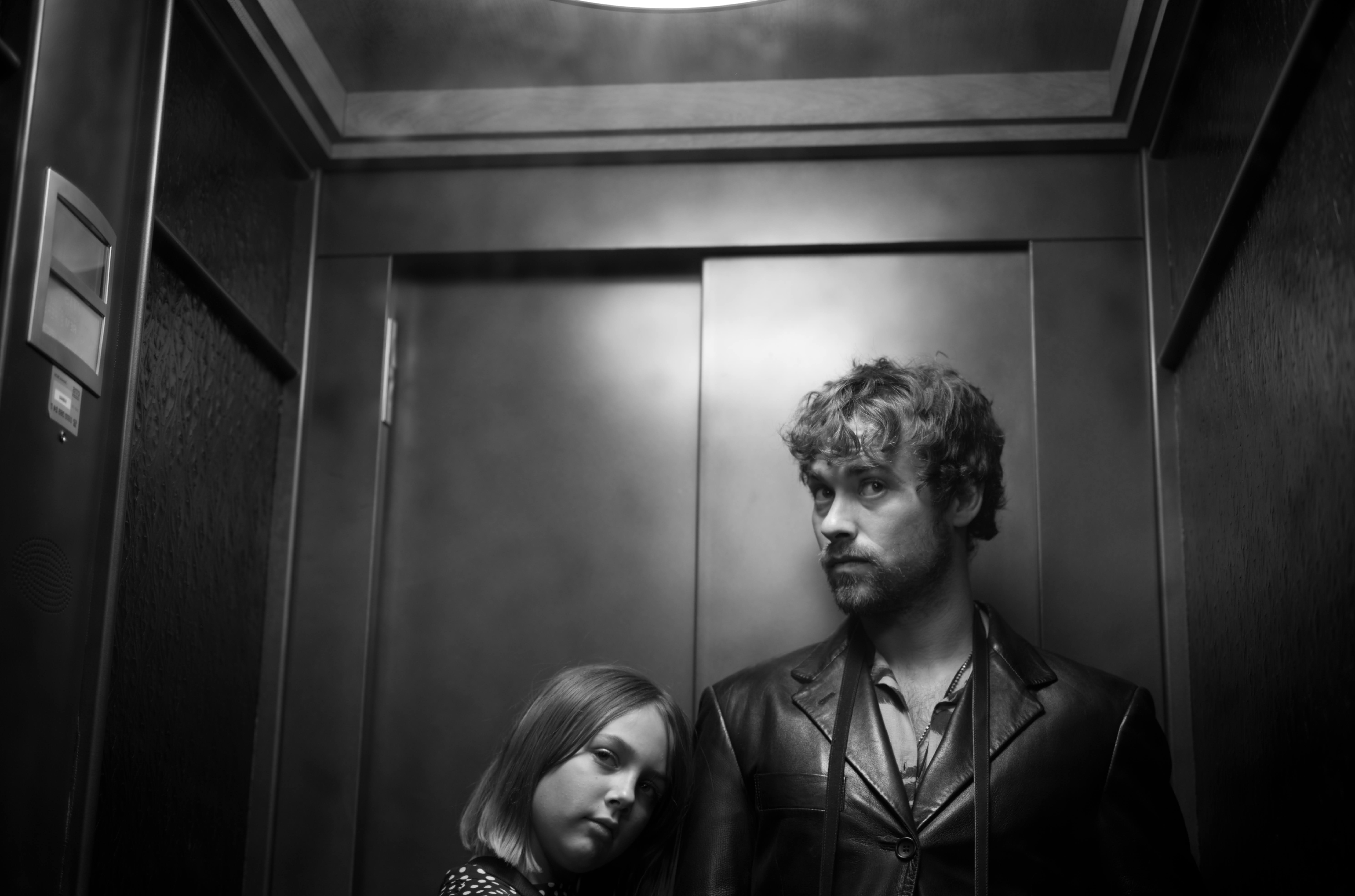

Self-portrait of Nachson Mimran and his daughter in Gstaad, Switzerland; October 2022; photographed by Nachson Mimran
The philanthropist entrepreneur
Who: Nachson Mimran
What: co-founder, to.org
Where: Switzerland Achievements: Developing a game-changing organisation combining philanthropy, investment, startup accelerator and socialenterprise multiplier.
LUX: Are the lines between philanthropy and profit-with-purpose getting blurred?
NM: Operationally, these lines cannot be “blurred” but business can support philanthropy. Our investment arm, TO Ventures, invests in teams that are building high-growth, high-impact, early-stage technology businesses across sectors to solve critical challenges for society and the environment. Returns from the TO Ventures programme finance the TO Foundation.
Additionally, in 2022, my brother Arieh co-founded with our nephew Joshua Phitoussi a dedicated decarbonisation fund, TO VC, spun out of the TO Ventures programme. Wasoko – a TO Ventures portfolio company – is Africa’s leading e-commerce B2B platform.
Working with major suppliers like P&G and Unilever, Wasoko accesses lower prices for mom-and-pop retailers across the continent, who can order fast-moving consumer goods on demand, allowing end customers to access goods more consistently and at more affordable prices. The company also recently announced that it is in merger talks with MaxAB, another TO Ventures portfolio company

In 2019, Olivier Wenden was appointed by HSH Prince Albert II of Monaco, Vice-President and CEO of the Foundation. Prior to this, he served as the Foundation’s Executive Director and Secretary General from 2014.
The national foundation director
Who: Olivier Wenden
What: CEO and Vice Chair, Prince Albert II of Monaco Foundation
Where: Monaco Achievements: Launching an ocean fund; running an annual ocean-week initiative bringing together investors, NGOs, philanthropists, entrepreneurs and institutions; creating a new Ocean Innovators platform.
LUX: How do you measure the impacts of your projects and initiatives?
OW: We ask each project we fund to complete final reports highlighting the results achieved in relation to the initial objectives. The indicators depend on the nature of the project itself and may, for example, indicate the surface area of a protected zone at sea or on land that the project contributed to extend, or the number of people in a community helped by a solution deployed.
Each year, we use this and other data to draw up an impact report, which we give to our benefactors so we can be transparent about the financial grants committed and the results achieved. Finally, we carry out audits on projects in the field to ensure that everything is aligned with our values and according to the established agreement.

Jessica Posner Odede is the CEO of Girl Effect, an international non-profit that builds media girls want, trust and need — from chatbots to chat shows and TV dramas to tech. Girl Effect’s content helps girls make choices and changes in their lives.
The female enabler
Who: Jessica Posner Odede
What: CEO, Girl Effect
Where: Kenya Achievements: running an international foundation bringing lasting education, enabling tools and enlightenment on fundamental health and education questions to girls in developing countries.
LUX: How do you leverage technology to achieve change?
JPO: Working online and offline, we move cautiously. We built a generative AI chatbot in a week to speak to girls about health and related questions for which they did not otherwise have access to answers; it spoke the way the kids speak, but it also “hallucinated”.
It made up information, whole sets of things that were just not true. So until we can launch a generated AI chatbot that doesn’t have the risk of promoting misinformation, we are using a much more manual chatbot.
Nonetheless, this project is a powerful example of how AI actually enables millions of girls across the world to access new opportunities and new services, and to enable themselves at massive scale, which we could have never done before.
A captured moment with Girl Effect, which supports girls in developing countries at every stage and pressure point in their life journeys
Read more: Hansjörg Wyss on his pioneering work in conservation

Ben Goldsmith is a British financier, philanthropist and environmentalist who has been at the forefront of campaigns for more rewilding in Britain and Europe. He founded and chairs the Conservation Collective, a network of locally-focused environmental foundations.
The conservationist
Who: Ben Goldsmith
What: Founder and chair, Conservation Collective
Where: UK Achievements: bringing together 20 individual conservation and environmental initiatives around the world under a single umbrella that provides expertise, leverage and effective tools.
LUX: Why does the environment matter?
BG: Environmental degradation is in a spiral with human suffering.
It’s always the poorest who suffer the hardest and the most when it comes to environmental pollution. The most obvious pathway to lifting people out of degradation is restoration.
More fish in the sea means fewer hungry people, healthier soil means more resilient food supply. Climate change is about a surfeit of carbon in the atmosphere; more nature means more carbon drawn out of the atmosphere.

Julie Packard is executive director of the Monterey Bay Aquarium, which she helped found in the late 1970s. She is an international leader in the field of ocean conservation, and a leading voice for science-based policy reform in support of a healthy ocean.
The ocean conservationist
Who: Julie Packard
What: Vice Chair, David and Lucile Packard Foundation
Where: US Achievements: Establishing and directing the gold standard for sustainable seafood; transforming the small fisheries industry in parts of Southeast Asia; funding education and research into ocean conservation in the US; founding the Monterey Bay Aquarium.
LUX: What have you learned through your educational programmes?
JP: When we opened the Aquarium 40 years ago, I thought the hardest part would be keeping the animals and exhibits healthy.
It turns out that our biggest challenge is on the dry side of the exhibits – how to engage people and get them to care on a personal level.
Our research has shown that it starts by drawing people into the awe, wonder and joy found in the ocean realm, then engaging them in learning more, casting a positive, hopeful vision of the future, giving people a way to help turn that vision into reality.
That’s true whether we’re talking to Aquarium guests about using less unnecessary plastic, or working with business partners to show the benefit to their bottom line of embracing sustainable seafood purchasing practices.

A mauve comb jelly, aka mauve stinger, seen at Monterey Bay Aquarium’s “Into the Deep” exhibition
Tom Hall is the Global Head of Social Impact & Philanthropy at UBS
“We have to be smart about how we allocate both philanthropic and investment capital, and we have to work in partnership with all of civil society”
Maya Ziswiler is Chair of the UBS Optimus Foundation
“How can you take advantage of your passion with rational thinking to ensure you’re actually having an impact, and working with others to maximise that?”
In association with UBS

Nina Hoas of LGT (right) and Silvia Bastante de Unverhau (left) of LGT Philanthropy Advisory in Kenya, tree planting
Global annual philanthropy giving today is estimated at over $1tr. The world will see the largest intergenerational transfer of wealth in history by 2045, some $84tr being passed down in US alone. Next gen inheritors are finding purpose in their wealth, responding to urgent causes, and driving change ‘in my lifetime’. LUX Leaders & Philanthropists Editor Samantha Welsh speaks with Head of LGT Philanthropy Advisory, Nina Hoas, on strategies for enhancing impact through collaboration, leadership, innovation and doing good, well.
LUX: What made you decide on a career centred on addressing inequalities and social justice?
NINA HOAS: I am Swedish, but when I was growing up my family moved and travelled around a lot, from Latin America to Asia, and I had the opportunity to live in places like Bangkok in Thailand where my family was for seven years. So I grew up in a family that was not afraid of being in different communities or sharing their experiences and being with different cultures. Every year from when I was one year old we would go to Kenya to stay with my godparents who lived in Nairobi and had a holiday home outside Mombasa. We would go to the Swedish school for a few weeks where my aunt was a teacher, and visit the nature conservation areas. Those experiences in Kenya really shaped my awareness of the socio-economic contrasts to my own home in Sweden as well as of course nature and biodiversity.

Preserving and replanting mangroves, which store carbon, preserve coastlines and act as biodiversity incubators, is important to many next generation philanthropists
LUX: What did that perspective teach you about privilege and shape your ambition?
NH: That holiday home outside of Mombasa was a different world to Sweden, with the housekeepers Kasongo and Yomo living a long bike ride away, in a mud hut, in a tiny village with no running water or electricity. Every year our family would visit and see their kids growing up. Back in the day we only thought in terms of charitable giving, not the empowerment approach we promote today. Donating clothes and food to their extended family was my first real experience of doing good. Schooling and education was not taken for granted for these children either, and all those experiences formed my career path. My godparents lived in Nairobi and were part of the United Nations (UN) community there, so I knew quite a bit about the UN and decided that was what I wanted to do. I therefore studied political science, and received a scholarship by SIDA, Sweden’s development agency, to make a MinorField Study in a refugee camp in West Africa for my Master’s degree. But already before University, I had interned in Kenya with an NGO and UNICEF which coupled with my studies set me on the path to a UN career.
LUX: What for you is ‘doing good, well’?
NS: Strategic philanthropy advisory at LGT is about encouraging more and better philanthropy. We share our network of experts and change-makers, provide platforms where philanthropists can come together, connect and learn from each other with the aim to help them embark on the philanthropy journey in a more strategic way. Strategic philanthropy is about the long term impact your wealth can have.
LUX: What is the approach to wealth in strategic philanthropy?
NH: The relationship managers in our office, together with family advisors, have conversations with clients around the elements of wealth as the starting point. How their wealth was created, how it is invested, how it is spent, how it is given and how wealth is governed and passed on. Every time there is a financial transaction there is an opportunity to have a positive impact. It is about how family values are passed on with the wealth and how these values are reflected in the philanthropic activities.

Rainforests are a carbon sink and produce life-giving oxygen; they are also essential for the maintenance of the earth’s biodiversity, which is inextricably linked to the planet’s habitability and sustainability as outlined by the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Follow LUX on instagram @luxthemagazine
LUX: Has your network been affected by the women social investment entrepreneurs’ (SIE) phenomenal growth globally, also why are they so successful in scaling?
NH: We usually talk about seven trends and right now next generation funders and specifically women funders is a significant one within those. Looking at our philanthropy network, we have a lot of women philanthropists we are working with and we noticed that for them it is not only about giving. They are keen to have a strategic approach to their philanthropy and ensure impact. Women drive a lot of the development and community. As a woman, I hence see it as not only the right thing to do, but also economically efficient to focus on the women in communities.
LUX: How far is technology influencing next gen investing strategies?
NH: Technology is very important, especially in scaling various invtiatives, which our Guide to Strategic Philanthropy we co-wrote with Pi covers this in one chapter. Though we increasingly see foundations start asking for technology and even AI and they want it because they understand they can grow and deliver faster services. On the approaches towards social good, the giving is one part, but it does not matter what the methodologies are that you are using, whether through impact bonds, mezzanine funding or partly impact investing or pure giving, whichever, you have a social goal and there are many approaches. We notice some entrepreneurs are very successful in using technology and are very often the ones that also want to adopt or adapt their skills and their experience to do good and they’re using that space.
LUX: Has ‘giving while living’ and philanthropy within a limited time frame created volatility and been disruptive?
NH: With next generation wealth holders in particular, they may have created a structure but want to show they are putting a time frame on it to clarify to donors, to family members and peers that if, for example, it is an endowment then they would spend down within 20 to 30 years. They are still relatively young, in the middle of their careers, and embarking on their philanthropic journey, and they want to act right now on the urgent issues, well before those issues worsen. They also feel strongly and passionately that they want to enjoy doing it in their lifetime and not leave the responsibility to another after their death.
Read more: Terre Blanche: The luxury resort pioneering sustainability

Recent research shows that forests are not just collections of distinct flora and fauna; they vast interlinked collective ecosystems which communicate with each other, and underpin sustainable development
LUX: What does inherited wealth mean to next gen U/HNWIs?
NH: LGT’s newest study is about wealth and about what wealth can do. We are asking only next generation wealth holders, the inheritors not the wealth creators (though some are both). Wealth needs to come with purpose. It is very hard for some of them inheriting and by being rich they do not want to feel poor. They want to separate themselves from their net worth and to have self worth. They want to use their wealth in a catalytic way to do good. They bring purpose to their own life if they can use their wealth through investment for a purpose to empower others. For example, one of our women philanthropists is working in communities in a few developing countries to empower women. In one community, she is reaching around 10,000 women and while they know the funds are coming from a specific foundation, they do not know that the founder is out there in person in the field alongside them as technical support; she remains anonymous to avoid the donor dynamic as she wants to be out there, able to hear if something is not right. She is caring for there to be a good systemic change on the ground and is concerned she will not get truthful feedback because the community will fear the funds will dry up if the project is not going right. She really wants to know what is going wrong so she can learn from mistakes, improve it and change it.
LUX: How does peer-to-peer collaboration help your clients?
NH: This is where strategic advisory comes in as well the connection to other philanthropic leaders. Our clients want to meet others who are focused on similar issues because they want to maximise impact and to collaborate to achieve that. Philanthropists can feel isolated so our purpose is also to connect philanthropists with one another, introduce them to others working in the same area, in order to learn and potentially to partner and to add value. This works well for example in the area of biodiversity and nature. We advise around 50 individuals that are focusing specifically on scaling conservation and nature-based solutions. In this context we took a group to the Massai Mara, which is one of the key initiatives of LGT Venture Philanthropy – the independent charitable foundation established by LGT Group Foundation and founded in line with the vision and values of the Liechtenstein Princely Family. The Princely Family’s long-term vision and commitment to sustainability are deeply rooted in LGT’s corporate culture, and they are very happy to collaborate with others also in philanthropy and impact investments.

Alan Lau and Durjoy Rahman. Photomontage by Isabel Phillips
Alan Lau is Vice Chairman of M+ Museum, the era-defining new institution in Hong Kong’s West Kowloon district. Here he speaks with philanthropist and collector Durjoy Rahman about why private individuals need to support artists and art activations, and how Asia is moving to control its own narratives in the cultural world. Moderated by LUX Leaders & Philanthropists Editor, Samantha Welsh
LUX: Why is private philanthropy and engagement important in bringing art to a broader audience in general and particularly in Asia?
Alan Lau: Private philanthropy and patronage are critical because governments rarely cover arts funding entirely. The percentage contribution from UK public sources is higher than in the US but patrons are needed not just for the money they bring in but for their networks, resources and connections that enable museums to develop.
One particularly interesting phenomenon is China where there are over a thousand private museums established by collectors. Many are located in Beijing, Shanghai and the largest cities, but a lot of them are set-up in corporate headquarters or the collector’s hometown, bringing art to a community that may not have had access to art before.

Alan Lau within the exhibition, ‘Yayoi Kusama: 1945 to Now’
Durjoy Rahman: Conventionally art philanthropy was the preserve of a small proportion of society. Patronage was offered by this tiny minority for centuries until now, in the 21st century. This is a new era for patronage. For our foundation, patronage involves strategic social investment into creativity and innovation for the wider public benefit. It takes account of our collective history, original cultures, and future directions and fosters the development of a more equitable, sustainable society.
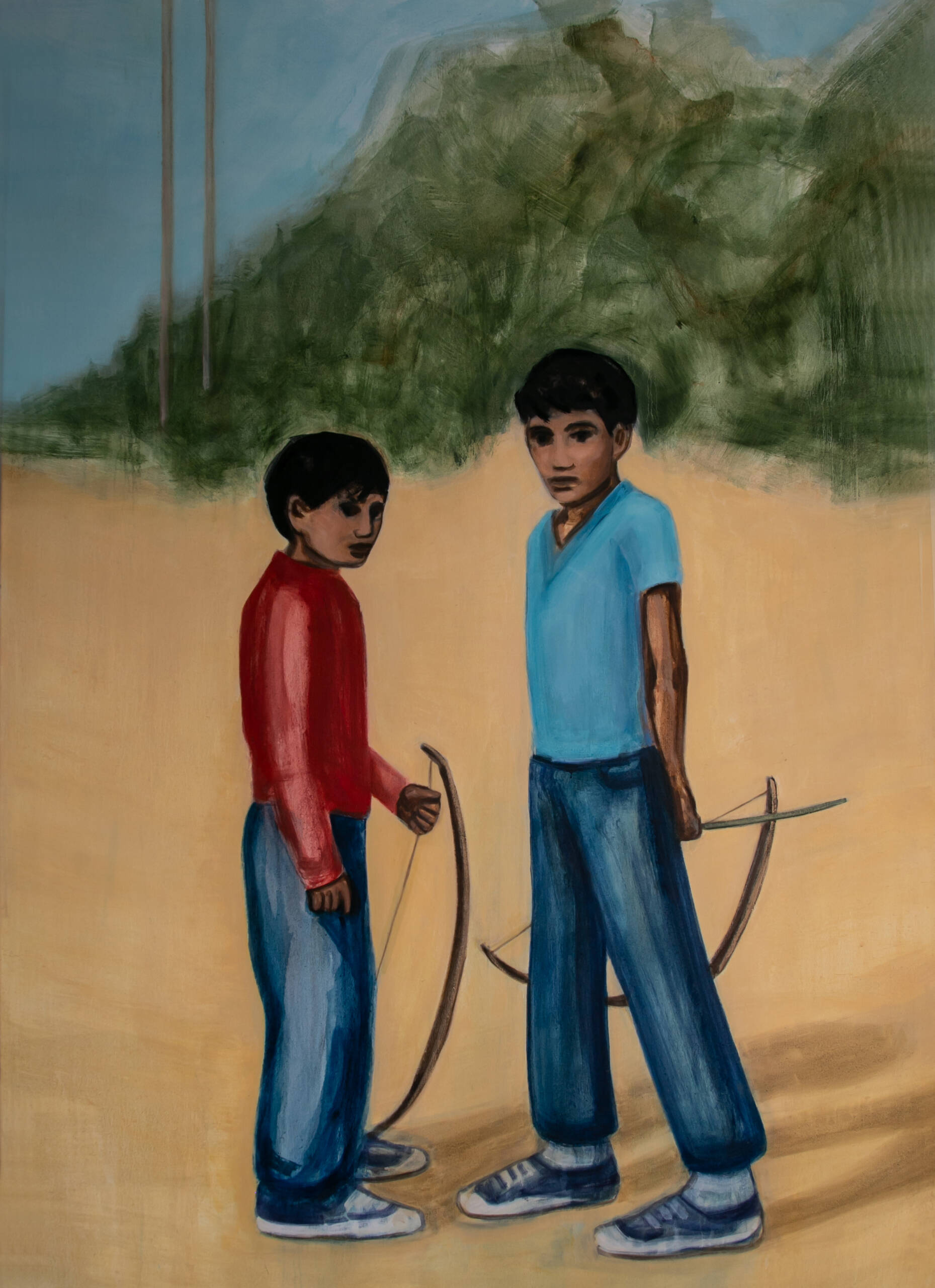

‘Archers’ (2021), by Matthew Krishanu, from the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation Collection
I am a business owner but I still felt that the economic landscape of GDP and foreign investment are not the only way to measure the development of a society. Art and culture help define who we are and where we came from, give rein to our imagination and support social justice.
LUX: Why is that particularly important in Asia?
AL: The benefit of not having a long history of arts philanthropy is that people experiment with different models. When wealth creation happens in this part of the world, it comes with the tradition of giving back and that is where the phenomenon of museums founded locally back in the hometown came from. The idea has propagated only over the past decade really.
Follow LUX on Instagram: @luxthemagazine
LUX: How has patronage and philanthropic support for institutions changed? And how should it change?
AL: It has always been the private patrons who have funded programs and supported curatorial roles, put their names on buildings and so on. There has been innovation in the institutional space about 20 years ago, starting from TATE Modern setting-up International patron groups in North America, Asia, MENA and growing to over ten committees. The Guggenheim and Pompidou have something similar. These patron groups bring people from different regions to support programming, curatorial research and exhibitions. So these are not municipal museums but institutions that serve a global audience and have a global perspective. The global patrons help attract resources into specific acquisitions and research. This is relatively new for museums. With corporate sponsorship too there is a lot of change.
DR: With patronage, we need also to open a conversation about overcoming cultural barriers. South Asia has a long history of art and culture but also long history of being colonised. So our arts and cultural heritage have not been projected properly. When global art movements started, the major arts and cultural institutions were set up in Europe. This meant that our legacy was not represented or discussed. The arts’ press, academics, art writers, also all were European, so there was no discussion or projection of our art heritage. We were left behind.
So with art philanthropy, what has changed over the past decade, has been led by major biennial art fairs and significant curatorial institutions, particularly in China, in Hong Kong like M+, India, Dubai and Saudi Arabia where I was recently in AlUla and Riyadh. We are all reassessing our lost identity, which was always there but not at the forefront simply because we did not own our story or have the press and art critics onside. You can have magnificent works but it is not enough if no one shares it with the wider audience.
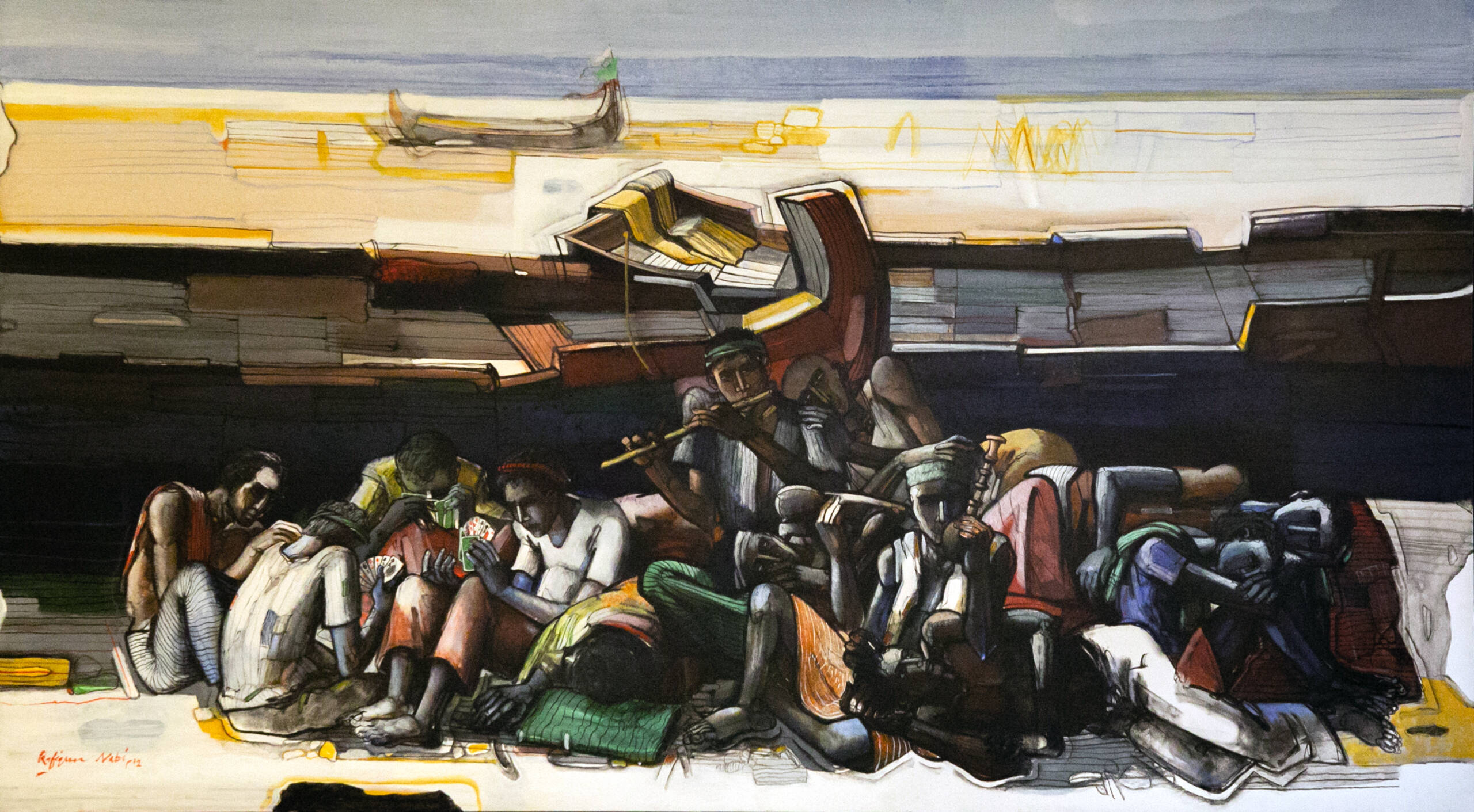

‘Fishermen at rest’ (2012), by Rafiqun Nabi, from the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation Collection
LUX: How does Asia overcome cultural barriers to art in terms of its creation and appreciation, as it’s still not considered a ‘real job’ in many quarters?
AL: There is a deep history of art in Asia but it is interesting you ask why art is not considered a real job here. Once you say ‘job’ that says there is a market and assumes a market for local art. That is a very interesting topic for Asian artists right now and comes down to cultural confidence. We see that in Korea where Koreans collectors like to buy Korean art. Hong Kong collectors have begun to collect Hong Kong artists in the last couple of years, and the Japanese are famous for not collecting Japanese art. The Chinese collected a lot of Chinese art around the Olympics and now they’re back to collecting western art.
It really comes down to cultural confidence, to what they think is good, so it is very easy to gravitate toward the Anglo-Saxon and Western art world. It’s difficult, but it’s the gold standard for whatever is best at the time, from Picasso or most recently to George Condo or Jeff Koons. Locals need to learn to develop that cultural confidence to buy local and to support local art for culture to flourish.
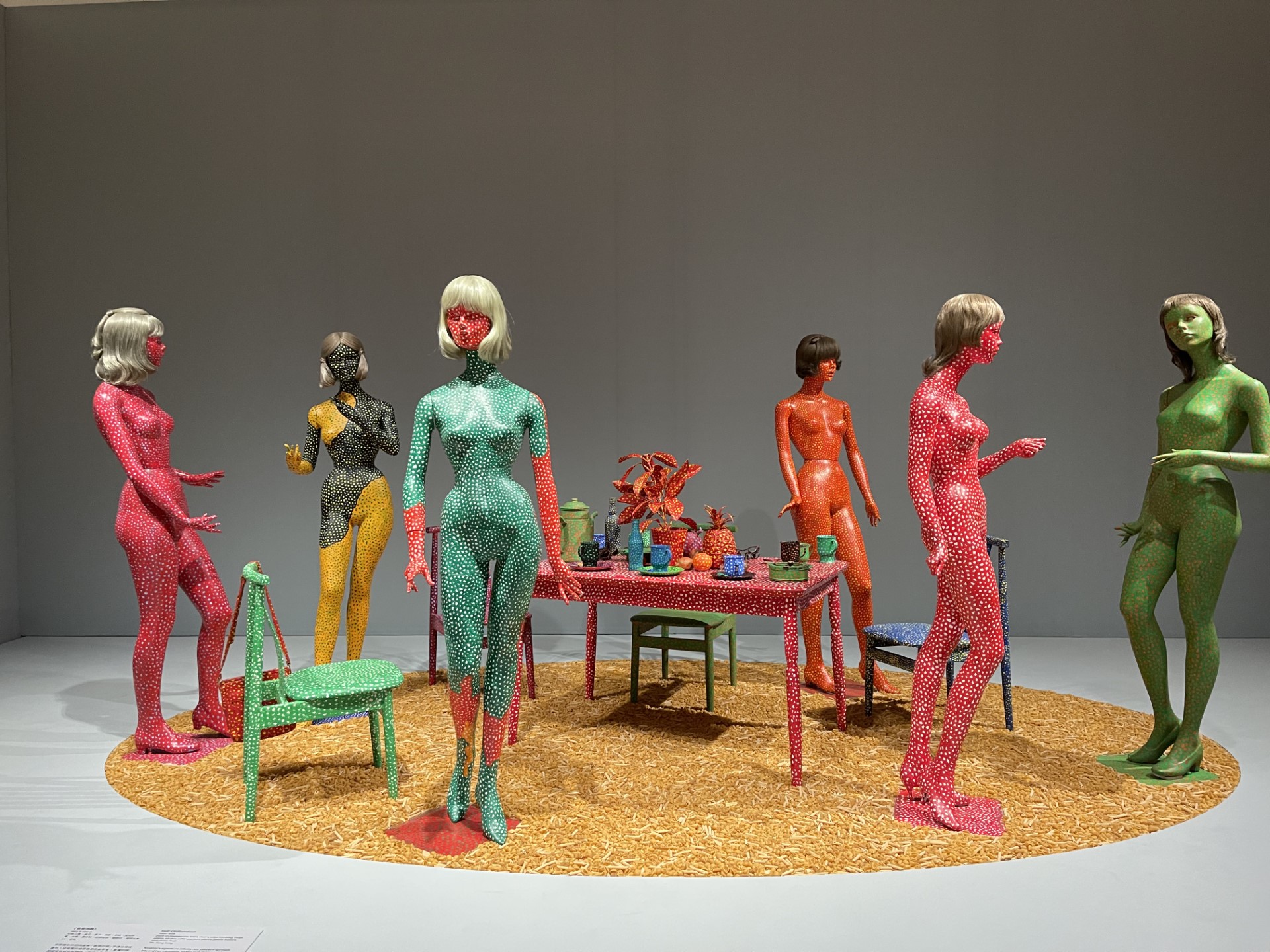

From the M+ exhibition, ‘Yayoi Kusama: 1945 to Now’
DR: When we talk about art markets, I agree with what you say, Alan. In South Korea, the Koreans are buying the Korean artists who are represented by the western galleries. So the locals are going to the western galleries originally from US and Europe, who are exhibiting at fairs in Korea, effectively buying their local artists via those western intermediaries.
In Bangladesh, as an example, we are a population of 180 million. If the 1% or .5% started buying art, there would be no supply in the market! So why is .5% of an entire nation not interested in buying art? It is because creative people, not only the artists but curators, gallerists, collectors are not creating the momentum to promote investment in art. And there is a problem with status and perception. In Bangladesh there is an appetite and a market for luxury brands but not for art. The wider audience does not aspire to buy local art.
In the western world, particularly where I have seen in France, Germany, Netherlands, Switzerland, and Canada where I lived for a long time, creatives are supported with subsidised housing or studio space so they can afford to produce art. That just doesn’t exist in a country in like Bangladesh. Artists graduate from an important school but change their profession for a better life.
I was preparing a lecture for my HK session for Sotheby’s Institute and commented that In Bangladesh we buy a lot of western art. Why are we buying so much western art and supporting western artists? Forget about aspiration, many of those artists are time-tested investments and our local artists are not. George Condo or Ai Wei Wei will be keeping value for decades. I want to and do support local artists but it’s a bigger picture.
LUX: How does Asia become a leader in art rather than participating in the so-called western gaze?
AL: No one will tell your story, you have to tell it yourself! While I love the Met or Tate or Guggenheim’s China show or Korea show, that is a fantastic spotlight but it is you who understands your story. One of the inaugurating shows of M+ was with Kusama and I think it was us telling that story from here in Asia that gave it a very different texture.

M+ Museum, is Hong Kong’s cultural hub for twentieth and twenty-first century art encompassing visual art, design and architecture, and moving image
M+ was set up to do just that, to be a Museum for Asia. One of the most touching things for me, two years after our opening when we welcomed the first group of visitors, was the overwhelming comment I heard from people saying is ‘Thank you! This is my Museum!’. These are not people from Hong Kong but from South Korea, Japan, Singapore and they see themselves in our collection. This is an Asian museum giving a voice and creating narratives and telling stories from an Asian point of view. We need more institutions to do that. You need to tell your own story.
LUX: What is it about being from Hong Kong and Dhaka that has contributed to your identity and vision for collecting?
AL: My collection is about stories that I feel privileged to talk about. The collecting vision is a reflection of who I am, which is someone born in Hong Kong, living in the city when it was a British colony, witnessing HK’s transition back to China, living through big changes, seeing the economic rise of China and the issues that come with all of that, living through all the tech development, broadband, now video, now AI. I have a strong link with artists from HK and the region and a strong relationship with technology with the context of my day job.

From Alan Lau’s expansive collection
DR: Dhaka is important in South Asia but for me Hong Kong is the centre of gravity in the so-called Far East because it is a connector to APAC and South Asia. Hong Kong and Bangladesh already had a connection historically and we represent a new “silk route”. We need to create Asian art power by amplifying the patronage of institutions like M+.
LUX: In what ways can innovative artists capture the essence of our time and realities?
AL: Artists are story-tellers, here to tell stories of our time. The best art is time-stamped but timeless. For example, at M+ right now, the most recent M+Sigg collection show is a controversial work by Chinese duo Sun Yuan and Peng Yu. It is set in an old people’s home, created nearly 20 years ago, taking the faces of the world political leaders at that time, and fast-forwarding them to when they are 80 years’ old sitting in automated wheelchairs that go round the hall so you see all these old people roaming around. Twenty years’ on how funny it is our world is still run by grey old men!
DR: That is true and sometimes when we talk about innovation, that does not mean it has to be technological innovation. At the end of the day you are talking about art. We are really talking about mental science and inventive hands that influence because it is about newness and original ideas. Art can’t be boring, or monotonous because we are not forced to look at art. Art has to inspire us and innovation is part of that inspiration process.
Organic To Organ – V (2022), by Shimul Saha, from the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation Collection. Crochet weaving, cotton yarn and cotton
LUX: How has your interest in innovation catalysed your collecting journey, Alan?
AL: I am fascinated by artists who are very resourceful storytellers. They always find find the latest technology or way of production to present their ideas in new ways that offer fresh perspectives. This creates all kinds of interesting dynamics in our human relationship with technology. We have futuristic, experimental tech, with artists like Cao Fei from China showing humans’ chaotic relationship with technology, Camille Henrot on the abuse of social networks, dystopic work from Jon Rafman, and then of course Beeple and other digital artists. We have a much more tense relationship with technology and that’s reflected in the artistic output and practices.
LUX: What are you looking forward to at the Venice Biennale?
AL: I’m definitely looking forward to what Hong Kong will present. Trevor Yeung is someone we know very well because we worked with him at ParaSite and we have really seen him grow. Another one that’s going to be in the main Pavilion is Isaac Chong Wai, originally from Hong Kong but representing the diaspora, based in Berlin, with a lot to say on global topics.
DR: There will be some artists from Bangladesh, India and Pakistan there and I will be looking out for their practices, how they respond to the concept that the curator has identified like displacement, the diaspora, identity and cultural history. I like go to a national Pavilion to see how that country is portraying their art and culture, rather than look for the presentation of a particular artist.
Read More:
durjoybangladeshfoundation.org
Alain Servais is an investment banker and collector of art-as-ideas, whose family collection is showcased in The Loft, a repurposed factory in central Brussels. In a conversation moderated by LUX’s Leaders & Philanthropists editor, Samantha Welsh, Servais speaks with South Asian philanthropist and collector, Durjoy Rahman, about supporting artists who give minorities a voice and make people think.

Alain Servais (left) and Durjoy Rahman (right). Photo montage by Isabel Phillips
LUX: How has business shaped your your passion for art?
DURJOY RAHMAN: I started my career at a very young age when I started my business in textiles and garments production. It was when I started exporting that I found that I experienced a negative perception about Bangladesh. I had to engage in a kind of cultural diplomacy when I went to business meetings! I would talk positively about the good things happening in Bangladesh, sharing what was interesting for buyers in course of business development.
ALAIN SERVAIS: For me it was about filling a gap rather than part of my business plan. Investment banking is about trying to understand human nature, anticipating what will happen, asking questions, maybe about the effects of a societal drift to the far right, or changing attitudes to minorities, the potential disruption from new tech and social media, and so on. So understanding herd instinct is very important. In its way it’s pretty sterile as it is all about money. You are missing the voices of so many different people. That is what is interesting in Art.
LUX: How did you become interested in art?
AS: I have no collector-parents, no experience of studying or making art at all, I fell into art by accident. It’s about the convergence of those interesting parts of human nature, professional and private, a kind of curiousness. And that came from working in investment banking, because you are so used to absorbing a massive amount of data and opinion to make decisions.
DR: It was an accident for me too. I was visiting New York and I first saw the silk screens of Marilyn Monroe and Ingrid Bergmann (which in fact I eventually collected). I decided to license and reprint the graphics on a European fashion brand T-shirt, by Replay I remember. It was this fashion x art collaboration which catalysed my art journey.
LUX: So discovery is a big part of your vision?
DR: Yes, I was frequently away on business in Europe and North America, and I would visit the many galleries and museums as I was passing through, always noticing the contrast with South Asia, where we had few institutions despite our long cultural heritage and traditional practices. So that’s why I decided that one day I would do something about it by creating a platform of my own.
AS: I love traveling, discovering other cultures, getting close to parts of the world that people have prejudice and ignorance about. I had the chance to go to Bangladesh and discovered a totally different, very rich culture. The way I process the experience is through bringing back works of art.
LUX: Should collectors open the door to alternative realities?
AS: We should stop making out that collectors are Superman/woman! We are just human beings finding outlets in art, revealing society’s many problems in the process. This is about my own interest in contemporary culture. I have a real problem with nostalgia and the selfishness of it all.

Artworks in a 2019-2020 exhibition at The Loft, the 900 square meter space which has housed the Servais family collection since 2010.
LUX: Is this why you collect ‘emerging’ artists?
AS: Emerging artists for me are the artists who are not selling-out to that nostalgic drive. It’s about the art created today that is worth preserving. Every major museum on the planet is based on the private collections of a few crazy collectors who plugged into whatever was going on in society at that time and collected artists who were expressing that in a particularly advanced way. For instance, forty years ago, Sophie Calle the French installation artist was already anticipating social media and reality shows – people want to watch people. So it’s about collecting and preserving artists’ works really early on, when Society does not yet understand their message.
DR: I agree, I really dislike the term ‘emerging artist’! These are claims not accurate predictions of who will be a great artist. In the art world, there is a structure, a platform, discipline, practice, so we can to an extent deduce who may emerge to be a strong or great artist. As to how successful they will be, that is far harder to judge. If you look at Bangladesh, Bangladesh is only 52 years old, so most artists here have actually been ‘emerging’ since 1971 ie post-Independence. DBF supports artists from this period and empowers them to create innovative bodies of work, influenced by social change. It’s about their context, their transmission of their knowledge and their influences.

Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation Creative Studio in Dhaka features works from around the Global South including, ‘Orator’ By William Kentridge (right) and ‘Rise of a Nation’ By Raghu Rai (left)
AS: Yes, yesterday I bought an innovative work from an artist from Bali. She had been totally underestimated to the extent she had never, in fact, even been called an ‘emerging artist’. She had, though, created new narratives through traditional Balinese painting and coloration, all pretty outrageous and about sexual liberation, lots of crazy images of penises, vaginas and everything. A good artist is someone that sends a message to the world, and a good collector is the one that understands this message before the masses. They are two sides of the same coin.
LUX: How is art messaging the voices of minority artists?
DR: We should first define what ‘minority’ means. After all, it means different things to different people. Sometimes, I feel like a minority when I enter the room at an event in the global North! It can be discomforting but I get over it with introductions and conversations.
AS: Yes, Durjoy, you’re right, you are a minority when traveling, and I am even an minority in Belgium – because when people visit The Loft they don’t get the art at all and probably think my kids should be taken into care! We are both minorities because we are both free-thinking individuals and non-conformists.

The Great Revel of Hairy Harry Who Who: Orgy in the cellar, 2015, by Athena Papadopoulos, in Dérapages & Post-bruises Imaginaries, the 2018-2019 exhibition at The Loft in Brussels.
DR: With the minority artists in Bangladesh, it’s not just about their religion or social status but can be about differences in cultural practice. For example, the remote Hill Tracts indigenous communities in Bangladesh are considered to be minorities, so when we talk about the cultural heritage of Bangladesh, DBF showcases their arts and crafts to the global North. By shining a light on their art we are bringing them into the discourse and including them in society. With our Future of Hope program during Covid, we included these indigenous artists from the Hill Tracts and two have become very prominent right now. Similarly, we took our project for Kochi Biennale from the remote northern region of Bangladesh. This was a very significant artwork created by ethnic communities who would never have been exhibited on the world stage.

Installation view of Bhumi, with support from The Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation, at the Kochi-Muziris Biennale, India.
AS: I learn a lot from the artists from the global South. Recently, I bought a work by a photographer from Bangladesh. It is an image around infrastructure, bridges, highways and I wanted it not just because I loved the aesthetic but because the message around it was deliberately unfinished. After I’d bought the work, not before, I made sure I sat next to the photographer at the festival dinner and was grateful for the experience of talking with him, on equal terms. It is a two-way business.
LUX: What is the responsibility of the audience toward the artist?
DR: Artists practice as they wish. It’s how the audience accepts their work that is the question. As a collector and as a founder of a foundation, we open up the opportunity for a deeper engagement from the audience with the artist’s social concerns. These activations are beyond direct action and inventions, creating a positive ripple effect. You have to ask yourself, ‘Am I here to change the world or to support a range of alternatives?’ We enable artists to create bodies of work that widen their potential for recognition on the world stage by bringing awareness of their voice and their cause.

Parables of the Womb by Dilara Begum Jolly at DBF Creative Studio.
AS: As far as the responsibility of the artist is concerned, I don’t like the quasi-deification of the artist. There are so many bad artists around! It is not enough to call yourself an artist to be an artist. I was with a collector in Istanbul last week and he told me he had reserved an exhibition space for a solo exhibition by an emerging artist, emphasising it had to be an artist with no gallery representation. It was to be for six weeks. He actually refused the the first offer, saying “I want to see if artists will fight for it!” For him, the fighting was an important element as so many artists were not thinking about what they are doing and why they were doing it.
LUX: Where do you think your art philanthropy will be, ten years’ from now?
DR: With DBF, we want to be an influential and vital activist who has used the power of art and culture to good effect, to make positive, impactful change in terms of social justice. I agree with Alain, we must question everything and that curiosity must inform our vision for the next decade.

Servais hosts exhibitions from his collection of international contemporary artists at The Loft, where he also hosts artists’ residencies.
AS: Because governments are funding the arts the arts less and less, I spend more and more time documenting the works I’m acquiring! I’m doing this to record for posterity the complexity of the artist’s thinking. I hope institutions give more power to curators to offer opportunities to interesting artists so we have the vital two-way discussions. I think we are going to go through extremely difficult times and I would not like to be this young generation. We need people like Durjoy, we need these discourses, we must give people a voice, and we must make people think!
Find out more: durjoybangladeshfoundation.org
Servais Family Collection on Instagram: @collectionservais
Pioneering entrepreneur and philanthropist Nachson Mimran has a show of his black and white photography at the Leica Gallery in London’s Mayfair. Compelling for many reasons, says LUX Editor-in-Chief Darius Sanai

Manari Ushigua – leader of the Sápara Nation, in Naku in the Ecuadorian Amazon; photograph by Nachson Mimran in March 2018
Through my years of commissioning photographers, across art, fashion, travel and portraiture, for LUX and Condé Nast, it has become evident that photography is a two-way lens. The image a photographer (or image-maker, as some prefer) captures is of them, as much as it is of their subject. Send two photographers on a similar mission, and you will see very different results.

A street art project in Libreville, Gabon; photograph by Nachson Mimran, November 2018
This becomes very apparent on viewing the images in Nachson Mimran’s debut show, Photographs from the decade that changed my life, at the Leica Gallery in London. Nachson, a contemporary renaissance man who is part creative, part philanthropist, part social entrepreneur, part philosopher and part tycoon, was not commissioned by anyone to create these images: they are a selection of photographs he took on his travels over ten years.
With his Leica Monochrom cameras (distinctive, niche, digital rangefinders) Mimran chronicled people and life everywhere from Bangladesh and Uganda to the Swiss Alps and West Africa, where he grew up.

Tribesmen from Turkana, Kenya; photograph by Nachson Mimran, November 2022
Mimran is best known for his stewardship of to.org, a philanthropic, creative and entrepreneurial ecosystem making real change. (He is also one of the owners of the hyper-chic Alpina hotel in Gstaad.) The red thread throughout is Mimran’s empathy and humanity: those who know him might suggest he is a modern-day humanist, above everything else. Particularly striking, because, as this is a personal chronicle, Mimran never intended to create anything for public exhibition.

Self-portrait of Nachson Mimran and his daughter in Gstaad, Switzerland; October 2022
A compelling show, and a window into the mind of someone who, in his own way, is changing the world.
Nachson Mimran: Photographs From The Decade That Changed My Life is on show at Leica Gallery, Mayfair, London until 11 February
Princess Alia Al-Senussi is a key figure in the development of cultural relationships between the West and the Global South, and in the growth of the art scene in Saudi Arabia. In a conversation moderated by LUX’s Leaders and Philanthropists Editor, Samantha Welsh, Alia Al-Senussi speaks with South Asian philanthropist and collector Durjoy Rahman about significant art world debates and developments at the nexus of the developed and developing worlds
LUX: Durjoy, is the relationship between art in the Global South and the rest of the world changing?
Durjoy Rahman: I have been collecting for the over 25 years, and I have always been passionate about creativity, both personally and professionally. Living in Dhaka, I have realised there is a lot of untapped creativity that can probably be moulded and presented to a wider audience, to increase visibility, benefitting Bangladesh, South Asia and, in a bigger picture, the Global South.
These days there is a very fashionable phrase: “Your West is my East”. What one person calls “West” is actually somebody else’s “East”. It depends on the position you are coming from. I have asked many scholars, and no one has been able to give me a clear definition of what the “Global South” is. I think the geopolitical or geographical definition has different meanings and narratives and I expect plenty of discourse and redefinition during the next decade.
LUX: Alia, what has your global vision of the art world been informed by?
Alia Al-Senussi: I came to the art world from a very established position, in the heart of London, so my view has been shaped by the Western perspective, an institutional perspective, a gallery art world ecosystem perspective.
I was very lucky to enter the art world at a time when these perspectives were changing. Tate Modern had just opened and revolutionised the way that we put art in context. There is no longer the “South Asian gallery”, the “Middle Eastern gallery” or the “Asian gallery”.

Alia Al-Senussi in AlUla, Saudi Arabia. She is a Senior Advisor, Arts, and Culture, to the Ministry of Culture in Riyadh
It was about showing art in conversation with itself, through the eyes of a subject, subject matter, or a generational perspective, rather than a geographical one. And, ever since, as much as I’m in the art world, my perspective on the art world is not as an art historian. It is very much about somebody looking at art, strategy and cultural strategy through the perspective of cultural diplomacy, soft power and how culture interacts with the art world ecosystem, but also very much with identities, governments and politics.
LUX: Alia, how have you noticed the art world changing in the Middle East?
AAS: My work in the Middle East started in 2007, when Art Dubai started. In the last five years, we’ve seen a rapid evolution in the Middle East, positive developments in Saudi Arabia, and Dubai becoming, in many ways, a platform for art from the Global South.
LUX: What do you think is the role of philanthropy in art. Does it engage, facilitate and shape discourse?
DR: This is what DBF is all about. From day one our approach has been very discursive, and we try to position our strategies in a very discursive manner.
For example, we work with photographers like Sunil Gupta, whose retrospective involved queer art. On the other side of the coin, we work with Wadham College of Oxford University, restoring the Holy Qurans, which we announced during the month of Ramadan.
My philosophy towards philanthropic activities and my involvement in the foundation is to challenge negative perceptions. It’s not only about Bangladesh, but the whole perception of South Asia, that I am trying to change through the activities that DBF undertakes. This is why we don’t only focus our activities in Southeast Asia but globally, be it in Europe or America.

Durjoy Rahman is a philanthropist and collector based in Dhaka, Bangladesh
LUX: Alia, could you share with us your belief about the role of art and philanthropy?
AAS: I think it is at the very heart of changing perception. I have a deep belief in – as Durjoy said – the power of culture to change people’s minds and perceptions. And I’m not just talking about the West, I mean: it’s even neighbour to neighbour.
For example, we’ve seen black art in the United States transform people’s perceptions of BLM and people’s perceptions of segregationist history. You walk around the Tate galleries, and you see two paintings facing each other in the room about conflict and war. One is about the pogroms in Eastern Europe, and one is about the massacres at Sabra and Shatila [of Palestinian refugees by Christian militias during the Lebanese Civil War in 1982]. These speak to exactly the same universal horrors that many people experience but are from two very different conflicts and parts of the world.
LUX: What responsibility or soft power do you feel you have?
AAS: I feel a deep sense of personal and professional responsibility. In any projects that I get involved in or commit to, I pay a lot of attention to professionalism. I teach a lot and one of the questions I often get asked is, “How do I get involved in the art world? How do I start my career?” I say, “Get involved, show up.”
I think the idea of showing up is really important. Someone invites you to something, go. Someone expects you to be at something, be there. Someone expects you to respond to your emails, respond; and I think that idea of showing up really illustrates a commitment to people.
LUX: What is soft power for you, Durjoy? How can you and/or art bridge discourse?
DR: Everybody wants to understand art. Even Picasso said, “Everyone wants to understand art. Why not try to understand the songs of a bird?”

An artwork from the Bhumi project, supported by the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation that was shown at the Kochi Biennale in India in 2022/23
When I invite people to an art show and they say that “Well, we don’t understand art.” I say, “There is nothing to understand. Just be there. Just try to comprehend that it is something interesting.” An example of how it’s not about soft power, but engagement, is what DBF did during the pandemic. All the major art institutions in South Asia closed for either health or commercial reasons. DBF decided to get involved with a community from north Bangladesh, which had hardly been hit by COVID-19. The project was called Bhumi and involved a minority group in the area who were craftspeople working in textiles. The project involved 260 people from 60 families, and it supported their daily livelihood. The project didn’t end with the pandemic, it was actually taken to last year’s Kochi Biennale to exhibit the works of the craftsmen and shows what is possible during difficult times.
This is an example of how art, philanthropy and art activism can show how culture can play an important role in times of crisis.
AAS: Just like Durjoy said, you see these very different and very nimble organisations involving themselves with communities and making a difference. The Islamic Biennale did exactly that. It was really revolutionary in the context of art in Saudi Arabia. The Islamic Arts Biennale was at the Hajj terminal in Jeddah, and offered locals to come to a place that they’d never entered because the Hajj terminal inherently is a place for Non-Saudis to come into Jeddah to then go on Hajj.
The locals could see this exceptional building, feel the power of Islam, but also of spirituality and of a community coming together. For people who were not Muslim, or had no connection to the Hajj, they saw objects and works of art in a contemporary and historical environment.

The Islamic Arts Biennale in Jeddah, 2023
Certain organisations have the power to be really nimble. They can profess their politics and support artists for art and culture. I think Delfina Foundation, for example, has been very clear about their support for artists from across a plethora of humanity and does it in a sophisticated, nuanced, and empathetic manner.
LUX: Where are you seeing Next Gen concerns amplified through art?
AAS: I think you see the next generation wanting to amplify diverse voices. There is this desire that art is geographically, ethnically, and sexually diverse so people can express the totality of who they are. There is a sense of activism to it, but there’s also a sense of declaration. I don’t always read into these institutional shows or works of art as activism. Sometimes an artist just wants to say, “This is who I am, and this is the art I make.” Artists are going to make art based on their life experiences.
LUX: Durjoy, where do you think the line is between declaration and activism?
DR: I think the majority of people want to see the origin of the artist, their background and their surroundings, reflected in the work they are producing. If I show a Bangladeshi artist and his or her work looks too different or has no context, sometimes curators even question it and say it doesn’t show their struggle or their originality. I’m not an art scholar or academic: I look at art based on whether I like it. But I think it’s important for an artist or a creative practitioner to show the origin, the struggle, and the history.
I think that we want to encourage artists going forwards to show their origin and their perception. An artist should be free to express their opinion, whether they are from Iraq, Lebanon or Africa. If they are willing to they should go ahead. DBF and I always try to work with artists who have enormous creative boundaries that they want to exhibit in front of their audience.

Al-Senussi in conversation with installation and media artist Chris Cheung during Art Basel in Hong Kong
LUX: To what extent do Next Gens feel obligated to witness and pivot or create change?
AAS: What I see more in my lecturing and my academic experiences, is that the next gen is very much about wanting to change the world and wanting to illustrate that. Through their careers and artwork, they want to be a part of the change in some way. It’s a little disheartening because there is this negative feeling about the future of the world, but at the same time there is a feeling that maybe we, collectively, can change the world.
You also see artists that are just reflecting on their own childhoods, like Farah Al Qasimi. She talks about her family home and the changes shifting in the UAE. It’s an activism, but then it’s also a reflection on the changing world.
LUX: Can art collaboration bring about changes of perception?
DR: Definitely. Art has a vital influence on culture towards current situations. I think art has a very influential way to foster international connections and collaborations and can question issues that are happening.
Read more: Maria Sukkar and Durjoy Rahman on supporting artists from your hometown
When I was in Paris at Asia Now art fair, I was talking to an artist from Israel and an artist from Jordan. When these two artists sat together, they realised where the problem lies. I didn’t see a division in their opinion, and I think this is an example of art bridging divides. Art can be used as a very strong tool to solve many of our problems including sustainability and global climate change.
AAS: I think art, at this time, is one of the only tools that we can look to, to unite us or to heal us. Unfortunately, it can also be used and utilised in other ways, but I have faith and hope that we will see a change.
Find out more:

Durjoy Rahman of Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation addresses the audience at the AVPN South Asia Summit
A pioneering conference in India is seeking to kick start venture philanthropy in South Asia
‘We had a strong sense that our projects had a lack of effectiveness. Add to that the lack of transparency as well as poor methods of measuring impact, and it became clear that something needed to be done.’
On a charity fundraising trip in 2002, Doug Miller realised the futility of his friends’ and his impact ventures in private equity. Unlike traditional investments, metrics were undeveloped, and methods and final impact opaque. In short, a lot of capital and time was being spent with the best of intentions but with limited results.
In response to this, Miller developed the European Venture Philanthropy Association (EVPA) in 2004 and the Asian Venture Philanthropy Network (AVPN) in 2011, bringing a collaborative approach to venture philanthropy through exchanges with impact investment.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
His successor is the overwhelmingly accoladed Naina Subberwal Batra, CEO of AVPN and Chair of the International Venture Philanthropy Center, proclaimed one of Asia’s Most Influential by Tatler Asia in 2021 and awarded awarded one of Asia’s Top Sustainability Superwomen by CSRWorks. Batra presided over the latest AVPN South Asia Summit in Mumbai earlier this month; it was the first of these conferences to take place in person, last year’s inaugural edition having taken place virtually. This year’s theme was ‘Bringing Fringes to the Fore”, and it brought together individual philanthropists from culture, education and social impact, and major global companies and organisations.
Durjoy Rahman, a philanthropist from Bangladesh engaged in South Asian art and culture, focused around the creative realm and cultural soft power. Speaking of the cultural world, he said that one of the missions of this Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation was to show that the cultural world “does not need to be seen or judged by the West’s historical perspective”. Durjoy said he is finding this message is finding resonance both in the rest of the Global South, and also in the traditional cultural capitals of the West.

AVPN South Asia Summit brings together philanthropists, venuture capitalists and other leasers to promote the field of venture philanthropy
“It is important to lead the conversation, and to do so needs to involve a multilateral, global conversation. It’s not about doing something and broadcasting information about what we do: multiple dialogues are the way to ensure we engage with like-minded individuals and institutions around the world.”
Durjoy also spoke about how the creative realm can contribute to future-ready education; and specifically, how the creative and cultural field can play a “soft power” role in influencing international views of Bangladesh, a country only founded in 1971 which previously had a negative economic reputation but is now one of the fastest-growing economies in the region.
The same panel, moderated by Vivek Agarwal of the Tony Blair Institute, also focused on educational reform, and featured Dr. Akhil Shahani, Managing Director of The Shahani Group, Dr. Nivedita Narain, CEO of OneStage and Rakshit Kejriwal, President of Phillips Education, speaking about empowerment in employability.
With a history of philanthropic infrastructure lacking in Asia, AVPN CEO Batra is building a network, catering to models that suit the collective regional story and its challenges, moving from a purist venture philanthropy, focused on empowering voices and expanding the network at all costs.
Venture philanthropy itself is a relatively new field, pioneered in the US and now making inroads around the world. It combines elements of traditional philanthropy, where a return is measured purely on the impact of the philanthropic aims, and traditional venture capital seeking a return. There is a prevailing view now that this maximises returns on both levels.
The AVPN conference is aimed to be an interregional weaving of thought leaders and industry experts, where a collective regional story is conducive to progress as opposed to challenging it. Its brief spans culture and education, as well as sustainable development goals.

Left to right: Vivek Agarwal, Dr Akhil Shahani, Rakshit Kejriwal, Durjoy Rahman at the AVPN Summit after their talk on future-ready education
A conference on social impact and sustainable development runs the risk of empty pledges. But not at AVPN – Lavanya Jayaram, South Asia Regional Director, ensured animated conversations, with stakeholders ‘debating unique regional challenges and solutions towards charting a roadmap for philanthropy and impact investing in the South Asian region.’. Founder Doug Miller’s aversion to inaction charged the summit, which hosted over 70 speakers over 27 sessions, a variety of panel discussions, keynote speeches, workshops and ‘fireside chats’. The agenda is also interspersed with networking opportunities, encouraging an ongoing dialogue between speeches, to expand the AVPN ecosystem, with over 600 members across 33 markets and its own academy dedicated to teaching skills in impact investment.
In the wake of environmental disasters that struck the region over the past year, the 2023 summit featured panel discussions on climate resilience and energy transitions in South Asia. Speakers such as Prerana Langa of Aga Khan Agency for Habitat India, developing network based models for disaster risk reduction and biodiversity conservation, spoke particularly to this year’s floods and industrial accidents in Bangladesh, bringing investors into contact with means of making effective impact.
Read more: Cyrill Gutsch on saving the oceans through art and collaboration
A panel discussion dedicated to ‘Bridging the Borders’ and ‘Global Perspectives’ brings as one of the speakers Sanjay Gujral of Everstone Capital, a private equity firm investing across the South Asian landscape, further engaging investment in a cross cultural design. Indian cricket legend Sunil Gavaskar also spoke about finding purpose in philanthropy.
The conference equally addressed gender gaps and supporting women within the economy through talks on gender lens investing, furthered by AVPN’s Asia Gender Network, backed by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, which seeks to advance equality through representation in leadership positions, economic empowerment and education, just to name a few.
Through a multiplicity of sectors and regions, the South Asian Summit is driving a collective effort in sustainable development and in centralising fringe communities in the discussion. The phrase ‘catalytic platforms’ is often thrown around, and yet could not be more apt in such dynamic conversations taking place. The Summit, through the focused involvement of leaders in their fields, is set to catalyse significant change in important and evolving areas. – Olivia Cavigioli
Find out more: avpn.asia

The Cyclades Preservation Fund runs a campaign to protect the vulnerable Posidonia oceanica meadows from anchoring. Courtesy of the Cyclades Preservation Fund
Philanthropy has a key role to play in initiatives to support ocean conservation, and in empowering communities with the ability to make a difference. Here, Darius Sanai outlines the importance of philanthropy, while Chris Stokel-Walker showcases seven philanthropic projects that are making waves
The German philosopher Immanuel Kant liked to talk about the categorical imperative: moral actions that have to be taken and do not broach any argument. Saving the oceans from further harm by humans is a prominent current example of a categorical imperative, one that would also likely receive the approval of moral philosophers from another prominent school of thought, utilitarianism, which espouses acting for the common good.
And significant positive change can be made – or, if you are a follower of Immanuel Kant, must be made – by people acting to their abilities in support of categorical imperatives. Philanthropists, such as those outlined over these pages, use their considerable means to try to make a difference in support of environmental initiatives, particularly in areas where other forms of capital are not able to work.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
The opportunities to create positive change, and leave a positive legacy, are immense. Philanthropy plays a key role, but works most effectively when it is at its most informed. The links between the chains of planetary and ocean degradation are complex. A zero-emissions container ship can transport invasive species around the world on its hull; sailing yachts destroy carbon-capturing seagrass with their anchors; recycling plastics can produce significant carbon emissions. So it is philanthropists who are as educated on the issues as they are generous, working with carefully-chosen experts, who tend to be the most successful.

Ben Goldsmith
“All across the world, small groups of committed, passionate, effective people are making extraordinary things happen, often on a shoestring budget, and they are nearly always funded by philanthropists,” says Ben Goldsmith, the British environmental campaigner and founder and Chair of environmental charity Conservation Collective. “Philanthropy is the most potent kind of funding, as it comes without any requirement to produce a financial return and has the flexibility to pay for almost any kind of work, from grassroots action to societal movement building. In the right hands, philanthropy can move mountains. This is why it is so important that those with the means to do so give away some of their money – in the most thoughtful and strategic way possible – to those at the cutting edge of changing our world.”
Philanthropic capital is critical to ocean conservation and regenerative initiat

Jacqueline Valouch
ives, says Jacqueline Valouch, Head of Wealth Planning & Philanthropy at Deutsche Bank Wealth Management. “Money provided by philanthropic entities for ocean conservation and regenerative projects allows for early funding, innovation and alignment with the scientific community,” she explains. “By providing much-needed seed capital, philanthropic capital can help to de-risk projects and attract more funding. In these ways, it can help companies and others to restore, renew, conserve and make bigger change.
“Philanthropists are one group of the many stakeholders needed to move the dial on crucial areas of exploration, research (including through scholarship programmes) and innovation,” she continues. “These are initiatives that would not be possible without the dedication and patience of philanthropists.”
Seven Philanthropic Projects In Ocean And Coastal Conservation
1) Deutsche Bank Ocean Resilience Philanthropy Fund
Founder: Deutsche Bank Wealth Management
This Deutsche Bank fund was announced at COP26 in 2021 and launched in 2022. The fund enables philanthropists to engage with scientists on projects to counteract damage to ocean and coastal ecosystems by supporting projects that use nature-based, rather than man-made, solutions. An advisory council of expert scientists and Deutsche Bank personnel review and select grant recommendations for projects. The first such project, the Future Climate Coral Bank, managed by the non- profit Maldives Coral Institute, aims to identify corals that are resilient to bleaching caused by warming, and create a gene bank to support global reef restoration.
2) Walton Family Foundation Oceans Initiative
Founder: Walton Family Foundation
Walmart founders Sam and Helen Walton knew all too well how much the earth’s waters contribute to their supermarket’s success, and the company’s foundation has sought to help ensure the health of the planet’s water for the future. Its Oceans Initiative is supporting 14 fisheries to adopt more sustainable practices, and has lobbied in Japan, the European Union and the United States to encourage buyers to purchase more sustainably sourced seafood. “We believe that the people closest to the problem are also critical to finding solutions,” says Teresa Ish, Head of the Walton Family Foundation Oceans Initiative.
Read more: Richard Spinrad on moving towards a blue planet
3) Salesforce ocean Sustainability Programme
Founder: Marc Benioff
Global cloud software company Salesforce has run its Ocean Sustainability programme since CEO Marc Benioff began it in 2021. At COP26, Salesforce committed to buying one million tons of blue carbon credits and is investing $100 million in grants to The Ocean Foundation, the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation and Wetlands International over 10 years – as well as investing in 1t.org, including a Guatemalan project to support sustainable livelihoods for 400 families. “Ocean health translates to the safety of our family, loved ones and communities around the globe, and the ability for them to thrive,” says Dr Whitney Johnston, Director of Ocean Sustainability at Salesforce.
4) Common Seas
Founders: Filippos and Andonis Lemos
The Lemos brothers are Greek shipping magnates – so they are aware of the biodiversity beneath the ocean surface. And they are conscious of the impact that plastics entering our waters have on the wildlife within. To help combat this, the Lemos siblings co-founded and are major donors to Common Seas, whose vision is to eradicate plastic from the oceans. Common Seas’ collaborative initiatives include partnering with governments to reduce plastic pollution; helping the tourism industry reduce its plastic use; and supporting education providers both to make their schools plastic free and to raise awareness among young people of the importance of keeping our oceans clean of pollution.

Common Seas incorporates education as part of their strategy to remove plastics from the oceans
5) Galapagos Life Fund
Founder: Pew Bertarelli Ocean Legacy Project
The Galápagos Life Fund (GLF) is one of the crowning achievements of the Pew Bertarelli Ocean Legacy Project, a joint initiative from the independent non-profit The Pew Charitable Trusts and investor and philanthropist Dona Bertarelli. It was set up with the shared goal of establishing the first generation of large, ecologically significant and effective marine- protected areas (MPAs) around the world. The GLF converts $1.6 billion in commercial debt into a loan, capitalised by a $656 million marine conservation-linked bond, generating more than $450 million to support marine conservation in the Galápagos Islands over the next 20 years.
6) Cyclades Preservation Fund
Founder: Conservation Collective
Nearly 220 islets and islands make up the Cyclades in the Aegean, which are home to a range of natural habitats being harmed by modern life. The largely female-led team behind the Cyclades Preservation Fund is part of Conservation Collective, a global network of philanthropic funds helping to preserve the natural environment. CPF programmes focus on biodiversity, education, local identity and marine conservation – all with the participation of local stakeholders. Among its biggest wins is supporting the establishment of a grassroots fishing protected area around the island of Amorgos, sustaining a local industry while keeping the marine population healthy.

Cyclades Preservation Fund Supports the fishers of Amorgos towards their vision for seas with more fish and less plastic
7) Plastic Free Ibiza and Formentera
Founder: Ibiza Preservation
Ibiza is a major hub for tourism, which buoys up the economy but has significant environmental impacts. In the west coast, there are 4.5 million pieces of microplastics in every square kilometre of sea – 30 times more than elsewhere in the Mediterranean. Nearly three-quarters of the waste collected on Spanish Mediterranean beaches is plastic. Set up in 2018, Plastic Free Ibiza and Formentera, promoted by Ibiza Preservation, is made up of 14 main members including local non-profits, and aims to eliminate single-use plastic in the islands by supporting citizens, administrations and businesses to promote sustainable practices. Initiatives include the certification of local companies as plastic-free.
This article first appeared in the Deutsche Bank Supplement of the Autumn/Winter 2023/2024 issue of LUX magazine

Patrizia Sandretto Re Rebaudengo
In the first part of our Italy art focus series, curated by Umberta Beretta, LUX speaks to Patrizia Sandretto Re Rebaudengo who founded her fondazione in Turin in 1995. Today, the extraordinary initiatives of Patrizia Sandretto Re Rebaudengo include transforming an abandoned Venetian island into a beacon for art and ecology
LUX: What was the first artwork you bought?
Patrizia Sandretto Re Rebaudengo: Anish Kapoor’s Blood Stone. It was on a trip to London in 1992 that changed my life.
LUX: What drives you to support art education?
PSRR: When we started in the 1990s, contemporary art received little attention in Italy. Education defines the fondazione’s identity and builds awareness of contemporary art in Italy. We offer a rich programme for schools, families and vulnerable people, and we train teachers. Our Young Curators Residency Programme sees three international graduate curators curate a joint exhibition from the work of artists they meet in Italy during a three-month stay. This develops curatorship and places Italian art in a global context. Campo is a similar course we have for Italian graduates.

A view of the Lucas Arruda exhibition at the Ateneo de Madrid
LUX: What are ArtColLab and Verso?
PSRR: ArtColLab is our non-profit project to produce collaborations between artists and designers in order to help widen engagement in art – for example, Nicholas Kirkwood and Paul Kneale created beautiful limited edition shoes. Verso focuses on empowering people aged 15 to 29 in democratic processes. It is an experimental, poetic pedagogical model of exhibitions, workshops and more, on themes of citizenship, inclusion and the collective construction of possible futures.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Tell us about your philanthropy in Spain.
PSRR: I love Spain and we established the Fundación Sandretto Re Rebaudengo Madrid in 2017. Madrid is a global capital and a bridge to Latin America. The fundación is now nomadic. We presented Lucas Arruda at the Ateneo in Madrid in 2023 and we’ve also brought the Young Curators Residency Programme to Spain.

1000 Pieces, 1983, by Anish Kapoor
LUX: Who are the artists exciting you today?
PSRR: Globally, they include the painters Michael Armitage and Lynette Yiadom-Boakye, and the work of Josh Kline, Marguerite Humeau, and Klára Hosnedlová. In Italy, works by Giulia Cenci, Giulia Andreani, Guglielmo Castelli and Ludovica Carbotta have joined the collection.

Installation view of Rough Rides, Police States, Broken Windows, 2015, by Josh Kline; Vandal Lust, 2011, and Slavs and Tatars, Mystical Protest, 2011, both by Andra Ursuţa, at the fondazione’s recent show, “Backwards Ahead”
LUX: What is the San Giacomo recovery project?
PSRR: This island, a military site abandoned for more than 60 years, will become an outpost of dreams, a place to produce and show art, and host research and discourse on contemporary culture.
Read more: Italy Art Focus: Umberta Beretta
With its delicate lagoon ecosystem, we will implement principles of sustainability and energy transition there. The fondazione will enable San Giacomo to become a meeting place for artists, environmentalists and the public.

The isola San Giacomo, which has been a pilgrim refuge, a place of quarantine and a military site, is being transformed by the fondazione in the name of art
LUX: What will be your legacy?
PSRR: I hope I am giving back to the community what I have been fortunate to learn during 30 years in contemporary art. Time passes and I think of my two sons, who are also passionate about art, so I am building something that will take on new shapes with future generations.
This article comes from a section of a wider feature originally published in the Autumn/Winter 2023/24 issue of LUX

Aurelie Cauchy and Leslie Ramos, founders of The Twentieth © Juan Cuartas Rueda
Leslie Ramos and Aurelie Cauchy are co-founders of The Twentieth, a pioneering art advisory that focuses on supporting the arts and culture. Following the launch of Ramos’ book, Philanthropy in the Arts: A Game of Give and Take, Samantha Welsh speaks to the founders of The Twentieth about the new generation of philanthropists emerging from around the world, with different motivations and priorities and what the future holds for arts philanthropy given the rapidly changing landscape
LUX: What compelled you to layer arts philanthropy onto traditional arts advisory?
Leslie Ramos: The simple answer is that we spotted a gap in the market. We saw more and more aspiring collectors coming to the art world eager to support the ecosystem they admired, but they would find that although there were many people helping them buy and sell, there was almost nobody actively encouraging them to give back and helping them to do it.
Aurelie Cauchy: Moreover, we also feel that the art world in general is becoming increasingly dominated by the art market, focusing very strongly on sales, sales, and more sales. We wanted to build something that tried to push back against that a bit and in a small way remind people that a good collector is someone who also cares about the art world ecosystem.
LUX: Does arts philanthropy today bear any resemblance to its origins?
LR: The basic system of the most privileged in society actively supporting something they care about hasn’t changed much. What does change all the time are the underlying dynamics, like people’s motivations. We are seeing a real shift today in the role status has in philanthropy, with younger philanthropists being much less keen to have their names carved above doorways, for example.
AC: The pandemic has also reinforced the desire to help locally, with a focus on causes such as health and poverty, at a moment when social justice became more prominent than ever. Without taking anything away from other extremely pressing causes, one of the missions that we feel we have is to show philanthropists how supporting the arts can be an effective way of addressing these other societal causes and something that should sit as part of their wider philanthropic portfolio.

The European Fine Art Foundation panel discussion on next gen collecting and philanthropy at the Art Business Conference in 2023 © David Owens
LUX: Why is arts-funding important amidst crises in education and healthcare provision?
AC: It is true that causes like poverty, health, and children will always, and perhaps should always, be more important causes for philanthropy than the arts, but that doesn’t mean the arts should be ignored. For one, art has incredible power within societies. As Leslie wrote in her book, ‘The power of art shows us that humans can dream and think about the world not only as it is, but as it could be’, and in this regard the arts are particularly powerful in conveying important messages about the world and society.
LR: One example that I think is quite potent and that I tell our clients, is to look at what the philanthropist Jeff Skoll has done with his film production company Participant Media. Almost every film in the past 20 years, that has spurred real conversation about important issues facing society, has been funded by Skoll. The collector and philanthropist Sarah Arison also described this very well when I interviewed her for my book. She said that, for her, we must change the way we think of the arts, not as siloed disciplines but collaborative and interconnected, and this is crucial to bringing awareness to all sorts of issues.
In the end, it is critical for people to really care about what they support. This is why the experiential and social part of the art world is actually quite valuable – the events, galas, previews, and perks offered to supporters are not only quite fun, but they help people learn and be more comfortable.
It is also why we guide (or drag!) our clients to artists’ studios, museums, and non-profits of all sizes to really understand what their money can do and reassure them that it will be well spent.

Jesus Rafael Soto, Penetrable, 1992. © Archives Fondation Maeght
LUX: You also advise museums and non-profits, artists, and some brands as well?
LR: Yes, we do a lot of work with museums and non-profits, advising them on all sorts of things, but mostly around improving their financial resilience or helping them execute their vision. Aurelie has been doing a lot of work with the Centre Pompidou, expanding its international circle of donors, especially throughout the US, to support the enrichment of its collections. At the same time, I have been working closely with the Fondation Maeght in the South of France, helping them build their first patrons’ scheme with supporters from across the world, and advising them on their capital campaign for a new extension due in 2024.
AC: Our work with artists and brands is not so dissimilar to what we do with collectors. Often successful artists get to a point when they want to give back and we help them build their philanthropic initiatives, like foundations and artist residencies. Likewise, many brands, particularly luxury brands, are looking for genuine engagement with the arts, whether it’s through strategic collaborations or philanthropic initiatives that resonate with their ethos and serve their client-centric strategy, corporate social responsibility, and branding.
LUX: How do you work with individual clients in terms of evaluating their intentions and guiding them?
AC: It varies slightly from client to client. One thing is enthusiasts taking their first steps in the art world, perhaps starting a collection, or beginning to get involved with institutions in a meaningful way. Theirs is more a process of discovery initially, seeing what resonates. Whereas long-term supporters who want to take their philanthropy to the next level and perhaps build their own foundation, for them it’s more about refining and executing their vision.
The common thread is that we view our role as a catalyst, helping our clients become respected forces in the arts and culture world. This means being independent, unbiased, and transparent, which is why, for example, we do not charge commissions on transactions like a lot of advisors do. We would rather that our clients can trust us and be sure our advice is completely independent than constantly feeling pressured to spend.
The other side of the coin is that we only work with clients who are, or want to be, philanthropic. We are very clear with that and we are different from most arts advisors in that regard.

Leslie Ramos at the launch of ‘Philanthropy in the Arts, A Game of Give and Take’, published by Lund Humphries in collaboration with Sotheby’s Institute of Art
LUX: Are there barriers and what is the approach to impact measurement?
LR: While measuring impact to some extent is valuable, it is much more so to identify non-profits who know what they are doing and whose mission aligns with the giver and then trust them to do what they do best. I think the best arts philanthropists instinctively understand the positive effect the arts can have. So many studies have shown the proven positive effects on mental health as well as the positive economic impact on communities.
LUX: How are newer players influencing codes and interactions?
AC: It’s difficult to summarise because there are new people coming to the arts from all over the place. Of course, a lot of the attention recently has been on the tech money, but although it might be a stereotype to say that tech millionaires have no interest in arts and culture, it does seem, for now, to be the case. There are exceptions of course, like Sean Parker’s Parker Foundation or Komal Shah and Gaurav Garg’s Shah Garg Foundation. Both are important collectors and philanthropists from that world doing truly wonderful work.
One of the most interesting areas of the world that we are keeping our eyes on is South-East Asia and the new generation of collectors in places like Singapore, Indonesia, and Taiwan. Indonesia especially is an incredibly charitable society with a high value placed on the arts. India has also recently seen the rise of its UHNW population, with first generation wealth and inter-generational givers alike showing great interest in strengthening the philanthropic culture and infrastructure.
LUX: Where is private philanthropy leading national conversations through art discourse?
LR: Private support can often act faster than governments and be more curious and less risk averse. This means that in countries where there is yet to be a state-backed cultural support system, philanthropists are often key to giving artists and non-profits the resources they need. After all, artists can be found everywhere, and thank goodness for that!

Eacheve, the independent non-profit organisation dedicated to creating new opportunities for Ecuadorian artists © Intemperie Studio
Take, for example, the work being done by the Ecuadorian arts foundation EACHEVE. For a few years now, the founder, Eliana Hidalgo, has been determined to give Ecuadorian artists global exposure and opportunities, supporting residencies, exhibitions, publications and soon a permanent exhibition space in Guayaquil. EACHEVE even published the first ever compendium of contemporary Ecuadorian artists, a book that has become a global reference and the first of its kind. This kind of work is where philanthropy can take a lead, and when done well, it can also be ‘contagious’, encouraging others to get behind a great cause and ultimately influence state decisions.
LUX: How can the State incentivise and direct giving?
LR: State support is critical in providing a supportive environment for philanthropy, and this doesn’t just mean providing tax incentives or funding matching programmes. Although they do work, it’s more about providing a framework and actively incentivising more philanthropists more holistically within your country.
Singapore is a great example of this. They have extended their (massive) 250% tax deductions for donations to 2026 to foster a culture of philanthropy, but it is combined with their SG Arts Plan (2023-2027), developed by the National Arts Council, which is designed to invigorate the art world more generally.
This is something I am hoping future UK governments will start improving because recently encouraging philanthropy in the UK has been neglected, in my opinion. In part, this is because it is viewed as a rather unfavourable thing to support politically. Having launched a successful £80m scheme to encourage more philanthropy in 2010, since then the current UK government has done very little. As things stand, the wealthiest in UK society only give a miserly 1% of their income to charity every year.

Centre Pompidou
LUX: Is there a downside to state intervention?
LR: Without wanting to get too caught up in a rather complex topic, there are obviously issues with censorship and oppression of artists and creatives in many parts of the world. Equally, there are many examples of populist governments taking control of museums and cultural organisations by putting their cronies in charge.
But I still believe that perhaps the most damaging thing a state can do is be ambivalent. This was often the case in Italy in the past, where especially state museums were resting on their laurels and simply stagnant. In 2014, the newspapers in Italy gleefully reported that the restaurant at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York made more money in a year than all of Italy’s museums combined. But since then, new government initiatives, the growth in corporate sponsorship from big Italian companies, particularly the luxury sector, and a general sense of key people wanting to put in more effort, means things are slowly going in the right direction.
LUX: How optimistic are you that arts philanthropy can catalyse a better world?
AC: Arts philanthropy is vital to fill the gaps, supporting artists, art education, and art institutions that struggle to secure adequate funding from just government and commercial sources.
Take arts institutions, from leading museums to small non-profits, who are the many beating hearts of the art world, it is important to allow them to continue their invaluable work and survive. The former Met CEO Dan Weiss wrote a wonderful book on the subject, saying that “museums have played a vital role in our culture, drawing on Enlightenment ideals in shaping ideas, advancing learning, fostering community, and providing spaces of beauty and permanence”.

Aaron Cezar, founding director of the Delfina Foundation in conversation with Leslie Ramos
Arts philanthropy is there for these institutions to ensure they can navigate a challenging landscape with financial resilience and be sustainable, relevant, and impactful in the long run, and in the end, it helps create a more vibrant and diverse society where everyone, regardless of background or financial means, can have access to art and culture.
LR: At the same time, I would like to finish on a sentiment that was shared by Darren Walker, the President of the Ford Foundation, in a recent interview. Walker, a great advocate for philanthropy, had come across something Martin Luther King Jr. had written, where King had pointed out that although commendable, philanthropists should recognise the economic injustice that makes philanthropy necessary. “King was saying that, yes, the work of philanthropy must be about charity and about generosity”, Walker said. “But it should also be about justice and dignity … It requires of the philanthropist an interrogation of our own complicity in the very problems we are seeking to solve.”
Find out more: thetwentieth.com

The Hepworth Wakefield Museum which will acquire the work of the winner of the second edition of the Spirit Now London Acquisition Prize, supporting young female artists
Now in its second year, the Spirit Now London Acquisition Prize in partnership with Frieze London, brings together and celebrates young female artists offering them a chance to be recognised by leading art institutions
While contemporary women artists are commanding increasing investment and attention, the global art market remains under the sway of male creators. Marie-Laure de Clermont-Tonnerre’s Spirit Now London is aiming to keep women in the art world’s spotlight.
Created in 2015, Spirit Now London is a philanthropic community of patrons and collectors aiming to support emerging artists and cultural institutions, with a focus on the work of female artists. Last year, they allocated a £40,000 grant to the Fitzwilliam Museum in Cambridge to acquire works from the Spotlight section of Frieze Masters; Sylvia Snowden was the artist selected, with her work Brown – Yo II becoming part of the museum’s permanent collection.

Sylvia Snowden, Brown – Yo II, c. 1978. Courtesy the Artist and Franklin Parrasch Gallery. Photo by Michael Adair
The Prize’s second edition is being held this year and aims to recognise and celebrate the outstanding achievements of women artists under 40, allowing one female artist exhibiting at the fair the unique opportunity to have her work acquired and donated to The Hepworth Wakefield’s permanent collection. The Hepworth Wakefield is a publicly funded modern and contemporary art museum located in West Yorkshire, established in 2011 and designed by London-based architect Sir David Chipperfield. The museum draws inspiration from the legacy of renowned 20th-century sculptor Barbara Hepworth, and remains committed to showcasing the works of other talented women artists.
Eva Langret, Artistic Director at Frieze London, said the fair was “honoured to be partnering with Spirit Now London,” also commenting that: “gender parity in the arts is an important conversation, as despite perceived progress, women artists remain underrepresented and undervalued throughout galleries, museums and auction houses.”

Marie-Laure de Clermont-Tonnerre, founder of Spirit Now London
Headed by Marie-Laure de Clermont-Tonnerre, founder of Spirit Now London, the 2023 Jury is composed of Laura Smith, Director of Collection & Exhibitions at The Hepworth Wakefield; Simon Wallis, Director of The Hepworth Wakefield; and “The Spirit of Giving” Committee, featuring 16 international women, art patrons and collectors, active members from the Spirit Now London community.
The winning artist will be announced on 11th October
Find out more: spiritnowlondon.com
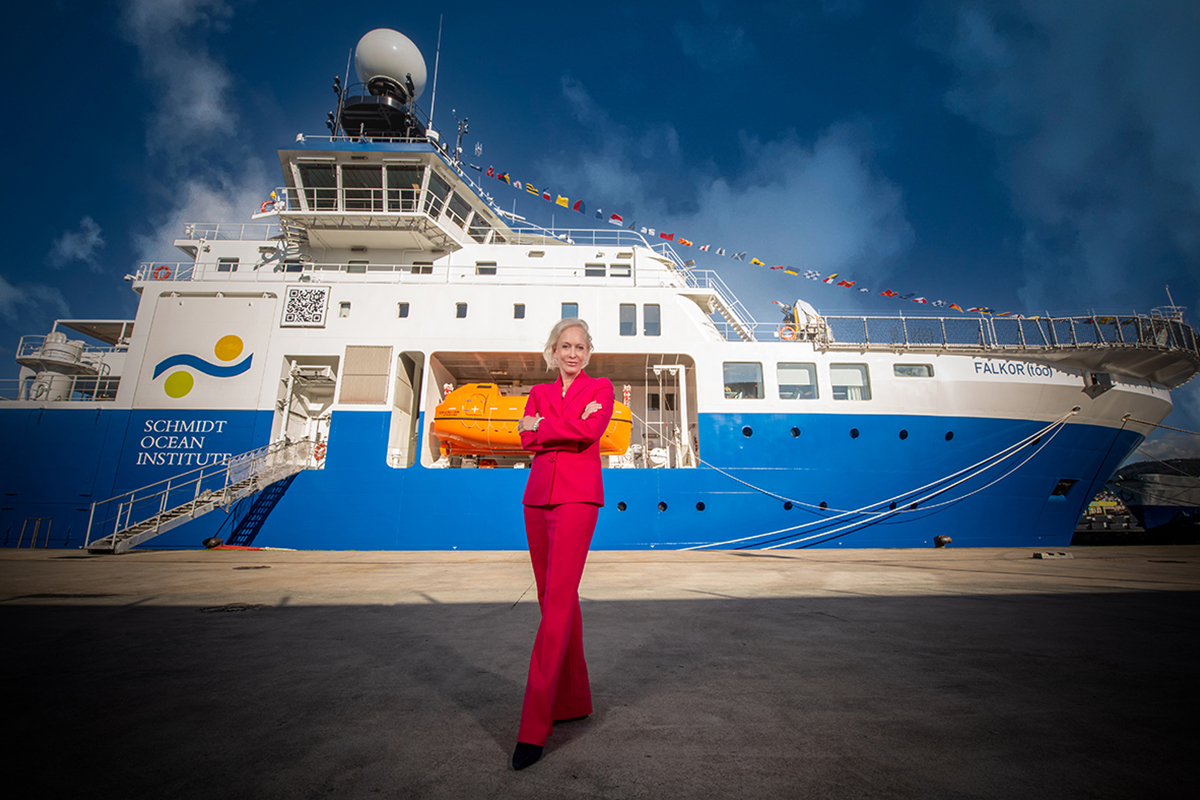

Wendy Schmidt and the R/V Falkor (too)
Philanthropist and investor Wendy Schmidt founded the Schmidt Ocean Institute in 2009 with her husband, Eric, former CEO of Google. Here, Wendy tells Trudy Ross about their new research vessel, R/V Falkor (too) and the importance of expanding scientific knowledge of the oceans’ unplumbed depths
LUX: Can you share the inspiration behind founding the Schmidt Ocean Institute and your vision for advancing oceanographic research and exploration?
Wendy Schmidt: My husband, Eric, and I began Schmidt Ocean Institute in 2009 after I learned to sail and to scuba dive and he went out and found an existing hull in a retired German fisheries vessel. Combining Eric’s interest in advancing engineering and technology and my growing passion for Ocean science and communications, we repurposed the old steel hull into the construction of a state-of-the-art oceanographic research vessel, launching R/V Falkor in 2012.
We had two ideas: first, as philanthropists, to provide ship time, which is in short supply, for marine researchers at no cost. Second, in exchange, we ask scientists and researchers to make their collected data publicly available for the broader research community as soon as possible, so we might collectively accelerate the pace of oceanographic research at a critical time in the life of the Ocean and our planet.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: The Institute has recently launched a new research vessel, Falkor (too) to embark on research expeditions and expand the capacity for ocean research. What is special about the ship and how has it been specifically tailored to advance marine science?
WS: Like our first research vessel, R/V Falkor (too) is built on a repurposed hull. The original ship was a service vessel built in 2011 to travel back and forth from Ocean platforms, including wind turbines. It came with an excellent seakeeping ability, which is a wonderful feature when you have robots diving beneath the ship.
We were able to successfully convert the ship for marine research at a shipyard in Vigo, Spain, during a remarkable 18-month period in the midst of the Covid 19 pandemic, during which we faced workers absent due to illness, local work strikes, broken supply chains that delayed needed materials and technical parts.
Nevertheless, R/V Falkor (too) sailed from Vigo in March, 2023, on her first shakedown cruise across the Atlantic Ocean to Puerto Rico in the Caribbean Sea. Falkor (too) is 50 percent larger than Falkor. Its technology expands the capability of Falkor with space for more scientists, offering eight laboratories, two moonpools in the centre of the vessel, a 150-foot-tall crane that can rearrange 20 shipping-size containers to create custom labs on a 10,000-square-foot deck. Modular space on the ship is designed to accommodate concurrent science projects as well as artists, who come along on most expeditions, to translate discoveries and scientific processes into art.

Wendy Schmidt inside the Falkor (too) control room
LUX: Can you speak more about the inaugural expedition of Falkor (too) in the Mid Atlantic Ridge and your findings there?
WS: A multidisciplinary team from 11 scientific institutions joined Falkor (too) for a 40-day inaugural expedition to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Scientists were searching for new hydrothermal vent fields–and found three of them–the first discovery of active hydrothermal vents on this section of the ridge since 1980. The vents occur when magma from the Earth’s core comes into contact with sea water, creating a chemical reaction that can look spectacular. “Black smokers” are what they look like, and they can spew upwards hundreds of feet. Vent fields were measured at up to 350 degrees Celsius.
These systems are important to locate and to understand because they are rich with minerals–sulfide deposits–that are one of the targets of deep sea mining. Scientists working aboard Falkor (too) discovered the new hydrothermal sites supported active ecosystems, teeming with rich varieties of marine life. Now that the expedition is concluded, scientists will study the samples they have of rocks, hydrothermal fluids, microbes and animals found on these vents.
LUX: Which were the most significant scientific discoveries or breakthroughs made aboard the The Schmidt Ocean Institute’s previous vessel, R/V Falkor?
WS: During the decade the ship was in service, scientists working aboard discovered more than 50 new marine species and underwater formations and mapped more than half a million miles of the sea floor in high resolution.
Notable discoveries include the world’s longest known sea creature, a 150-foot-long siphonophore, and a coral reef standing taller than New York’s Empire State Building alongside The Great Barrier Reef in Australia. Our underwater cameras also caught rare footage of the ram’s horn squid, the glass octopus, and a 1 cm pygmy seahorse.

Rare sighting of a glass octopus, a nearly transparent species whose only visible features are its optic nerve, eyeballs and digestive tract, as seen from the R/V Falkor
LUX: How important is the role of new technology as a facet of ocean research?
WS: New technology is essential for advancing our understanding of the ocean. Imagine exploration in Space that didn’t take advantage of ever newer systems to enhance the missions we are able to accomplish. We know so little about the ocean and most of it is still unexplored.
Schmidt Ocean supports the development and use of transformative technologies that can scale our efforts at a time when government funding for early research and development in applied sciences won’t make it happen. We support new technologies for data collection and analysis, and others, like autonomous robotics, augmented and virtual reality, machine learning, and artificial intelligence that have the promise to rapidly advance our understanding of ocean systems everywhere we go. Our Executive Director, Jyotika Virmani, chairs the UN Ocean Decade Technology Group.
LUX: You have said before that: “We can’t take care of something that we don’t understand”. Can you speak on existing accessibility barriers relating to the world of ocean research?
WS: The ocean has mostly been inaccessible to most humans throughout our history. It’s dark, cold, the pressures will crush you. We can’t breathe in the ocean without special equipment. Sea water is corrosive, and the ocean is filled with creatures that can sting you, bite you–even completely consume you. How do we reconcile that reality with the other side of the truth: the ocean is the source of all life, provides half the oxygen we breathe, controls the temperate climate that allowed civilization to advance in the places humans settled over the past 20,000 years? All that, and we have barely scratched the surface of other ocean benefits for humanity–the products it produces to enhance our well being, supplying us with protein, and even curing disease. And yet, through my entire lifetime, the ocean has been under attack—from chemical runoff and pollution, discarded fishing gear, overfishing practices, ocean noise from the 55,000 container ships that cross our seas every day, and the constant pumping of excess C02 into our atmosphere from the burning of fossil fuels.
The people we want to engage in our outreach probably don’t live anywhere near the Ocean. They may see it from aeroplanes or ferry boats, and think it doesn’t matter to them. I didn’t know it mattered to me until I started to really look at it. Now I can’t stop looking.
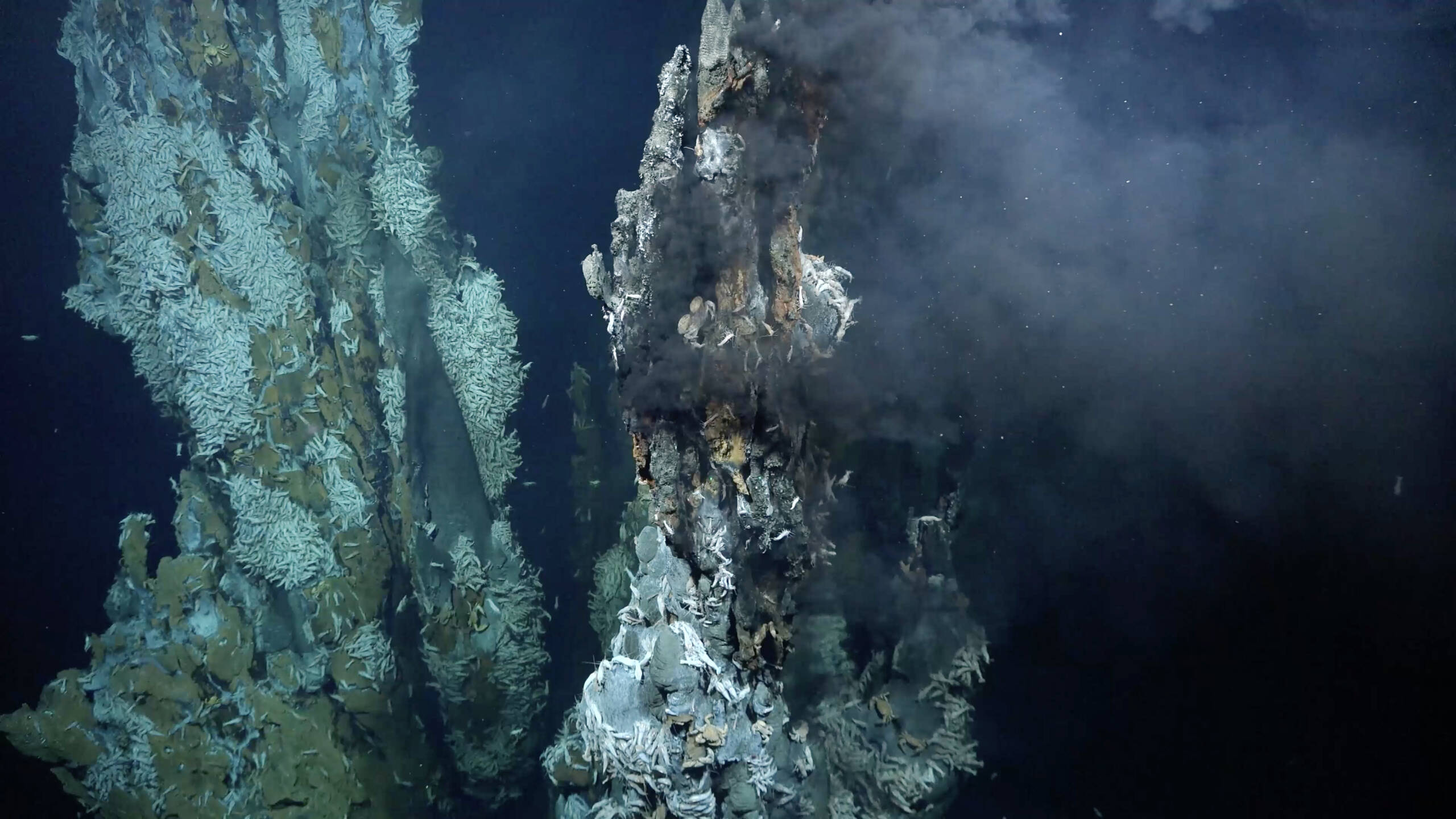

Newly Discovered Hydrothermal Vent Field on Puy des Folles Seamount in the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
LUX: In addition to oceanography, your philanthropic endeavours also cover other areas, from AI to renewable energy. Can you tell us how you go about identifying areas to focus your support across a diverse range of fields?
WS: We are living in a revolutionary time in human history, and, unlike people alive during earlier times of revolution, we actually know it. We experience it every day and for many people, the world has become a confusing place that changes too quickly for us to understand.
We have a corresponding opportunity in such a world to use the emerging tools of technology to rethink the human relationship to the finite resources of the Earth: our soils, atmosphere, fresh water and energy sources, and, of course, the largest living space on the planet, where 50-80 percent of all life resides–the ocean. Our planetary systems are deeply interconnected —in ways we are only beginning to understand because our technologies allow us, for the first time, to observe and to measure what was either hard to encounter or simply invisible to us.
With today’s growing suite of technologies that help us to see, analyse, understand and encounter what is here, and to incorporate Indigenous wisdom that supported human life on Earth for millennia, we have the chance to pursue human activity as a part of the living systems of the world. We work to help build a world with energy and food systems that are regenerative by design, accessible for everyone, and that respect human rights and dignity, even as we bring AI and machine learning into our work in ways that can amplify human potential everywhere.

An aerial image of R/V Falkor (too)
LUX: In your view, how crucial is the role of philanthropy in furthering the cause of ocean conservation and wider issues of sustainability?
WS: Philanthropy holds a unique position when it comes to problem solving. Think of philanthropic funding as a kind of philanthropic capital invested in activities of transformation. I think of our funding as energy, or velocity, brought to the work. Our risk profile for return on investment is far higher than what could be borne by industry or governments. We are patient and recognize the transformation of existing systems is a marathon, not a sprint. But over a decade, over two, you can see the shift happening in the way people think about what is possible.
Our work through Schmidt Marine Technology Partners for example, has been groundbreaking in getting useful technology that might otherwise remain a pet project into development and into the hands of marine researchers and ultimately into a global market that includes governments, research institutions, coastal and fisheries planners and managers, and many others.

Reseach Vessel Falkor photographed off the NW coast of the United states. Photo by Shelton Du Preez/SOI.
LUX: What are your future aspirations for the Schmidt Ocean Institute and its impact on advancing scientific knowledge, ocean exploration, and conservation efforts?
WS: My husband, Eric, and I look at Schmidt Ocean Institute as one of our legacy institutions–one that will live well beyond our own lifetimes. Its mission is so extensive and so critical to future life on Earth, and we know we are only at the beginning of the journey that brings humanity back to the ocean as its stewards and guardians.
I’ve been saying how little we know about the Ocean. Let me give you a few examples. There are up to 10 million marine species, bacteria and viruses in the ocean, but only 10 percent of them have been classified. That’s like saying, we don’t really know what life on Earth looks like. What we see on land is only a small part of it.
Read more: Jackie Savitz on why governments much protect the oceans
Only about 25 percent of the estimated 140 million square miles of the ocean floor has been mapped in high resolution so far. We know more about the back side of the moon than we do about our own planetary surface. Most people would be surprised to learn about underwater rivers, mountain ranges, kelp forests or how one researcher described her submarine journey into the darkness of the deep, saying everything was lighting up around her: “It’s the 4th of July down here.”
In the past, explorers had ships from which to encounter the ocean and mechanical instruments with which to sample and measure its activity. We have rovers and deep sea robots that never tire, high resolution cameras, high performance computers and AI that can see things invisible to the human eye, and make sense of information that we can’t without impossibly long periods of analysis.
If we can’t learn the Ocean with all these tools, it would be a failure of humanity to understand what our life on Earth really is, and would likely spell our doom, because with “life as usual,” we are destroying our life support system. We have a responsibility to use this extraordinary opportunity to explore the frontiers of our planet in a way that is ethical and inclusive, that will serve all peoples of the world and preserve the integrity of the living systems that support us all.
All images courtesy of the Schmidt Ocean Institute
Find out more: schmidtocean.org

The Syväysjoki peatlands within the Koitajoki Basin, Finland. Peatlands like this have been damaged through drainage, peat-mining, and planting for commercial forestry © Mika Honkalinna/Snowchange.
Financier, philanthropist and environmentalist Ben Goldsmith explains how environmental conservation became such an important aspect of his life and why it should be at the forefront of all philanthropists’ agendas
I am lucky enough to be raising a family on a former dairy farm in an area of low agricultural productivity, in South Somerset’s Selwood Forest. Until the Victorian era, a great mosaic woodland stretched across this landscape, from Bath to Wells and down to Frome. This was a landscape of extraordinary natural abundance and vibrancy, in large part on account of the grazing, browsing, rootling and dung of the free-roaming hardy pigs and horned cattle that were turned out by villagers into the forest. These were of course proxies for the wild boar and aurochs of an even earlier age, keystones of the forest ecosystem.
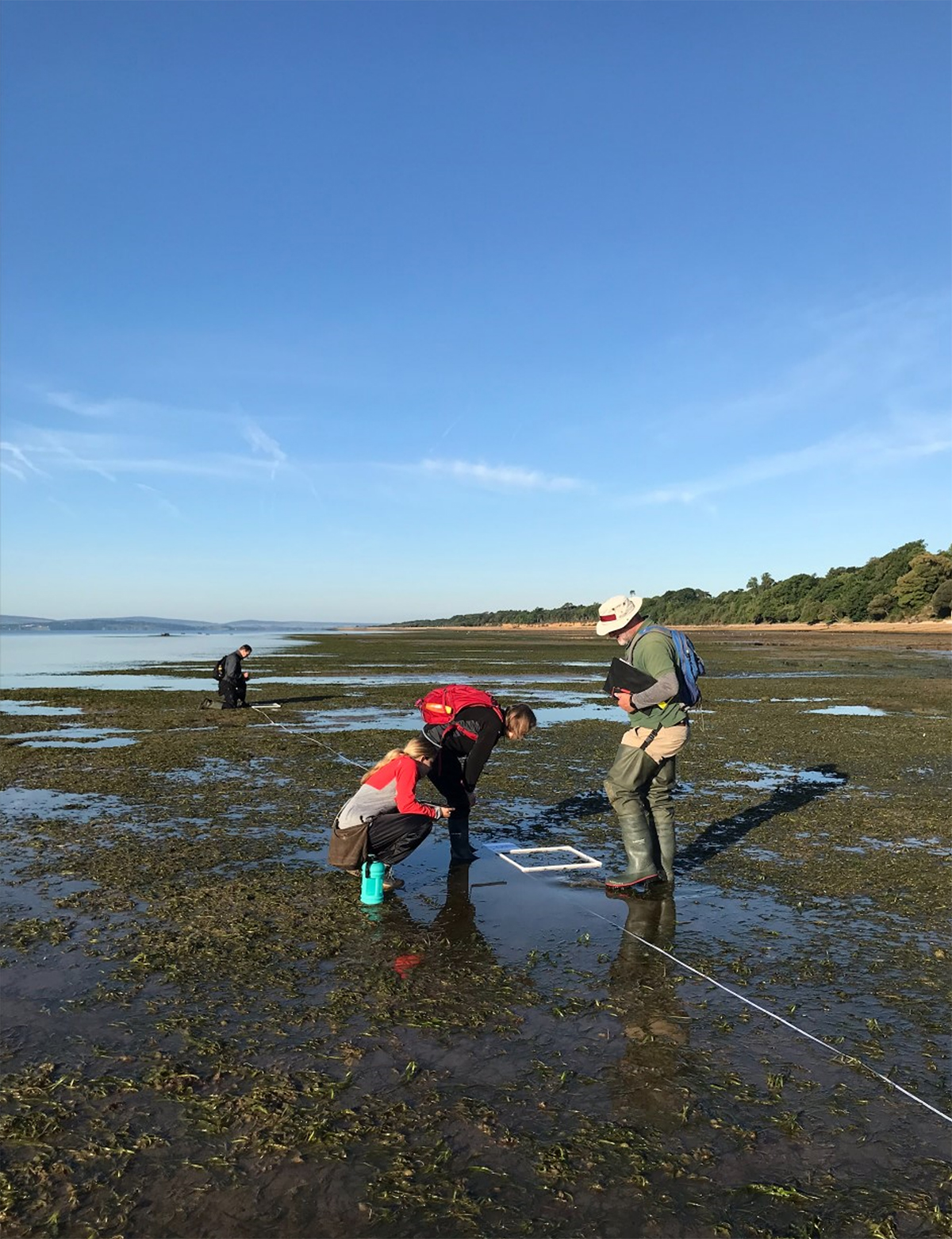

Solent Seagrass Champions restoring seagrass meadows on the Isle of Wight © Hampshire and Isle of Wight Wildlife Trusts/Blue Marine Foundation
Recently, alongside two neighbours, we decided to set about reviving the lost woodland. We tore out fencing, switched to native cattle in far lower numbers, rewiggled streams and revived ghost ponds. As the field shapes have begun to dissolve into the landscape, and little patches of crab apple, hawthorn and willow have begun to emerge everywhere, the results have been both startling and magical.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Life has poured back in; the birdsong in spring is at times overwhelming in its intensity, a string of dammed pools created by beavers along the bottom of the valley now abounds with amphibians and dragonflies, the open areas are a riot of wildflowers and tiny chirruping crickets. By comparison, the surrounding landscape seems silent, drained of colour.

A baby Hawksbill sea turtle in White Sands, Canash Beach, St.Vincent. Photo by Stephan Hornsey
Immersing myself in this transformation has brought me a greater sense of joy and meaning than anything I’ve done in my life. The natural fabric of the world, in other words that vast life support system on which we depend utterly for everything we have and everything we do, is quite simply blinking out all around us. And yet, here in Selwood, I have seen first-hand that nature rebounds with astonishing intensity and speed. All we need to do is give it the chance. In the grand scheme of things, this is not expensive to do. So why are philanthropists, large and small, not grabbing the opportunity to participate in a movement that is at the same time so vital and so rewarding? Owning land is a niche privilege which appeals to some; but participating in the restoration of nature need not be.

The critically endangered monk seal. In Turkey the project is establishing marine protected areas along 500 km of coastline. Artificial nesting platforms have been constructed, which are increasing the monk seal’s breeding success © Fauna & Flora
Just 3% or so of all the money given away philanthropically is directed towards the protection and restoration of the natural environment. Almost ten times as much is given to the arts. Happily though, modest amounts of environmental philanthropy, well directed, is capable of catalysing great change. Lisbet Rausing’s marvellous Arcadia Fund has created an Endangered Landscapes Programme, which dishes out grants of up to €5 million towards the long-term restoration and protection of Europe’s largest remaining intact landscapes. The money is geared towards piecing ecosystems back together, reintroducing missing species, and perhaps most importantly, establishing long-term local prosperity arising from richly abundant nature. It works. Great swathes of Europe are coming back to life as a result of this one programme.

Questelles beach, St.Vincent successfully hatched hawksbill nests in 2022. Photo by Stephan Hornsey
Sir Christopher Hohn’s Children’s Investment Fund Foundation has made huge contributions to the Foundation for International Litigation on the Environment, as well as underwriting the spectacular growth of Client Earth. These two organisations are using the law all across the world to win key environmental battles on everything from air pollution in cities to the protection of old growth forests. Each successful case sets a precedent which makes the cost of trashing nature that much higher for companies or governments which might be tempted. This is game-changing work.

Reintroduction of large herbivores in the Danube Delta, including König horses, is restoring dynamic ecological processes in the floodplain © Andrey Nekrasov/Rewilding Ukraine
Meanwhile, the big idea of Conservation Collective, which I chair, is that people are far more likely to give their time and money towards restoring nature in the place that they love. There are now twenty locally-focused Conservation Collective foundations across the world, from Barbados to the Balearic Islands, Devon to the Dalmatian Coast. Each one of these is comprised of a dozen or more supporters who give in the thousands rather than the millions, their money strategically distributed to the most effective grassroots restoration and activist initiatives in the place that is closest to their own heart.
Read more: Kering’s Marie-Claire Daveu on the future of sustainability
Vultures are recovering from near extinction in Cyprus, new forest corridors in Sri Lanka are enabling leopards to move between protected areas and the ban on killing sea turtles in St Vincent and the Grenadines is being enforced by local monitors. The network is growing beyond our wildest imaginings, because playing a part in the dramatic recovery of nature is hugely appealing, and ultimately addictive.

One of Wilpattu National Park’s dominant male leopards, the Kumbuk Villa Male, doing his morning rounds. Photo by Yanik Tissera
Every important victory that has been secured, from the saving of the whales in the 1970s to the turning of the tide on the destruction of the ozone layer in the 1990s, has happened because of small groups of passionate, brilliant people – supported by the generosity of philanthropists large and small. Giving a small amount each month to one of these organisations is a meaningful, radical and powerfully rewarding act, one which far too few people in our society have discovered.

Ben Goldsmith and his family
The three most effective things any one of us can do towards fixing this, the mother of all issues, and moving our civilisation into a new age of harmony with nature are: to vote with nature in mind; to buy stuff mindfully; and to choose a nature organisation to support with whatever regular amount you can afford. Once you start, you won’t stop. And when your children or grandchildren one day ask you what role you played in all of this, you’ll have an answer for them.
Find out more: conservation-collective.org

Left to right: Philanthropist Durjoy Rahman with collector Maria Sukkar and LUX Editor in Chief, Darius Sanai
In the fourth of our series of online dialogues, Maria Sukkar, one of the most significant collectors in the UK and Co-Chair of the Tate Middle East North Africa Acquisitions Committee, speaks with philanthropist Durjoy Rahman, moderated by LUX Editor in Chief Darius Sanai. Their wide-ranging conversation covers the need to support artists from your place of origin, the western eye, and the emergence of new art powerhouses, among much else
LUX: Durjoy, you are from Bangladesh and Maria, you are from the Lebanon. Is it important to you to collect art and to support artists from your home countries?
Durjoy Rahman: I’m based in Bangladesh, but with collecting I extend to a broader South Asian perspective. We were an undivided subcontinent before partition in 1947, and to understand the development of art in the region, we must understand that context. My collections also include the diaspora of South Asian artists in Europe and the Americas, and artists from other regions whose practice have relevance to South Asian practices. Bangladesh has a long history of art but, because of colonialism – Bangladesh did not become independent till 1971 – much of our culture was lost. I recommend that collectors from this region start their art and philanthropic activities here, to restore lost heritage and give future generations evidence of our identities and history.
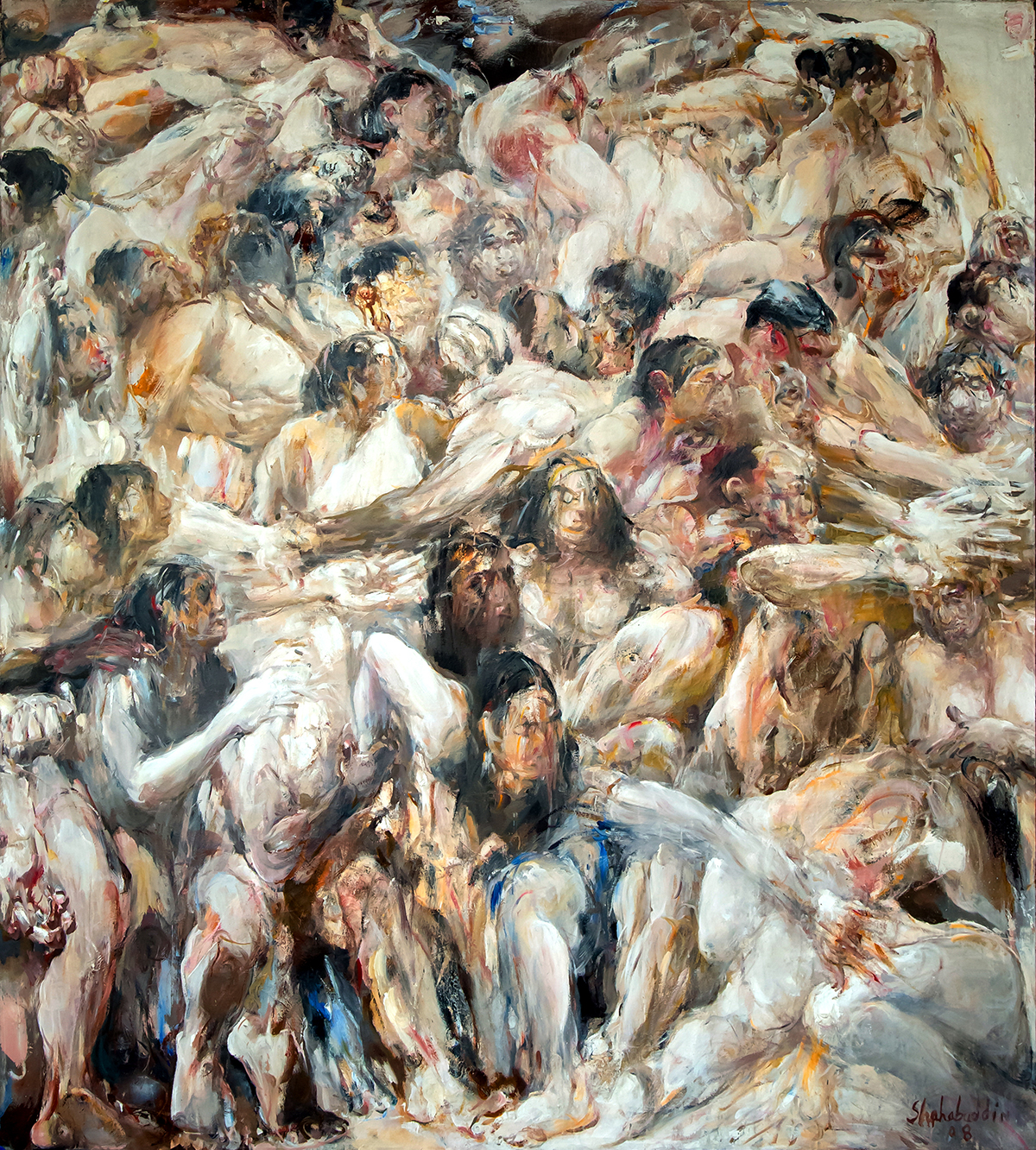

Festival by Shahabuddin Ahmed a Bangladeshi painter whose works are part of the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation’s Collection
Maria Sukkar: I agree. I also think you gravitate towards artwork from your region because it tells your story, and it helps define who you are. I started collecting on a small scale with my husband when we were married 25 years ago, but when we moved to London it snowballed, and we collected art from everywhere. Maybe my relationship with Middle Eastern art intensified because it reminded me of things I love about my roots. I believe collecting art from the region one comes from adds a beautiful layer to your life.
LUX: Is there a dialogue between South Asia and the Middle East in terms of art?
DR: I believe so. The Sharjah Art Foundation in the UAE did a Pop Art exhibition last year, “Pop South Asia”, and the curator included work from my collection because it represents the development of Bangladesh art specifically, but also relates to the South Asian stream, going beyond to MENA and on to the European school. We collaborated with Art Dubai this year, and one of the curatorial topics was food politics and identity. We featured the South Asian famines of 1944-45, and how the colonial powers orchestrated them.
MS: From my experience in the Gulf, Dubai, UAE and now in Saudi Arabia visiting the Islamic Arts Biennale, there has been a huge effort to showcase different talents and disciplines, and there are fewer and fewer taboos. What you see is impressive and sometimes daring. They are mixing media and there is a lot of photography and textiles, and very impressive installations.

Maria Sukkar’s ISelf Collection displayed at the Whitechapel Gallery, London, showed many works from Akram Zaatari’s The End of Love series
LUX: What’s the best way for influential collectors, like yourselves, to support artists today?
MS: First, collecting an artist’s work opens doors for others to see them, and displaying works at your home with work by artists from other regions means people see the works in a different light. Secondly, if you can bring an artist to an overseas residency, they can do research, meet new people, visit new institutions and museums and return home feeling culturally enriched, ready to explore other avenues and create great work. Thirdly, you can sponsor shows abroad, both financially and by organising events around them. A fourth idea is to host events for visiting artists. When I know a Lebanese artist is coming to town, I open my home. Finally, if an artist is representing your country at a biennale, support them. It’s a great way to show your country exists. Putting a pavilion together costs a lot of money, so supporting the artist elevates them and makes some noise, enabling people to learn about your country and your artists.
DR: I would just add to support emerging curators as well as artists. And one important addition to the art ecosystem would be to support publications, so curators are aware of developments and practices of artists in the region. Publications will remain as archival facts, which are very much missing in South Asia – and much needed.

An Eye for an Eye, 2008 by Ayman Baalbaki, ISelf Collection
LUX: Is the art world still judged via the lens of the Western eye, or are artists being validated via another lens that doesn’t require Western perspectives?
DR: I call it the ‘Western gaze’. The Western art ecosystem has developed very structurally, it is very professional in exhibiting and documenting what it has, and Western art education is very forward-thinking. So, the West has had the liberty to look at the South Asian ecosystem however it wanted to, and it has been West looking at East. But this has been changing in the past decade with so many developments in these regions – the Biennales, Desert X, museums and major art fairs. These activities are important catalysts to changing the Western gaze and shifting things so that the East also looks at the West. The West is also sometimes dependent on what is happening in the Eastern art market.
MS: In recent years, with the mushrooming of art fairs and the changing communication between countries and organisations, the Western gaze has subsided. If you walk, for example, through the Tate display rooms, you see the artwork is grouped thematically, not chronologically or by country, so you see artists from different countries side by side. So, I personally do not see that sort of Western look at Eastern art.
Untitled, 1994 by Hassan Jouni, ISelf Collection
LUX: Is there a barrier to people becoming artists in MENA and South Asian countries? Is there a taboo, that you need to become a doctor, lawyer or engineer?
DR: When you become a professional, you know you have a career path that will give you a living. Being an artist is tough, a lottery. Even in Europe, an art career was traditionally supported by the wealthy, such as the Medicis, because they knew artists needed support. So an art career was challenging a thousand years ago and it is challenging now. Maybe it’s more challenging, because today you have a lot of eyes looking at you from different perspectives – a contemporary perspective, a social perspective, an activist’s perspective. I think it is more of a difficult life than a taboo or social restriction.
MS: Being Lebanese, I think people of my generation would have found it difficult to choose a career in art. You had to pick a profession that would put food on the table. And I agree, Durjoy, sometimes it’s a lottery, sometimes you cannot find your niche. There’s a lot of competition and you can spend your life not making it. But I feel there are more opportunities for our children to be successful artists today. The question is, do we let our children follow their passion, or do we still dictate what they should do?

Gandhi-IV by Shahabuddin Ahmed. Part of the Durjoy Bangladesh Collection
LUX: Many women drive the art world in the West, but the societies we are discussing are often patriarchal. Has that been detrimental to artistic development?
MS: I think patriarchal societies have left so many interesting women artists in the dark for such a long time. But hasn’t this been the case at the West as well? Look at amazing women like Louise Bourgeois, who had retrospectives in their late years. I noticed the power of women in Saudi, where they are incredible – a force – and one has no idea until one visits. If you look at the directors of many major UK institutions now – Tate, Whitechapel, Nottingham Contemporary – they’re women. Then there is the book by Katy Hessel, The Story of Art Without Men. So the tide is turning, but it will take time because change takes time.
DR: The South Asian art ecosystem is very much influenced by female curators, gallerists and collectors. If you name the top curators from South Asia, more than 60 per cent are female. There is a South Asia male dominance but, in terms of creative matters, if you have talent, if you have the energy, nobody can stop you. And I think women are ahead in our part of the region in art-related philanthropy.

Cedar, 2009 by Nabil Nahas, ISelf Collection
LUX: In the 1990s, there was much less global awareness about these regions artistically, and that has changed beyond recognition. What will these regions will be like in the next 30 years?
DR: Today, you could say the European art hubs are Paris and London; in America, New York and LA. In the future, I don’t think there will be major hubs, because so many things will happen across the globe. We will be more diverse, and there will be developments in technology and in the transmission of information. So, I think there will be a global platform in 30 years, not a specific centre like the Gulf, or South Asia or Europe. You will be a player in a global arena without regional or continental divides.
MS: I think what’s helping this is the curiosity the West has towards the East. Don’t forget these countries were very private for many reasons. Art from Asia and the Middle East was not always something you would see on museum walls in the West, but this exchange and curiosity is allowing people to visit, to come back with things, to unify countries. I think we’re on the way.
Find out more:

Whose Sari Now, 2007, by Charles Pachter
On the 75th anniversary of the end of British rule in India, LUX’s Maya Asha McDonald speaks to Durjoy Rahman, Bangladeshi philanthropist, art collector and founder of the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation, about the legacy of colonialism and Bengali art
At midnight on 15 August 1947, British India ceased to exist. As the British Empire receded into the history books, the vast land was divided into two dominions largely along religious lines: Hindu-dominated India and Muslim-dominated Pakistan. Marred by large-scale violence and mass migration, the controversial division of the subcontinent would be known as the partition.
With 2022 marking 75 years since the end of British rule, it is a time for reflection for many in these countries, not just about politics and history, but about the art and culture of the region, traditions that stretch back millennia but are now in the same vortex of globalisation as others on the creative planet. Durjoy Rahman founded the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation (DBF), a non-profit organisation, in 2018, with a mission to support and promote art from South Asia and beyond in a critical, international- art context. There is, he believes, a vantage point from which we can examine the past, understand the present and envision the future.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Speaking with me amid his art collection, in Dhaka, Bangladesh, Rahman says it is important to acknowledge the weight of the moment. “This is a big year for the Indian subcontinent: it’s 75 years since partition. 1947 may sound long ago, but my parents and many others retain vivid memories of that time,” he says. A seismic event, partition saw the migration of 14 million people and laid the groundwork for a second postwar revision of the subcontinent’s political cartography some years later: the creation of Rahman’s native Bangladesh, from what had been East Pakistan.

Durjoy Rahman, founder of the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation, whose mission is to support and promote South Asian artists in a global context
“It is important to consider that Bangladesh was born in 1971, much later than India and Pakistan,” says Rahman. “Since we were established further along in the historical timeline, Bangladesh is behind in development compared to the subcontinent’s other countries. But our rich heritage and culture, originating in Bengal, has helped us reclaim our reputation.” The historic region of Bengal, to which Rahman refers, covers present-day East Bengal in Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal.
The Dhaka-based entrepreneur turned cultural activist is playing a vital role in rebuilding his country’s national voice, working diligently to elevate his homeland’s artistic titans and emerging talents. In establishing the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation, Rahman also committed to furthering decolonisation. By incorporating his country’s name within the foundation’s title, in place of his surname, Rahman shares the DBF’s accomplishments with Bangladesh. In fact, ‘Durjoy Bangladesh’ means ‘Invincible Bangladesh’.
A cardinal tenet of the DBF’s mandate is to preserve the canon of Bangladeshi artists who flourished throughout the 20th century. “I have consciously collected works by artists who shaped the practice of modern art in Bengal,” says Rahman, whose foundation has created the first online personal-collection resource on Bengal Masters. “Murtaja Baseer, Mohammad Kibria and Safiuddin Ahmed are among those names. They have all sadly passed, but held great artistic influence before and after partition. Today, their work continues to inspire.”
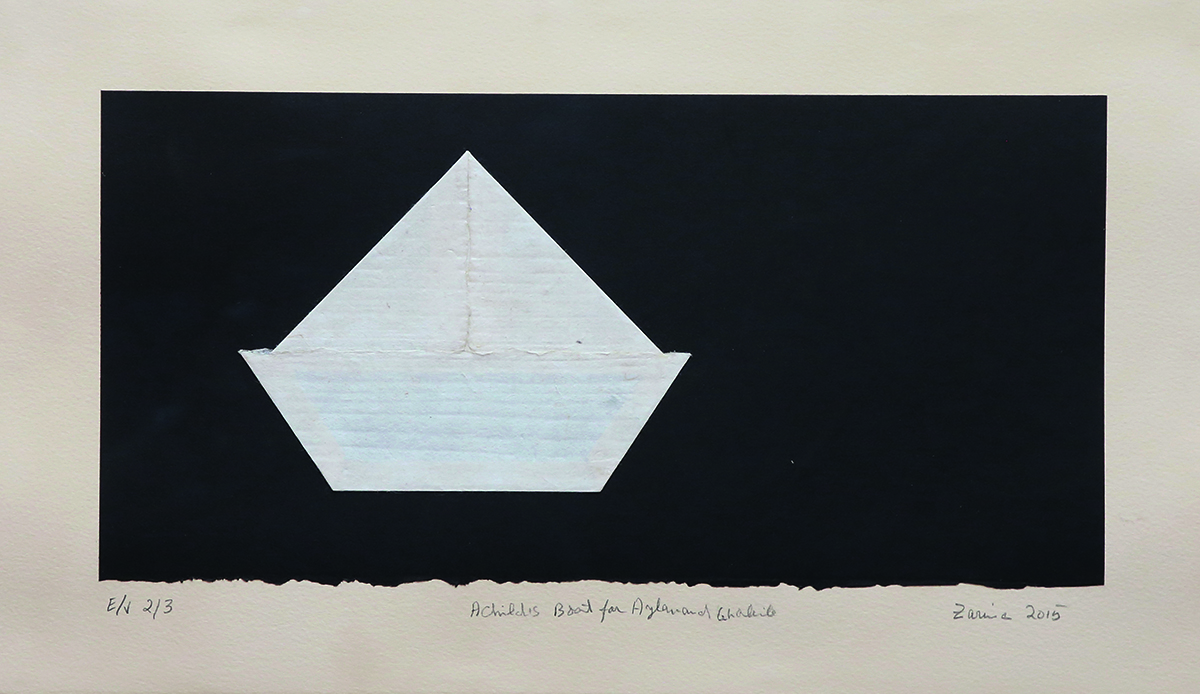
A Child’s Boat for Aylan and Ghalib, 2015, by Zarina
And so to the art collection. Pleased to share his Bengali treasures, Rahman directs my attention to Murtaja Baseer’s 1967 work, The Wall, from his series of the same name. Depicting a brick wall in the Dhaka Central Jail, the painting references the harsh realities of life in the 1960s under the dictatorship of Ayub Khan, the general who had seized the presidency in Pakistan (including East Pakistan, later Bangladesh). Composed of precise lines and balanced colours, this influential work of abstract realism is also broadly interpreted as a critical commentary on society at large.
Next, Rahman shows me two pieces by Mohammad Kibria and Safiuddin Ahmed, both created in 1980. At a glance, it is clear that Kibria and Ahmed share Baseer’s desire to visualise history. Ahmed’s copper engraving, aptly named The Cry, is a witness to the volatile period, including partition, that the artist lived through. Similarly, Kibria’s painting, Memorial, functions as precisely that, a visceral ode to the many souls lost during Bangladesh’s bloody Liberation War of 1971. In recent years, Kibria’s emotionally charged netherworlds have realised prices far above estimates at Christie’s auctions. It would seem Rahman has prophetic instincts.
Executed with a Bacon-esque flair and featuring baroque-like figures, Rahman’s masterwork by Bangladeshi artist Shahabuddin Ahmed, Untitled, 1975, is instantly one of my favourites in the collection. “His style may be slightly more European,” says Rahman, “but his subject matter is always something close to home.” With its dynamic composition, the scene emanates a kaleidoscope of emotions. Ahmed’s cosmic dancers at once invite the viewer to come closer, while alluding to the turbulence surrounding the 1975 Bangladesh coup d’état.

Herself, 1983, by Andy Warhol
To a large extent, Ahmed’s seminal work epitomises what Rahman believes art ought to be at its highest ideal. “Art should address the common man. It should not be completely detached from our daily life and society; if it is, then art won’t survive,” he expounds decisively. “That being said, creativity should be exercised with tolerance. Artists should look outside themselves and respect all peoples, regardless of race, religion or region.” Unsurprisingly, Rahman’s collection reflects his artistic philosophy.
Consequential and bewitching, Rahman’s modern works by South Asian artists offer a powerful visual chronology of the Indian subcontinent. I stare at them in awe. To my right, Nandalal Bose immortalises the struggle against British colonial rule in India with his 1936 portrait of a freedom fighter, Untitled (Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan). Further down, Sayed Haider Raza sharply illustrates the Bangladesh Liberation War, with partition as its antecedent, in a lithograph, Untitled (Bangladesh), created around 1971. And hanging above where Rahman stands, Atul Dodiya takes on the mantle of decolonisation by reversing the Western gaze, in his 1999 diptych, German Measles: Kiefer’s Cell. And that is only to examine three artworks out of hundreds.

From the ‘Soaked Dream’ series, 2013 ongoing,
by Firoz Mahmud
Rahman has a special place in his collection for those artists of South Asian origin who left the subcontinent and settled in the West. “The legacy of partition is fundamentally linked with the concept and experience of displacement,” he explains. “This concept applies to diaspora artists, too, such as Rasheed Araeen and Zarina Hashmi, known professionally as Zarina.” Araeen is a celebrated Karachi-born conceptual artist living in London, and the late Zarina was a trailblazing Indian-American minimalist active in New York City. Both artists are in the permanent collections of Tate Modern and The Metropolitan Museum of Art.

German Measles: Kiefer’s Cell (diptych), 1999, by Atul Dodiya
Another prominent artist from the South Asian diaspora community for whom Rahman is a patron is the rising star Firoz Mahmud. Originally hailing from Khulna, Bangladesh, Mahmud lived in Japan and now lives and works in New York City. “The DBF is always engaging with projects that deal with the topics of migration and displacement,” says Rahman. “Mahmud is an expert at tackling these issues in his multidisciplinary exhibitions.”

Noakhali, November 1946, 2017, by Atul Dodiya
Indeed, Mahmud’s ongoing series, ‘Soaked Dream’, begun in 2013, which features displaced minorities including the Rohingya people, has received critical acclaim and was nominated for the 2019 COAL Prize at the Centre Pompidou, Paris. The harrowing yet hopeful photo-sculpture series depicts migrant families envisioning their dreams through green sci-fi glasses, crafted with found objects from shelters and symbolising each family’s resilience and commitment to making a better life. It was photographed in Bangladesh, which has accepted more than 900,000 Rohingya refugees. Rahman says the series helps bring awareness to an issue that has largely faded from the West’s consciousness.

Untitled, 2015, by Rasheed Araeen
Several works in the collection address both Eastern and Western canons. One such piece is Atul Dodiya’s monumental 2017 collage, Noakhali, November 1946, which was shown at Art Basel 2018. As part of his series ‘Painted Photographs/Paintings Photographed’, Dodiya juxtaposes Europe’s first half of the 20th century against the same period in British India. “A dramatic shift took place, particularly in France, with artists such as Henri Matisse, Pablo Picasso and Marcel Duchamp,” Dodiya wrote of the work. “During this period, India was fighting for freedom, which resulted in Independence from British rule and ended with Gandhi’s assassination.” Feeling almost inconsequential in its presence, I would suggest that this is Rahman’s most significant artwork.

Portraits by Matt Holyoak
As a cosmopolitan figure, the DBF founder’s collection also contains works from the Western canon that often wink at the Global South. These include enviable acquisitions, such as Charles Pachter’s witty 2007 painting, Whose Sari Now, and Andy Warhol’s iconic 1983 screenprint of Ingrid Bergman, Herself. Both Pachter and Warhol famously travelled to India, voyages that would inform Pachter’s subject matter and influence Warhol’s affinity for using vibrant swathes of colour in his work.

Untitled (Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan), 1936, by Nandalal Bose
Unexpected links arise, too. Even Ingrid Bergman has a connection to the subcontinent through her one-time husband, Italian film director Roberto Rossellini. Rossellini rather publicly left the Casablanca star in 1957 and eloped with Bengali screenwriter Sonali Dasgupta, to whom he remained married until his death in 1977. Clearly, Rahman’s collection is saturated with buzzworthy creations, rich in historical and cultural intrigue.

Untitled (Bangladesh), c 1971, by Sayed Haider Raza
Tearing my gaze from a brightly coloured Bergman, our conversation flows away from Rahman as collector to his ever-expanding identity as an international change agent. With the continued reverberations of the partition top of mind, the philanthropist draws a straight line between the largest mass migration in human history and the DBF’s mandate.
Read more: Shezad Dawood: Out Of The Blue
As a fledgling foundation itself, Rahman believes the DBF can empathise with the South Asian struggle of trying to gain purchase on the global stage. To help others avoid the similar exclusionary effects of colonialism and partition, he says, “many DBF initiatives work to help individual South Asian artists claim recognition outside the Global South. Part of that process means taking up space, both physically and metaphorically.”
Find out more: durjoybangladesh.org
This article first appeared in the Autumn/Winter 2022/23 issue of LUX

Alex Mustard photographed healthy reefs in the Maldives
As our oceans warm up, the spectacular coral reefs of the Maldives archipelago are dying. Michael Marshall reports on the new philanthropic project aiming to make them more resilient to climate change
Beneath the glittering cerulean waters of the Maldives archipelago, trouble is brewing. The extraordinary coral reefs that encircle these islands are being damaged by climate change, threatening the country’s very survival.
Fortunately, help is at hand. A local research and conservation institute has bold plans to strengthen the reefs by breeding the most resilient corals and seeding them in the waters of the Maldives. With the help of a new philanthropic initiative, led by Deutsche Bank, the project is ready to set sail.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
The Maldives is one of the countries most affected by climate change. “You couldn’t find a place more in the front lines,” says Callum Roberts, Professor of Marine Conservation at the University of Exeter.
As the Earth’s temperature warms, driven by greenhouse gas emissions, the oceans are being reshaped. Most obviously, sea levels are rising – and for low-lying islands like the Maldives that is an existential threat. But there’s more: seas are warming, the water is becoming more acidic and low-oxygen zones are spreading. These changes threaten all marine life.
Climate change poses a particular threat to corals. These tiny animals live in huge colonies underwater, and over thousands of years the skeletons of dead corals build up to make vast structures called reefs. The Maldives themselves are coral reefs that grew until they reached the surface, and the country’s islands are ringed by underwater reefs. These are home to an extraordinary range of animals, from sharks to starfish.

More photography by Alex Mustard of healthy reefs in the Maldives
“Your first experience of a coral reef is completely unforgettable,” says Roberts. “You dive over the reef crest and into that area where it’s just a huge blaze of fish of all varieties and colours.” It’s utterly immersive, he adds; you can “feel yourself being completely consumed by an ecosystem”.
Corals are particularly vulnerable to warming. “It doesn’t take more than a rise of about 1°C above their normal thermal maximum for corals to get into deep trouble,” says Roberts. “That’s what’s been happening.”

Callum Roberts
In 1997-98 and 2015-16, spikes in ocean temperature caused mass coral bleaching events. The corals expelled the algae that live inside them and that they depend upon for nutrients. As a result, the corals turned ghostly white. The first bleaching event killed an estimated 95 per cent of shallow corals. They then underwent a partial recovery, before the second mass bleaching event caused about 65 per cent mortality. “That level of coral death is extremely worrying,” says Roberts.
In a 2018 report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change stated that “coral reefs would decline by 70-90 per cent with global warming of 1.5°C, whereas virtually all would be lost with 2°C.” So far, the Earth has warmed by an estimated 1.1°C.
To save the corals, and by extension the Maldives, the country’s former president Mohamed Nasheed founded the Maldives Coral Institute (MCI). The MCI aims “to help coral reefs to survive and adapt to the changing climate”. Roberts is one of its scientific advisers.

Alex Mustard also photographed bleached, dead corals highlighting the abundance of sea life at risk if corals are left to decline
The MCI is now being financially supported by Deutsche Bank. In November 2021, the bank launched its Ocean Resilience Philanthropy Fund, which is intended to support nature-based solutions to marine conservation problems. Deutsche Bank committed an initial $300,000 and hopes to raise $5 million over the next five years. The MCI was brought to the bank’s attention by Karen Sack, Executive Director and Co-Chair of the Ocean Risk and Resilience Action Alliance.

Jacqueline Valouch
“The lack of funding is one of the big recognised barriers to nature-based solutions,” says Jacqueline Valouch, Head of Philanthropy at Deutsche Bank Wealth Management in New York, who was involved in setting up the fund.
“We’ve got this massive problem, the Maldives Coral Institute has a mission, and Deutsche Bank is funding a really important piece of work to begin with,” adds Roberts.
The funding will enable the MCI to launch a project called the Future Climate Coral Bank (FCCB). The idea is to find corals that have proven resistant to climate change and breed them in a controlled environment, creating more resilient strains. “We’re going to have a living propagated coral farm underwater in which the idea is to explore and test ways of assisting evolution,” says Roberts. These resilient corals can then be reintroduced to the ocean, particularly to reefs with a poor supply of coral larvae. In the long run, this will hopefully mean the Maldivian corals become more resilient.
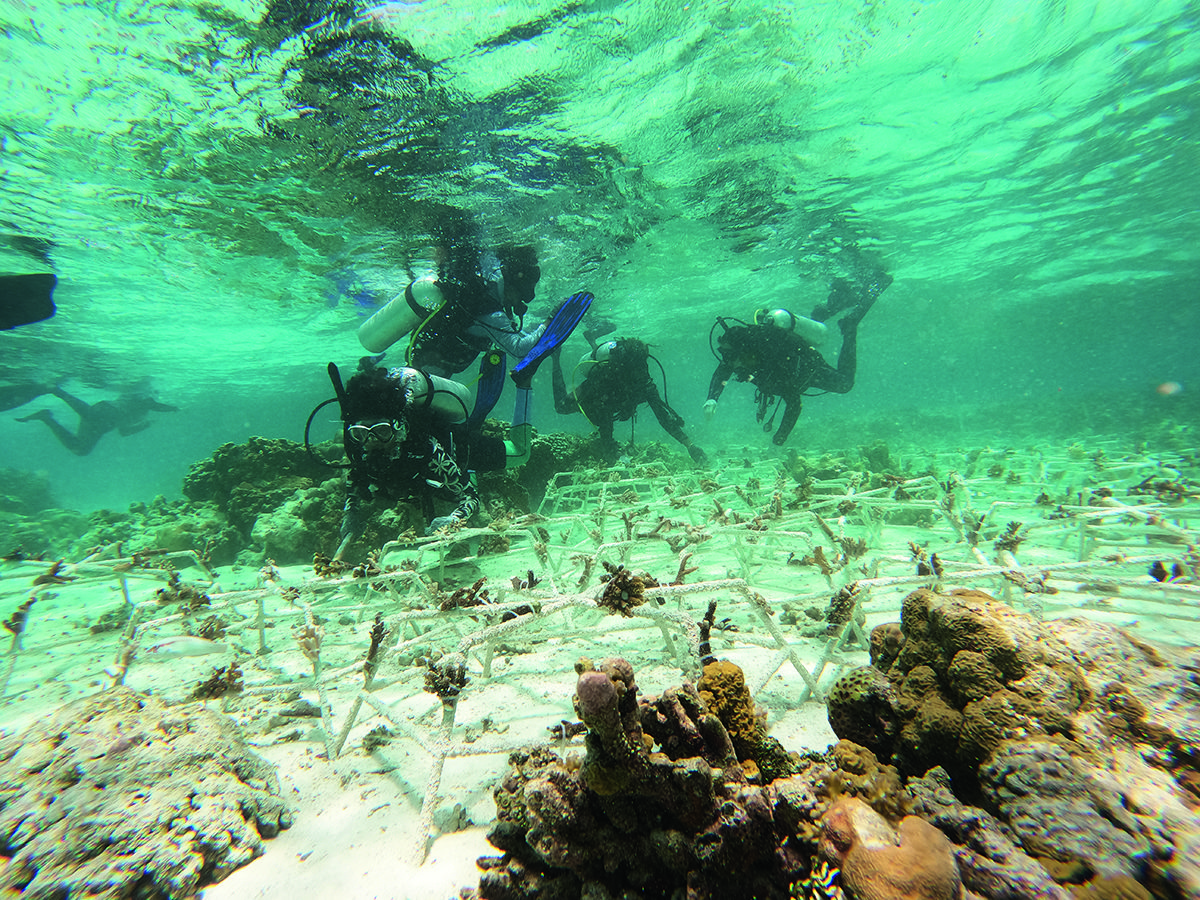

The MCI works on conservation projects including this one at Fulhadhoo, where divers installed a silt screen to prevent sediment from nearby construction from damaging the corals
“The magnitude of that impact to us was unmatched in many ways,” says Valouch. She says the FCCB “could last for many generations,” which is crucial, because her philanthropic clients want “to make an impact on the causes they care about”. “They’re multigenerational families coming from many different regions of the world and they have their family members living in different parts of the globe.”
Valouch and her colleagues plan to spend much of 2022 talking to donors. “We are looking to kick all that off now,” she says. A key element will be introducing prospective donors to the project team, so they can appreciate the talent and passion of all involved. Deutsche Bank is also recruiting a panel of experts who will advise on which projects to fund. “To be able to have that kind of innovation and creativity sit at the table with us is just extraordinary,” Valouch says.
For her, philanthropy can provide the seed funding for ambitious projects such as the FCCB. “It allows other donors to come in,” she says, and enables organisations like the MCI to recruit enough staff to become sustainable.
“I think the private sector has a greater appetite for risk,” says Roberts. That’s especially true for projects such as the FCCB. “This is not research that ends when you publish a study. This is something that has to make a difference on the ground and in the water.”
The hope is that, with the right investment, the corals of the Maldives will thrive for decades to come.
Five approaches to regenerating the world’s coral reefs
- Reducing agricultural runoff into the sea improves water quality and coral health.
- Coral IVF grows baby corals in the lab and seeds them on damaged reefs.
- Artificial reefs can be sunk in oceans to provide homes for corals and other sea life.
- Corals can even be given ‘probiotics’ to help boost their health.
- Most importantly of all, limiting climate warming to a maximum of 1.5°C and lowering global greenhouse gas emissions to net-zero will minimise the threat to the world’s coral reefs.
— Michael Marshall

Former President of the Maldives and environmental activist Mohamed Nasheed discusses climate change with children at the Maldives Coral Institute’s Coral Festival in 2020
A partnership of positive steps
The Ocean Risk and Resilience Action Alliance (ORRAA) is helping to drive a global response to ocean-derived risks. Backed by organisations ranging from the World Wildlife Fund to Deutsche Bank as global lead banking partner, it wants to save the oceans by deploying the power of the financial world.
Read More: Jean-Michel Cousteau: Choose Life
Its mission is “to pioneer new and innovative financial products” that will tackle climate change, protect ocean biodiversity and help coastal communities become resilient, says Karen Sack, Executive Director and Co-Chair of ORRAA.

Karen Sack
“We aim to drive at least $500 million of investment into coastal and marine natural capital, or ‘blue nature’,” says Sack. She argues that this is in everyone’s interest. The global ocean economy has a total asset value estimated at $24 trillion, but in the past decade only $13 billion has been invested in sustainable marine projects. “We need to change that,” says Sack. “And we need to act quickly.”
Hence the Maldives project. Deutsche Bank were looking for ways to have a positive impact quickly, as well as over the long term, and Sack suggested supporting the MCI. “Lessons learned in the Maldives will help heal and strengthen coral reefs around the world.”
Michael Marshall is a renowned science journalist specialising in the environment and life sciences
Find out more: deutschewealth.com/oceanfund
This article appears in the Deutsche Bank Supplement of the Summer 2022 issue of LUX

Marine biologist Matt Sharp was awarded the Ocean Conservation Photographer of the Year in 2020 for his incredible images, such as this one of a wave breaking in the Maldives in 2019
Marine life is threatened by climate change, pollution and overfishing. And depleted oceans risk collapsing the whole global ecosystem. A new generation of business startups is aiming to reshape the ocean economy, making it both truly sustainable and profitable. Michael Marshall reports
The blue economy is gaining momentum. Hundreds of startup companies around the world are aiming to protect, and even restore, the oceans, while making a profit. They want to get food and other essential resources from the sea in ways that benefit marine life – or at least don’t harm it. What’s more, there are plenty of organisations that aim to support these startups, whether with money or expertise or both.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
“We are not going to save the oceans if we don’t change the economy,” says Tiago Pitta e Cunha, the CEO of the Oceano Azul Foundation, a Portuguese non-profit that supports a variety of initiatives designed to stimulate the growth of the sustainable blue economy. The good news is that the business case for ocean conservation is real and growing. “There’s a wonderful opportunity for startups and new companies to develop business models,” says John Virdin, director of the Oceans & Coastal Policy Programme at Duke University’s Nicholas School of the Environment in Durham, North Carolina.
The ocean certainly needs our help. It faces three big problems – overfishing, pollution and climate change – that “tend to make each other worse”, says Nancy Knowlton, a professor of marine biology and Sant Chair in Marine Sciences at the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C. However, she adds, there have been some real success stories for ocean conservationists in recent years. Take Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), for example. These are regions of the ocean in which extractive industries are either banned or tightly regulated, and they have proven highly beneficial when implemented fully. In 2020, fully implemented MPAs covered 5.3 per cent of the ocean, and this area is growing every year. As a result, some animals that were once considered on the brink of extinction have increased in numbers, including many whale species.
At the moment, the blue economy is dominated by “a few really big fish”, Virdin points out. In 2021, he co-authored a study that found 60 per cent of all revenues obtained from the ocean came from just 100 companies, almost half of which were from the oil and gas industry. Such companies have “rigid processes in place, for good reasons”, says Alexis Grosskopf, the founder and CEO of OceanHub Africa in Cape Town, South Africa, an accelerator for ocean impact startups. Those processes “could not be disrupted smoothly and quickly enough, without blowing up or imploding”.
This is where startup companies come in. Small outfits with radical technologies and new ways of doing things can overthrow existing practices, if they’re successful enough. And in the blue economy there are now hundreds aiming to disrupt a variety of industries, from fishing and aquaculture to renewable energy, pharmaceuticals and waste management. Some want to take an existing industry, such as fishing, and do it better, causing less harm to the ocean ecosystem. Others are aiming to restore and repair, actively improving the marine environment while also making a profit.
As with all startups, the challenge is to survive long enough to build a customer base and break even. A startup company may attract an initial burst of funding on the basis of a good idea, which enables it to start operations. But they then face ‘death valley’, when they risk running out of money before they start earning any.

Intertidal seaweed beds on the west coast of Jersey, UK, in 2020
To address this challenge, a number of incubators and accelerators have been established in recent years to help ocean startups become profitable. These include Katapult Ocean in Oslo, Norway and OceanHub Africa in Cape Town, South Africa. Another is Blue Bio Value, which was set up by the Oceano Azul Foundation and the Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation in 2018 to “help entrepreneurs create commercially viable and sustainable businesses” and thereby “accelerate the transition to a global and sustainable blue bioeconomy”. It is now on its fish set of startups.
Previously, the Oceano Azul Foundation – which owns the Lisbon Oceanarium – had focused on ocean education, but its leaders decided this was not enough. “We thought that, as a credible foundation, we need to also put our money where our mouth is,” says Pitta e Cunha. “We only accept startups that, through their production, will ease decarbonisation of the planet or high consumption of natural resources.” Many of these startups are led by scientists, he explains, who have essential specialist knowledge but little experience of markets or running businesses.
Alongside the accelerator, the team has also created an ideation programme to link academic researchers and business leaders, to encourage the formation of new businesses. “We are trying to manufacture new startups, because they are needed,” Pitta e Cunha says.
With so many funders, incubators and accelerators entering the ocean economy, the challenge for the owners of a new startup is how to navigate this business world. Several organisations have now been set up to organise everything and help startups find their way.
At Investable Oceans, in New York, the co-founder and principle, Ted Janulis, likes to say he was “born with an ocean gene”, which means he “can’t walk past a body of water of any type without jumping in and splashing around”. Several decades in finance convinced him that there were market-based opportunities all over the ocean economy. But the investors were scattered and disconnected. “The people who invested in plastic mitigation weren’t necessarily the people investing in better fisheries or aquaculture,” he says. So he set out to create a single platform where people could come and learn about investment opportunities in the blue economy across all asset classes and sectors. “We’re not an incubator, we’re not an accelerator, we’re not a fund and we’re not a broker dealer,” he says. “Our goal is to connect people.”

Plastic pollution along the beach– knee-deep in some places – in the Maldives in 2019
More recently, an umbrella organisation called 1000 Ocean Startups was launched in May 2021 to accelerate ocean impact innovation by bringing together “incubators, accelerators, competitions, matching platforms and VCs supporting startups for ocean impact”. Its members include Katapult Ocean, OceanHub Africa and Investable Oceans and so far it has backed 168 startups: 115 focused on sustainable use of ocean resources, 33 addressing pollution and 20 tackling climate change. “We’re still in the infancy stage,” says Grosskopf. The aim is to back 1,000 startups by 2030.
The challenge for all these companies will be to compete against existing ocean businesses that are not making efforts to be sustainable, and therefore have lower operating costs. Some consumers are prepared to pay extra for sustainable products, but many will not or cannot, so the startups must compete on price to attract mass-market consumers.
Fortunately, there are many routes to success, says Janulis. “Some of it might be that it’s a standalone company that becomes really big,” he says, but startups can also be absorbed by larger companies that see their methods as an opportunity.
Janulis says there is also “a rising sensibility and more awareness”, a point echoed by many. “I was born as a digital native,” says Grosskopf. People from the generation below, he says, are “sustainable natives”. “The consumers of tomorrow, the employers of tomorrow… they have sustainability in their DNA.”
It will soon be impossible for companies to behave unsustainably, Virdin suggests. “These issues of sustainability of ocean ecosystems and communities, they’re not luxury issues,” he says. “These are core issues to the future of the business model, whether it’s social licence to operate or whether it’s risks to your operating environment in the coming decades.”

Duncansby Stacks last year, on the exposed north- east coast of Scotland, where seals and seabirds thrive
Knowlton cautions that it’s unlikely startups alone can fix the marine environmental crisis. “The problem is that we’re kind of in a race against time,” she says, so there will need to be top-down action as well. “The role of government is really important because it can motivate change quickly.” However, she acknowledges, startups are where creative ideas can be brought to fruition quickly. “I think you have to encourage entrepreneurship – and much of it will fail, but some of it will work.”
Read More: Kering’s Marie-Claire Daveu on benefits of the blue economy
In other words, it’s not a choice between buccaneering startups and rules-based government. To save our ocean, both will have to work together.
Savvy Ocean Startups
Pesky Fish: Many of the fish that are caught at sea, particularly by trawlers, are wasted. Because they aren’t fashionable, they are discarded as ‘bycatch’. The British company Pesky Fish aims to change that by allowing fishers to sell directly to consumers. It has a rapidly updated online shop and overnight delivery service.
Recyglo: Plastic waste is one of the biggest problems facing the ocean ecosystem. Today most plastic enters the ocean from east Asia, where waste management systems are poor. Recyglo is aiming to change that by bringing modern recycling to the region. It already has branches in Myanmar, Singapore and Malaysia.
Cascadia Seaweed: Farming seaweed has enormous potential to feed the growing human population, remove carbon dioxide from the air, and restore the ocean by providing habitat for marine animals. Canadian firm Cascadia Seaweed is turning kelp into food for people and farm animals. It is working in partnership with First Nations groups.
This article appears in the Deutsche Bank Supplement of the Summer 2022 issue of LUX

Traditional net fishing from a boat
80% of the earth’s biomass is concentrated in the oceans. But how do we put a value on the deep sea? As the concept of natural capital — putting a price tag on the services nature provides — enters the mainstream, ocean expert and activist Karen Sack tells LUX Editor-in-Chief, Darius Sanai, why valuing nature needs to encompass more than just the dollar sign
Sack has over three decades’ experience in ocean conservation, law and policy, and currently serves as Chief Executive of Ocean Unite (co-founded with Richard Branson and José María Figueres) and Executive Director of the Ocean Risk and Resilience Action Alliance (ORRAA). Here, she explains why the time has come to incorporate ocean measurements into sustainability metrics, and how nature-based solutions should be at the forefront of any ocean investment strategy
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: The concept of natural capital — of nature having value in and of itself — has historically been ignored. Why is it important?
Karen Sack: I do think it’s important, but we need to be careful not to reduce nature’s value to just a monetary value. The reason we have to put a value on nature is so that we can understand and incorporate it into the economic system that we all exist within. While, for me, this in some ways runs contrary to what we want to do – we want to just value nature in and of itself — we still need to incorporate nature into our valuation system. If we don’t, we will very quickly have to pay the consequences. We already are seeing this in terms of what is happening with the climate crisis.

Fan Corals in Belize Barrier Reef
LUX: Can investment in ocean conservation be furthered by investment in the private sector?
KS: We need to blend together different types of finance to focus on the ocean’s protection. One of the issues that has arisen recently is how we account for the costs of marine protection. We’re focusing a lot on the question of what it costs in terms of potential revenue in terms of fisheries and other lost revenues. Yet we don’t apply that same standard when we think about providing a fishing company with a licence to fish; we don’t price those costs into that fishing licence. The private sector has been very involved in the extractive activities that take place in the ocean, and in some ways have been subsidised quite substantially by the public sector, so that those activities can continue.
The role of philanthropy in the ocean space is oftentimes to kickstart some of these discussions, to act as a springboard for investment from other areas. And oftentimes that’s what we need to paint the picture, so we understand the benefits of investment from the private and public sector.

Sri Lankan fisherman throwing a fishing net near Mirissa
LUX: When people speak of the blue economy, there might be an assumption that it is inherently sustainable. But the term can also encapsulate bottom-trawling and oil extraction.
KS: It has to be further defined. The Stockholm Resilience Centre has coined an interesting term: it talks about the development of the blue economy as a ‘blue acceleration’. If you look at different sectors of the economy that are investing in this space, you can see how lopsided and inequitable some of that development is. For example, small island developing states have protected something like 13% of all marine protected areas, which are in small island developing states. We call them ‘big ocean states’, because they have these amazing ocean real estate areas. That’s huge, yet the investment from other sectors of the economy, for example aquaculture, has been located within those small island development states.
Renewable energy is another example of where there has been a 500-fold increase in investment in offshore renewables over the past 20 years. Not one of those wind shore turbines have been located in a small island developing state. That is just so indicative of the lop-sidedness, because those countries require diesel fuel to be imported and yet are the most vulnerable to climate change.

A Humpback Whale
LUX: Does there need to be consolidation of a single set of rules and definitions for companies, investors and governments to follow?
KS: There needs to be a standardised accounting methodology that’s used, so that when you’re looking to invest in a space, you understand that that standardisation has happened. Otherwise, the opportunity for greenwash or bluewash is very high, and something that we have to guard against. It’s just too easy right now to argue that your investment is sustainable without those standardisations being in place to show that it truly is.
LUX: How does one measure the effect of either one’s donation or investment in sustainable terms?
KS: Right now, it’s very difficult to say there is any kind of comparability between, for example, one scheme that invests in seagrass to capture carbon and promote biodiversity, via another one in coral reefs. It’s what people are most interested in investing into at the moment. We understand the difference between the level of impact from a storm surge that a healthy coral reef can deflect versus a mangrove. But comparing ecosystems with one another is really difficult: it would be the same as comparing the carbon sequestration potential of the Savannah to a cornfield in Montana.

A fisherman holding a shoal of big Common Silver Barb
LUX: What needs to happen in terms of legislation and the way large institutional investors behave?
KS: We need to incorporate ocean measurements into some of the tools the financial world now uses when they measure their sustainability metrics. We don’t want to have some completely separate ocean-based metrics. For initiatives like the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TFNFD), we need to incorporate the ocean into that. We need to look at some of the taxonomies that are being created for example by the European Union, and ensure that it is not completely different from whatever is created in the US or in other countries around the world, or in China. And then a focus on innovation, and the types of KPIs that need to be developed. So this is all beginning to happen, it’s a very fast moving space, but right now it requires certainly scientific advice and a lot of listening.
LUX: Will blue economy investment always be a kind of blended opportunity, or is it something that is seen as a P&L play?
KS: With the Ocean Risk and Resilience Action Alliance, one of the initiatives that we are working on is the development of what we are calling a Sea Change Impact Financing Facility (SCIFF). When, a couple of years ago, we started doing some work on financing, we asked some partners to look at what was needed to increase investment. We found that we needed a whole new ocean finance ecosystem. Spaces that are particularly important include the coastal ecosystems, the seagrass beds, the coral reefs: places that are helping to both be nurseries for biological diversity, sequestering carbon and providing food security for coastal communities. So if you don’t have that surrounding ecosystem, that is literally money down the drain. That will probably require blended finance, and looking at things such as the development of blue carbon credits. Then we need to look at how to drive the big investments into the space, and ask what type of equity capital we need to drive big investments. I mentioned offshore renewables, an amazing opportunity for investment that is still seen as quite risky.
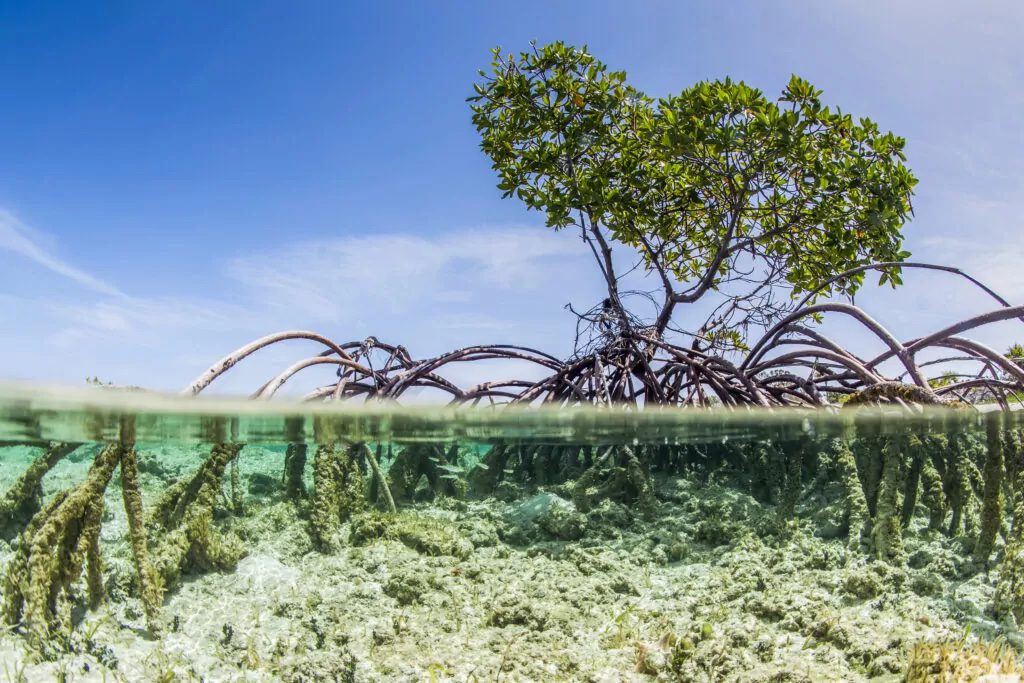

A mangrove tree in clear tropical waters near Staniel Cay, Exuma, Bahamas
Thinking about greening shipping, it is a huge emitter of CO2 but 80% of our trade in the world travels by ship. So how do we transform our ports and harbours, so they both have the infrastructure for green shipping? The third piece is what we call the ‘risk wrappers’. These are the public sector guarantees that can lower the risk of some of those opportunities for investment and drive public sector capital into the space. But if we’re looking at developing countries, and small island developing states, that’s not where the private sector is going. So how do we drive investment into some of those projects, and reduce transaction costs? Those are some of the issues we need to tackle as we move this new ocean financial ecosystem forwards.
LUX: Should nature-based solutions be the most important focus of investment currently, or one of many?
KS: From my perspective, nature-based solutions should be at the core of an investment strategy when it comes to the ocean. We’ve got 80% of the biomass, 80% of life on earth is held within the ocean. It doesn’t cost a lot, but the returns are incredible. We should be supporting, particularly for small-island developing states, and developing countries, investments into nature again for the reasons of resilience, food security, biodiversity positive outcomes, and also carbon sequestration. The more life we have, the stronger the carbon carrying capacity is. We also know that these are tested, as nature has been adapting for millennia. We need to learn from nature, and this is where we are seeing the results of that investment into nature being so significant.

Local women working in a fishing village
LUX: Do you see abating ocean industries as all part of the same investment parcel? Is it better for an institution to invest $500 million in a scheme that makes ships more hydrodynamic, or to invest in mangrove planting?
KS: The thing that is impacting the ocean the most right now is our CO2 emissions. So, any kind of investment that gets us to net zero as quickly as possible is helping the ocean. That is key. We must then look at the risk multipliers, for example pollution, whether it’s wastewater or nutrient runoff. These are not sexy things to invest in, but a sewage treatment plant can make the difference between a coral reef that survives and one that does not.
Read more: Melissa Garvey On Saving The Oceans
Bottom trawling is a fundamentally destructive fishing practice. Investments into things like bottom-trawling should just not happen. Offshore oil and gas is another one. So: stopping some investments to begin with. Next, investing in getting to net zero as quickly as possible. Third would then be looking at investments, particularly in coastal areas that are biodiversity positive in terms of their net result, so that we can rebuild those ecosystems.
It’s interesting to look at some of the work that’s now being done on technological solutions to address the climate crisis. We know, for example, that in a marine protected area that’s fully protected, the increase in biomass over 10 years can be 400% or even higher than that. I can’t think of a bank where I would put an investment in and get a 400% return on that investment, but nature gives us that. So, looking at those kinds of investments is really impossible. And that goes back to the question of valuing nature and understanding that that value isn’t just in the dollar value.
Karen Sack is Chief Executive of Ocean Unite and Executive Director of Ocean Risk and Resilience Action Alliance (ORRAA)
Find out more:

Founder of Fondation Thalie, Nathalie Guiot
The Brussels-based French founder of Fondation Thalie is from one of France’s biggest retail families. Nathalie Guiot speaks to LUX about the need for an all-round vision in facilitating arts and culture to support sustainability and biodiversity – and why you shouldn’t call her a philanthropist. Interview by Anne-Pierre d’Albis-Ganem
LUX: What prompted you to start your foundation?
Nathalie Guiot: The aim was to support contemporary art linked to societal issues with three objectives. To give more visibility to female artists, as I don’t think they are represented enough; to promote dialogues between visual and savoir-faire craft, such as ceramics and textiles – I come from a family of entrepreneurs in retail and textiles; and to be involved in the ecological transition, to invite artists and scientists to create new narratives to call for action. It’s a multi-disciplinary foundation connected to new narratives, contemporary writing, new forms of creative writing, as well as visual arts and ecological transition, and how we can address this urgent topic.

Artworks by Kiki Smith at her solo show at Fondation Thalie
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Do you think of yourself as a philanthropist?
NG: I come from a family where we don’t really use that word. I don’t know why – it’s more like we are taking action, but we are not considering it as philanthropy, even if it is actually philanthropy. It’s a way of interacting with contemporary art creation now and how can we help these artists make their projects.
LUX: How can artists address the environmental issues?
NG: I think they have a vision that we don’t have. They have a vision to
project what the future will be. I think about Tomás Saraceno… it’s not only visual art, it is also in cinema, like the amazing film maker Cyril Dion. He just came out with a new movie called Animal talking about the end of biodiversity.

Nathalie Guiot speaking to a group at the Kiki Smith exhbition at Fondation Thalie
LUX: You are involved with artists and biodiversity.
NG: Right now, it’s more about conversations online, and from these conversations we will publish a book of 12. It’s about supporting people who are doing things. We are partners of the festival Action for Biodiversity in Arles at the end of August. I am also involved in the family business, which is Decathlon (the French sports retailer), as a board member of the Transition Committee. We’re working with the École des Arts Décoratifs in Paris, on a three-year research programme for the next generation of designers. It focuses on how to create products without destroying natural resources. Artists and designers will work with mycelium, for example. It will be inaugurated in September.

Artwork by Kiki Smith
LUX: Is it a duty or a privilege for those with means to support the arts, given the pressures on public sector funding?
NG: I think it is a privilege to commission artworks, and to enable the creation of a community of patrons and collectors sharing the same passion! More than ever, we need creativity and poetry regarding our dramatic political context of the war in Ukraine. I am grateful to enable the support of artists in this context of a private foundation and to build this art collection over time.

Fondation Thalie
LUX: What changes have you seen around the ecosystem of supporters of the arts/philanthropists, foundations, and museums in the past five to 10 years?
NG: They are more present and active – in particular, in Brussels. When I arrived 18 years ago, there were no galleries, artist-run spaces or contemporary centres. Nowadays, even my baker has an artist-run space!
Read more: Marina Abramović: The Artist As Survivalist
I am kidding, but Kanal Centre Pompidou (museum) has opened in an old car factory downtown, Wiels (contemporary art centre) has a cutting-edge programme of exhibitions, and numerous other galleries and private foundations are there now. Brussels is becoming the place to be!
Find out more: fondationthalie.org
This article appears in the Summer 2022 issue of LUX

The Nature Conservancy has grown to become one of the most effective and wide-reaching environmental organisations in the world. All images copyright: Carla Sanatana/ TNC Photo Contest 2019, Ethan Daniels, Randy Olsen, TNC Belize, Claire Ryser/TNC Contest 2019, Julieanne Robinson Stockbridge
Non profit environmental organisation, The Nature Conservancy, has over 400 scientists working and impacts conservation in over 75 countries and territories. With the UN Ocean Conference currently taking place in Lisbon, Melissa Garvey, Global Director, Ocean Protection at The Nature Conservancy speaks to LUX about the effectiveness of philanthropy and investment to protect the oceans
LUX: The Nature Conservancy has an interesting niche, combining philanthropy and investment. How does that work?
Melissa Garvey: The Nature Conservancy is a global environmental nonprofit working to create a world where people and nature can thrive. Building on nearly six decades of experience, we’ve protected more than 280 million acres of ocean, 119 million acres of land, and 5,000 river miles. We are able to accomplish so much because we make careful use of our resources, maximising the philanthropic and public funding that goes toward our science-driven program work.
We are also able to leverage philanthropic funding with innovative finance strategies. The Nature Conservancy has an impact investing unit that works with our conservation colleagues and collaborators around the world to source and structure investment products that support TNC’s mission at scale. With partners, we have been able to originate, structure, fund and close investment vehicles representing more than $2.3 billion of committed capital. Philanthropy is instrumental in supporting our teams to develop, execute and manage innovative finance strategies that allowing TNC to help countries access billions of dollars in long-term funding for conservation.

LUX: Financing is a key barrier hindering ocean protection. How are you overcoming this barrier?
MG: The Nature Conservancy’s Blue Bonds Strategy is one solution. We transform debt into conservation action at scale.
At the heart of these projects is a basic deal: A coastal nation commits to protect approximately 30% of its near-shore ocean areas. In support, TNC refinances the nation’s sovereign debt, leading to lower interest rates and longer repayment periods. The government uses the savings to capitalise a conservation trust fund to support new marine protected areas to which the country has committed.
TNC’s role is to assemble the deals, use our science and a stakeholder driven marine spatial planning process to facilitate the design of a system of protected areas and create a trust fund that holds the government accountable to its commitments—ensuring that we finance real conservation, not paper parks.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
An example of this is the $553 million debt refinancing we completed in Belize in November 2021. This project enabled the Government of Belize to reduce its debt burden and generate an estimated US$180M for marine conservation in support of Belize’s commitment to protect 30% of its ocean, strengthen governance frameworks for domestic and high sea fisheries, and establish a regulatory framework for coastal blue carbon projects. This is especially meaningful to the people of Belize as the country’s tourist-based economy continues to suffer from the impacts of COVID-19
Our goals is to project 4 million square kilometres of ocean and unlock $1.6 billion for marine conservation.

LUX: Are blue bonds going to become more significant elements in the market?
MG: The TNC Blue Bonds debt conversion structure is highly scalable and replicable. Transaction sizes and overall market are limited by three criteria:
1)Countries committed to achieving the conservation outcomes. As the threat of climate change and awareness of the role that natural resources and biodiversity play in economic growth rapidly increase, most developing countries will require additional financing for conservation.
2)Availability and affordability of credit enhancement, whether through the US Development Finance Corporation or development banks to do more deals in more markets.
3)Availability of debt to refinance: while debt conversions work well with sovereign debt trading at a discount in the capital markets, they are not exclusively for countries threatened by high debt distress. Many countries have high-coupon bonds. Even if these trade at little to no discount, they can still be refinanced with lower coupons and longer tenors to create significant funding for conservation. Many also have commercial bank loans that may be candidates for refinancing into a lower interest rate and/or longer tenor loans.

LUX: How will sustainable blue economy finance need to develop over the next few years?
MG: Sustainable blue finance is essential to national economies and the 3 billion people rely on healthy oceans for their livelihoods. Financing often holds back countries from implementing ocean conservation that will ensure oceans are sustainable into the future. Philanthropic and public funding is essential but insufficient to close this gap.
Today the challenge of financing the sustainability of our oceans is compounded by the Covid 19 health pandemic and the financial crisis, which has placed unrelenting pressure on public finances and slashed tourism revenues. But there is hope. Innovative debt and market approaches can help bring in new funding at a scale that can address the problem.
LUX: Are you looking for UHNWI individual investors, institutional investors or philanthropists?
MG: Philanthropy is instrumental in supporting our teams to develop, execute and manage strategies, policy and partnerships – including innovative finance strategies — that allow TNC to help countries access billions of dollars in long-term funding for conservation. We simply couldn’t do our work without the generosity of individual and institutional supporters.

LUX: Do governments need to become much more active on ocean protection?
MG: Governments are already active in ocean protection, and there is a lot more to do. We are already three years into the decade during which we have to bend the curve on biodiversity loss. So, this year the global community must finally agree a new and ambitions Global Biodiversity Framework, including a target to globally protect 30% of freshwater, land and the ocean. To deliver against this target, countries must also conclude negotiations in 2022 on a new treaty for the protection and sustainable use of the High Seas with clear powers to establish protected areas in areas beyond national jurisdiction. But we can’t wait for these treaties to be negotiated before we act. The UN Ocean Conference is an opportunity for the ocean community to both demand action and offer solutions.
LUX: Is there is a risk of creating an uneven market with low-regulation governments allowing exploitative practices on a large scale?
MG: There are always a risk like this. But investing in the health of oceans creates long term benefit. Globally, the gross value of marine ecosystem services is estimated at US $49.7 trillion. This suggests that the economic benefits would far outweigh the costs of establishing a 30% global MPA network. We are developing a costing framework to help decision makers in individual countries better understand today’s costs of implementation and management of ocean protection as well as the long term benefits of marine conservation so that governments, NGOs and the private sector can make more informed choices.
LUX: How important will the role of science and innovation be in the Blue Economy? Can you give some examples?
MG: Science and innovation are essential for Blue Economy interventions that change the way that we protect and value oceans. For example, did you know that you can insure the protective value of nature? You can.
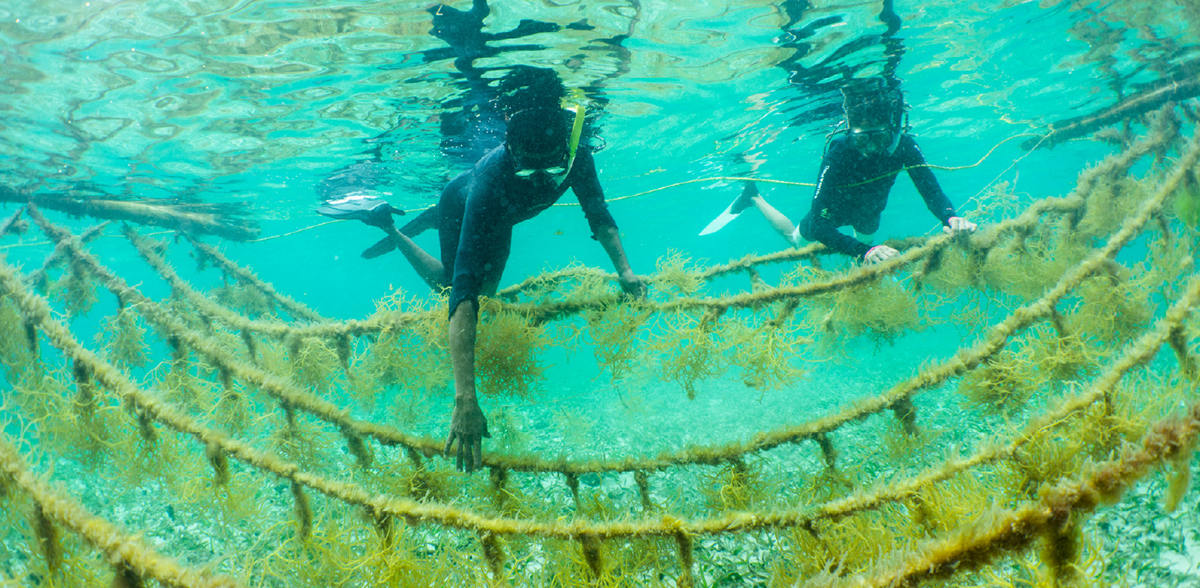

It works like this: We know that reefs can decrease the power of waves coming on shore by about 97%. That is really important during the ever more frequent – and increasing more severe – storms. But these storms also take a toll on reefs, which leave coastal areas at greater risk to future damage if the reef isn’t restored. We worked with the insurance industry and put that science into insurance models. Together, we came up with the world’s first insurance policy to insure a portion of the Meso-American reef in Quintana Roo, Mexico that protects areas near Cancun and its $10B tourism industry from hurricanes. If a storm hits, the insurance is triggered to ensure that the reef can be quickly restored. This insurance was tested in the Autumn of 2020 when Hurricane Delta hit. The $800,000 insurance payout funded vital reef repair activities. This is a win for nature, a win for coastal communities and will drive further interest in conservation finance and the need to protect marine ecosystems across the globe.
Read more: Julie Packard: All In Together
LUX: There is no metric to compare the value of different nature-based solutions in ocean conservation, and no consistent measure of the effectiveness. Is this true, and is it an issue?
MG: I don’t agree that we can’t measure nature-based solutions. The reef insurance I mentioned above is one example. Here’s another: Blue Carbon Resilience Credits. We know that the coastal wetlands provides a unique opportunity for climate finance. If we restored even a quarter of these habitats, we would add 10 million hectares of carbon-trapping wetlands to our coastlines. That is an area equivalent in size to Iceland. In addition, protecting existing coastal wetlands would prevent the release of 80 million tons of carbon emissions currently being stored by these habitats.

TNC worked with international experts to develop science, flood modelling, and carbon and resilience methodologies for the Blue Carbon Resilience Credit. These credits support not just carbon mitigation, but also quantifiable, verifiable resilience benefits like flood reduction to adjacent communities. We have identified projects across the US and globally and are bringing our first supply of Blue Carbon Resilience Credits to market.
LUX: You say a comprehensive approach is best for ocean investment. How should this work?
MG: To achieve truly durable ocean protection, we have to focus on scale and representativeness of the areas we conserve, as well as ensuring long term financing for conservation, and equity and sustainable livelihoods for the people who rely on oceans. Our global ocean protection program drives new protection, restoration, and management improvement in support of biodiversity and communities.
We work at multiple scales. We address the long-term need to secure large-scale new protection and sustainable financing for marine conservation while we tackle today’s urgent need to restore critical coastal ecosystems — like coral reefs and coastal wetlands — and improve management of our oceans, while we build capacity for communities to manage their marine resources.
Find out more: nature.org

Painting by Christopher Cheung. Displayed at Spectrosynthesis II, Bangkok Art and Culture Centre
Patrick Sun is pushing forward a movement very close to his heart through his foundation Sunpride, which seeks to give equal opportunities to LGBTQ+ artists in Asia. Here, Sun speaks to Samantha Welsh about what his foundation has done for him personally and the wider impacts of his projects

Patrick Sun, Founder of Sunpride
LUX: You grew up in Hong Kong, in a traditional family, when sex discrimination laws were undergoing limited amendment (HK 1991). When did you realise that the problem was with society?
Patrick Sun: Coming out is never easy and it was especially daunting in the 80’s when society was hostile and gays were seen as perverts. My mother insisted that I seek help from a psychiatrist, and I obliged, not because I thought there was anything wrong with me medically or psychologically, but I needed the doctor to tell her that I am “normal”. Soon after that I participated in a panel discussion with legislators who sought to decriminalise homosexuality in Hong Kong and that was when I realised that rather than resigning ourselves to adversity, we can try to do something to change society.
LUX: Suggesting the hidden, the forbidden, taboo; did your curiosity inform your early collecting?
Patrick Sun: My earliest collection was traditional Chinese paintings. While I had no intention to collect such works with a gay theme, one of my favourite paintings depicted two boys sharing a stolen watermelon which evoked to me a forbidden love. I can draw parallels to LGBTQ artists who do not specifically depict a gay theme in their work, yet somehow who you are and what you can reveal can be found if we look in the right place.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Inequality, invisibility, social exclusion and marginalisation; many artists’ works show a longing to belong, through juxtaposing what is with what is not there. Which of your works exhibited have had the most impact?
Patrick Sun: One of my favourite works from our exhibition in Bangkok was Arin Runjang’s “Welcome To My World: Tee”, which takes us into a large dark room with 5 giant screens showing different views of a naked transgender person. The work questions one’s perception of what makes a “perfect woman”, as well as one’s reaction when confronted with something unfamiliar or “abnormal”. It addresses all the issues you mentioned such as invisibility, social exclusion, marginalisation and inequality in one powerful installation.

Installation by Jun-Jieh Wang. Displayed at Spectrosynthesis, MOCA Taipei
LUX: Through Sunpride, you are renowned for your ground-breaking super-scaled public exhibitions, the biggest in Asia. What is your thinking here?
Patrick Sun: Sunpride Foundation hosts large-scale exhibitions with an LGBTQ theme to promote awareness and respect of our community in Asia. We anchor our events at public institutions because they provide a platform to reach out to the general public. Like movies and novels, we see art as a more equanimous way of communication and strive to promote people’s understanding and acceptance of a more diverse society.
LUX: What is the symbolism behind Spectrosynthesis, and what was the ambition for the Taipei, Bangkok and the recent Hong Kong exhibitions?
Patrick Sun: Spectrosynthesis is composed from two words – spectrum which represents diversity as in colours of the rainbow, and photosynthesis which is how plants convert solar energy into nourishment. We believe if one source of energy can bring life to all living creatures, then diversity could lead to a better and healthier society.
Taipei and Bangkok were our first two exhibitions and we are happy to see that they were both well received by the art circle and general public. We hope to bring similar exhibitions to other parts of Asia where the voice of the LGBTQ community need to be heard.
When Sunpride presented our first exhibition there was some skepticism about the possibility of bringing Spectrosynthesis back to my home town, Hong Kong. I am particularly proud to see the materialisation of a major exhibition at Tai Kwun in 2023.

Installation by HOU, Chun-Ming. Displayed at Spectrosynthesis, MOCA Taipei
LUX: Why not shine a light on the SE Asian countries which criminalise LGBTQ+ people, such as Myanmar, Bangladesh, Malaysia? Surely in Taiwan and Thailand there have been achievements in equality and diversity?
Patrick Sun: One of the criticisms we received from our shows in Taipei and Bangkok is “are we preaching to the converted?” My answer is, while both places have better achievements in equality and diversity, there are still discrimination and inequities that need to be addressed. Our show in Taipei happened at the time when same-sex marriage created huge controversy, and the one in Bangkok was presented when a new bill on civil partnership was discussed at the Justice Ministry. While it may seem impossible now to host such a show in countries like the ones you mentioned, I am optimistic that the world is changing in the right direction with regard to equality and diversity. A good example is India – removal of penal code 377 and decriminalisation of homosexual acts was only accomplished in 2018 and the scene has flourished in leaps and bounds.

Installation by Sornchai Phongsa. Displayed at Spectrosynthesis II, Bangkok Art and Culture Centre
LUX: How significant are the partnerships with MOCA, BACC and recent Tai Kwun?
Patrick Sun: Our partnerships with MOCA Taipei and BACC were paramount in importance. They helped pave the way for our future exhibitions, not just in showing what an LGBTQ-themed exhibition is, but also allaying fears of what we are not. It is not a show built on homo-erotica, nor is it confrontational or offensive. It has a wide array of themes and mediums, and provides platforms for communication between the gay community and the general public.
The recent collaboration with Tai Kwun is equally if not more significant. I believe the exhibition is important not only to the LGBTQ+ community but to everyone in showing how Hong Kong remains a diverse and inclusive society.
Read more: Umberta Beretta on fund-raising for the arts
LUX: Does your activism drive you to work with institutions beyond SE Asia?
Patrick Sun: We have been approached by institutions in Europe and America to bring our show there. We declined because our focus remains in Asia, where exhibition like ours is more direly needed. However, we have made friends with many art professionals including curators from art institutions in other parts of the world who have formed an invaluable network of information with Sunpride Foundation.

Photo by Ren Hang. Displayed at Spectrosynthesis II, Bangkok Art and Culture Centre
LUX: How has the public-private partnership guided your process in how to buy and what to show?
Patrick Sun: Sunpride Foundation collects with an aim to exhibit. Whilst ultimately it is the curators’ decision on what to present, having a large sample in our collection helps them build the exhibition, with additional works to borrow or commission to help put together a coherent show. When we look at a work, the first question is always “how would it work in an LGBTQ-themed exhibition?” This question helps us set aside personal preferences and think about logistic issues such as medium, transportation, storage etc.
LUX: If a member of the public asks you how they can support LGBTQ+ rights, how do you answer them?
Patrick Sun: Speak Up: if you hear something offensive about gay people, tell them it is not ok. Words can hurt and when you speak up, you let people know those words are not acceptable and prevents similar slandering or mockery in future. Another way would be – allow me to do a bit of promotion here – come see one of our exhibitions, or read up on them, to see for yourself that the LGBTQ community is perhaps just as normal and talented as the rest.
Find out more: sunpride.hk

Legendary shoe designer Christian Louboutin. Copyright and courtesy Christian Louboutin
Superstar shoe designer Christian Louboutin, whose signature red-soled pumps with vertiginous stiletto heels are the de facto shows for glamourwear, has dominated luxury footwear since the nineties. Harriet Quick speaks to him about his long career, his charity work with actor Idris Elba, Kate Moss and sailing down the Nile
Good ideas take time to mature and, when entwined with hope and empathy, they can flourish. Such was the situation when Christian Louboutin picked up the phone to his friend, the actor Idris Elba, after the tragic murder of George Floyd in May 2020. Both were in deep shock, amplified by the isolation of lockdown, and wanted to do something, to take action. Louboutin, remembering his friend enjoyed sketching designs for shoes, proposed a philanthropic venture: Walk a Mile in My Shoes. In essence, a capsule collection of shoes with 100 per cent of the profits going to benefit charities fighting oppression and advancing racial justice, equal rights and access.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Elba immediately said yes and proposed the idea to his wife Sabrina on her birthday. She was over the moon. “Not to act, to remain silent was not an option – I knew this in my heart,” says Louboutin. “We decided that if there is a message – it has to be optimistic. I don’t want to emphasise the toughness of reality and we picked organisations that are proactive. We want to show that we can all do better and drive optimism,” says Louboutin.

The 1988SL high-top sneaker designed by Idris Elba from the Walk a Mile in My Shoes collection. Copyright and courtesy Christian Louboutin. Image by Julien Vallon
The friends got to work choosing designs for the collection, which was launched in June 2021. It includes the 1988SL sneaker designed by Idris, a suede calfskin pump with the Walk a Mile message embroidered in signature Louboutin red on the upper, and a birds-of-paradise print skate shoe and stiletto. The phrase was chosen by Elba and references Kim Abeles’s 2014 public artwork dedicated to Martin Luther King in Los Angeles. “I wanted to make sure the styles were already in my collection, as this is about giving money to people and not using funds for design and research. Sabrina really drove the charity side, choosing organisations that have a positive impact,” says Louboutin of the beneficiaries, including the Somali Hope Foundation, Purposeful in Sierra Leone, which supports marginalised young women, Gathering for Justice in the US founded by Harry Belafonte, the Be Rose International Foundation’s work in Sierra Leone, and Immediate Theatre in east London.
Read more: Emilie Pastor & Sybille Rochat on Nurturing Artistic Talent
The scale and scope of the initiative is impressive and inspiring. While charitable products often fall short on desirability, here is a collection that one would be proud to wear, as it is infused with the wit, optimism and elegance that is part of Louboutin’s DNA. The French Egyptian designer, now 58, has always been driven by passion coupled with a deep knowledge and expertise in his craft. Louboutin became fascinated with shoes in the mid-seventies. A visit to the Musée national des Arts d’Afrique et d’Oceanie on the Avenue Daumesnil in Paris was a turning point. It was there that he saw a sign from Africa forbidding women wearing stilettoes from entering a building for fear of damage to the wood flooring. Louboutin was enraptured by the poster image of a stiletto and set out to create designs that made women feel empowered and not embarrassed or compromised. “I could not believe the elegance of these shoes and became obsessed with them,” he remembers.

Small tote bag from the Walk a Mile in My Shoes collection. Copyright and courtesy Christian Louboutin.
With no formal training, Louboutin learned by sketching and by studying the craft until he was hired by Charles Jourdan and, later, the highly inventive shoe maestro, Roger Vivier. By 1991, Louboutin had opened his first store in the Galerie Véro-Dodat and went on to sell internationally, building fame and fortune around his bestselling black patent, red-soled stilettoes that rose to 120mm and showed off ‘toe cleavage’. Indeed, it was Louboutin who became one of the first superstar shoe designers building a brand that became associated with fetish and fantasy. He has been to court on numerous occasions to protect the trademark red sole that over the decades has been widely copied. To balance and dance gracefully on these leg-lengthening, needle-thin points was, and still is, considered the quintessence of chic, a triumph of style over the quotidian. Like Manolo Blahnik, Guiseppe Zanotti and Vivier, Louboutin excelled in making the shoe an object of wonder. “My wardrobe is brimming with Louboutins,” Kate Moss told Vogue in 2014. “The classic Pigalle stiletto in patent or matt-black leather is my go-to shoe. I have so many pairs that Christian designed a style with a sharper point and nail-thin heel which he named the So Kate.”

Louboutin’s reworked Double L sandal for the Oiseaux du Paradis capsule collection, launched in September 2021
As we all adopted Birkenstocks and trainers during 2020, it might not have been a great year for heels but it was a significant year for Louboutin. He spent much of it in his home in Portugal, blessed by the fact he could enjoy his garden and the company of his children. “There was a form of solidarity as everyone was in deep shit. Businesses were drowning and it was happening across the board. I understand that I could not get too pissed or angry if I had no control over the situation. Why beat your own head? I was not locked in a small apartment, and I took measure of the levels of comfort and privilege that surrounded me. I took the upside: there was no way to complain about my situation,” says Louboutin, who talks energetically and whose conversation is constantly punctuated with smiles and those inimitable French hand gestures and raised eyebrows. “It slowed my pace and that’s a good thing. I had more time to think and concentrate. I took it as a message, an opportunity to reformulate, and go into ideas, develop creativity. You realise nature is constantly replenishing – after three months the air was cleaner, the waters were clearer in Venice and Paris, and animals returned to the city. If we give nature a chance, it will recover much more quickly. We all experienced that reality,” he says of the learning.
Read more: Prince Robert de Luxembourg on Art & Fine Wine
Out of adversity, there come opportunities. Louboutin also had the chance to weigh up and analyse the future of his business, which encompasses sales through approximately 150 department stores in more than 35 countries, a beauty line that he launched with nail lacquer in 2014 (it is now licensed to Puig), men’s and women’s collections as well as accessories. A promising suitor came in the shape of Exor NV, the luxury group owned by the Agnelli family in Italy. In March, Louboutin sold 25 per cent of the business for €541m, a figure which gives a clear indication of the value and promise of the brand which has seen remarkable success in Greater China where there are six stores. Exor, which is chaired by chief executive John Elkann, also has investments in Ferrari, PartnerRe, Shang Xia and Juventus FC.

The Hot Chick pump and Fun Louis sneaker from the AW21 collection. Copyright and courtesy Christian Louboutin
“The best business partner is one that enhances your way of thinking. We will remain the same and no one wants to interfere with how we do things – we have the same team and now we have solid partners who are great thinkers. The Agnellis are a family of entrepreneurs and I respect that,” says Louboutin, who works alongside his business partner, Bruno Chambelland.
“In the next five years, we will ‘muscle’ digital. We already have a successful e-commerce [side of our business] but digital is a bigger world encompassing operations and logistics. And we will also be looking at sustainability but not as a trend. In these matters, because sustainability is a complex science, you need to practice precaution and responsibility and have the time to take the right measures. It’s not about jumping on the first idea – this is a serious issue, and you have to be accurate,” says Louboutin, taking a balanced approach to fashion’s hot topic.

The Loubishark Flat trainer from the AW20 collection. Copyright and courtesy Christian Louboutin
Louboutin has a fresh outlook. He also sees great potential in the gaming world and has created a dematerialised Loubishark sneaker with a Pop Art graphic shark-tooth-style sole for sites. “Gaming has an interesting aesthetic and there is a distinct visual language which I find so fascinating. Since I was a teenager, I have liked calligraphy and optics and this is like learning a new code,” he says. Take a tour of the brand’s Instagram feed and its website and you can see playful virtual and augmented realities in the LoubiFuture world. The retro-futuristic vibe is playful and dynamic, just like the vibrantly coloured collection. There was also the chance to immerse yourself in Louboutin’s imagination at ‘L’Exhibition(niste)’, a monograph show at the Palais de la Porte Dorée in Paris in 2020 where the designer’s sense of showmanship and theatre were celebrated.
Read more: Molori Designs Founder Kirk Lazarus on Ultra Bespoke Luxury
His own sense of luxury is more shaped by the real world. He owns a 13th-century château in the Vendée and a beautifully restored 100-year-old sailing boat which is moored on the river Nile. When visiting the boat, he says, “by the second night, the stress of the city has evaporated. I’m looking at this beautiful panorama at a pace that is caressed by the wind. There is no motor, so if there is no wind, you stop. I love to sketch on the river with the landscape passing by. Everyone is affected by stress – even if you adore your working life, it’s important to extract yourself,” says Louboutin.

Christian Louboutin in Egypt, 1999. Copyright and courtesy Christian Louboutin
“Luxury – it has to create a form of reverie. Yet, it’s a huge word and belongs to so many territories. My luxury is not to buy expensive things – I see luxury as a door, an exit that allows for the freedom of mind and identity. And to have that escape is necessary for wellbeing,” says Louboutin. Being able to realise his own dreams has also made him something of a role model for a younger generation. If his twenty-year-old self could see his fifty-something self now, what would he see? “I would see a man living through his dreams. I would look at that person and see someone who tried not to live through preconceived ideas and who has a voice and that means someone who also listens,” says Louboutin. “Success is an added value.”
Christian Louboutin on how male/female fluidity is affecting his design thinking
“Something that has affected my design in recent years is the shifting of identities and the fact that I was compartmentalised between men and women before. That has dissolved for me into another way of thinking about male and female identity. Now, I have a freer way of designing. Outside of the traditional stereotypes, there is a bit of the showman in every man, and this is a new discovery.”
Find out more: christianlouboutin.com
This article was originally published in the Autumn/Winter 2021 issue.

James Chen, Chairman, Chen Yet Sen Family Foundation and ‘Vision for a Nation’
‘Moonshot Philanthropist’ James Chen speaks to LUX about the importance of risking capital for a mission that matters
James Chen is on a mission to tackle a major problem that most of humankind doesn’t even realise exists. There are more than two billion people worldwide who suffer from debilitatingly poor vision, with no recourse to help. And yet all it would take to transform their lives is a simple pair of prescription glasses. Poor vision is a life sentence that could easily be lifted, with just a little help. In what he refers to as ‘moonshot philanthropy’, Chen – softly spoken, thoughtful and himself a wearer of prescription glasses – set out to change the world.
During his eighteen-year philanthropic journey, Chen has pioneered developments in optical technology through his company Adlens and overseen its implementation in the developing world through his NGO, Vision For A Nation. In July this year, largely due to pressure from his campaign Clearly, the UN adopted a Vision for Everyone resolution, which was unanimously agreed upon by all 193 member states. By recognising vision as a basic human right, the resolution will kickstart a global effort to help 1.1 billion people with poor vision by 2030. Here, Chen speaks to LUX about his mission.
LUX: You were influenced by your father to become involved in philanthropy. Tell us about that.
James Chen: When my father retired from business, he devoted himself to philanthropy in his hometown. I think a lot of people at that time were very generous, [but] they [only] wrote cheques. The difference with my dad was that he actually went there himself, a few times a year: he made that seven-hour trip [to his hometown], got to know the people and their needs. He set up schools, hospitals, town halls, and everything in between. Later, when he got old and stepped back from it, [I used it as] impetus for setting up the family foundation. Personally it was very gratifying to work with the family, and to build on his legacy, in China. But I wanted do dig into something meaningful globally. I had no idea what it would be.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: So how did the problem of vision come onto your radar?
Jame Chen: I came across this Oxford professor [Dr. Rob Stevens] who invented adjustable-powered lenses, and it immediately clicked with me. I grew up in Nigeria, where our family business still is, and for most of my career I’ve also been in developing Asia. The thing that struck me was that very few people wore glasses there – either because they don’t need them, or they don’t have access to them. When I met this professor, I could see how I could help solve the problem.

Thanks to Chen’s campaign Clearly, the UN is aiming to help 1.1 billion people with poor vision by 2030. Image by Sarah Day
LUX: Adlens is the vehicle you created to tackle this. What was that journey like?
James Chen: I formed Adlens with [Dr. Stevens]. We wanted to develop the technology and apply it commercially in the developed world, and socially in the developing world. My team spent two years knocking on the door of the World Bank, which ultimately rejected us. The industry and professionals said that it couldn’t be solved, but their model of delivery of glasses is to high resource environments: that model falls over in the developing world. That’s why we set up Vision For A Nation, an NGO, to test our model in a low-resource environment. We picked Rwanda, and developed a protocol to train nurses in three days to do a good enough eye test, and to dispense glasses. In five years, we screened 2.5 million of the 12 million population in Rwanda and dispensed 300,000 pairs of glasses. We left at the end of 2017, [having] done the thing that the policymakers said couldn’t be done.
LUX: How did you scale that model?
James Chen: Instead of replicating the program one country at a time, I knew that this was a global problem: we had to think differently. That’s where I applied my risk capital to start the Clearly Campaign. Our target was to get policymakers to understand what we called ‘the problem that the world forgot’. We said, ‘if you have uncorrected poor vision, how are you going to achieve your sustainable development goals?’. For someone who has poor vision, it’s probably going to affect their educational outcome, their productivity; even gender equality is affected by poor vision. That’s the crux of our campaign.
LUX: This concept of philanthropy and vision, had anyone done that before you?
James Chen: No one [has] thought of it in terms of a bigger scale. That’s why I had a brick wall when I first started looking into this. People do these programs [where they] go to a village and take glasses, but that doesn’t, to me, solve the problem. Poor vision is always put into the health silo: in the priorities of what governments have to tackle in developing countries, there’s a whole list of things that are perceived as higher priority than blurry vision. But there are 2.2 billion people in the world who have poor vision, of which, for at least 1 billion people, all they need is a pair of glasses to correct it.
Read more: Gaggenau’s Jörg Neuner on embodying the traditional avant-garde
LUX: Why do you think it took a philanthropist with no prior knowledge of the sector, instead of scientists and governments, to solve the issue?
James Chen: A key problem in the world of aid is there is very little risk capital available. As a philanthropist, I am in the privileged position of being able to take risk with my capital. If it’s successful, it’s hugely impactful. If it fails, I can absorb that loss. It’s now my prime mission [to incentivise] the high net-worth community to do the same. I coined this phrase ‘Moonshot Philanthropy’, and I came up with a tagline: ‘privatise failure, socialise success’.

Chen delivering a speech at a Sightgeist event in London
LUX: What would you say to people to encourage them to do ‘Moonshot Philanthropy’?
James Chen: Recognise the superpower that we have as ultra-high net worth individuals: we can deploy our own capital, and we can take as much risk as we want. Most of the high net-worth community do not deploy that superpower.
LUX: Do you think there is enough dialogue between philanthropists?
James Chen: No. There’s still a lot of scope [for that]. There’s all this noise around impact, investing, and social enterprise, and lots of donors have become confused. Most people who call themselves philanthropists are really doing charity or patronage. With the ‘Moonshot Philanthropy’ idea I want to plant that seed so that there is a model for people to use. I think I’m in a unique position to reframe this, to help people to grasp it. That’s the good thing about philanthropy: it’s different from business. In business you’ve got a great idea and then you try to maximise the value. In philanthropy, if you think you have a great idea, share it, and let people run with it. That’s the best way to scale it.
LUX: What’s next?
James Chen: I’m very focused on proving the link between vision correction and its impact on things like productivity and education outcome. We need to provide the evidence base so that governments will invest. It’s not just helping me by doing all this; I’m bringing more awareness, and capital, and support to the whole sector.
Find out more: jameschen.vision

Emilie Pastor © Kate Martin.
Emilie Pastor is a scion of the Monaco real estate and art collecting dynasty; Sibylle Rochat works with her as art advisor. Here, they speak to Samantha Welsh about their unique style of spotting and supporting artists
Emilie Pastor was born into art. She is a scion of Monaco’s renowned real estate family, and her father Michel Pastor was one of the most significant European art collectors of the 20th century. Emilie has teamed up with London-based art advisor Sybille Rochat, herself a significant figure on the collecting and consulting scene, to found the philanthropic organisation Concrete Projects. Pastor and Rochat are supporting emerging talent by providing financial and logistical support and expertise, and catalysing some exciting new collaborations with the music scene.
LUX: What made you want to engage in the art world together?
Sibylle Rochat: We started to see how, because of commercial pressures, everything was looking the same. It’s always the same artists represented by these mega-galleries that can produce big shows for a museum. We realised that a lot of young and mid-career artists were talking about projects that were impossible because of a lack of funding. The art world needs new voices, new ideas, new concepts.
Emilie Pastor: I wanted to give back and to make sure that creativity would go on, that it would not become too business oriented. That’s why it challenges us, to know that we are able to give this little bit extra, to have exhibitions that couldn’t be realised without us.

Concrete Projects supported Our Product, an exhibition by Pamela Rosenkranz at the Swiss Pavilion, Venice Biennale, 2015. Image by Marc Asekhame.
LUX: The two things you offer are financial and technical support. How does that work?
Sibylle Rochat: When there’s a big project that we want to participate in, it’s quite challenging financially for galleries because they always need private support, especially with all the cutbacks in the culture sector. But what we offer is never big, big financial support. Rather, we’ll pay the technician, or for the water for the swimming pool, or the painting. For technical support, we have a solid network of art technicians and art handlers – very specialised craftspeople.
Emilie Pastor: For sustainability, we will try to have local support, too. That’s important for us.
Sibylle Rochat: Yes, we try to never fly anyone in for a project. We’re very careful about our carbon footprint. It’s good to source locally, for the community around the museum, for the artists to know the city, and so forth.

Sibylle Rochat © Kate Martin.
LUX: You also support Chisenhale Gallery.
Sibylle Rochat: I really like Chisenhale’s programme – the work they do and the space they give to new voices. They have an amazing track record in terms of artists. They’ve been showing Lynette Yiadom-Boakye since very early on, as well as Camille Henrot, Caragh Thuring and other young artists. We supported the work of Hannah Black there – she’s a very political artist who’s leading challenging conversations about change.
LUX: What does it take for a work to resonate with you?
Emilie Pastor: I need to feel something. I need to understand it, to see if it makes sense in my collection, if it’s coherent. I think about my children when I add to my collection – it’s a kind of legacy. I want to leave them something that has a meaning, that tells them something about the time they grew up in.
Sibylle Rochat: Kids only ever know them as parents. Art allows children to see and know their parents better.

CAT’S PAW by Abbas Akhavan was also supported by Concrete Projects at Chisenhale Gallery, London in 2021. Courtesy of the artist. Photo by Ali Sadeghian
LUX: What projects do you have coming up?
Sibylle Rochat: We noticed the strong rap scene – grime especially – in places in south London like Peckham. Some of the musicians were looking at contemporary art for their album covers, but there was no bridge. So we decided that it would be good to put the two together to create an art video and track. (Think about Kanye West, who asked Louise Bourgeois to do his album cover.) We expose them to another scene. It’s an opportunity for both sides to find another world and be enriched by that. What I see is these young kids creating songs which resonate with video artists today. They need to do something together!
Find out more: concreteprojects.co.uk
This article was originally published in the Autumn/Winter 2021 issue.

Surina Narula, founder and patron of the UK-based Consortium for Street Children
Based between London and Delhi, Surina Narula has founded philanthropic endeavours as diverse as Jaipur Literature Festival, the Consortium for Street Children, and the TVE Global Sustainability Film Awards, among others. The governing principle underlying them all? A passion for learning and justice. Here, Narula speaks to Samantha Welsh about personal responsibility and the importance of South Asian representation.
Surina Narula is on a mission for social justice. Having dedicated the best part of three decades to delivering aid to women and children in the UK and India, she is also a patron for South Asian art and a fervent advocate for sustainability through the medium of film. If those causes sound disparate, they are deliberately so – for Narula is dedicated to equality above all else.
LUX: When did philanthropy become a way of life for you?
Surina Narula: I don’t think I had anything specifically in mind [when I started]. I just believed in justice and in a fairer world. It all changed when I had to fight for justice for my sister’s murder, which made me think a lot about human rights and justice for all. I realised it’s a very unfair world in India, where only people like us, with money and contacts, get any kind of justice. So, I started advocating for the most vulnerable sections of society. I knew it would take an entire lifetime to make a tiny difference, but it didn’t mean I had to stop enjoying my life. It is a basic responsibility for every able-bodied person to engage and make a difference.
LUX: Your work spans literature festivals to film awards, sustainability to women’s rights. Is there a single philosophy underwriting them all?
Surina Narula: You could say that everything I’m engaged in is interconnected. Everything is for a cause but also satisfies my desire to learn. [That’s why] I started fundraising through art exhibitions, theatre productions and literary festivals. I first began with working for street children through the Consortium for Street Children (CSC), based in London, and then looked at communities supporting children through Plan UK and helping charities like Women and Children First. My focus now is on advocating for environmental causes and global sustainability through the Television for the Environment (TVE). I felt the environmental crisis was becoming the greatest cause of human suffering, with the worst affected always being women and children. My philanthropic journey has been a continuous and evolving process.

Surina Narula celebrating Diwali at COP26
LUX: Your own involvement in these projects frequently transcends setting up foundations and providing aid. Why is it important that you engage on a deeper, more personal level?
Surina Narula: The personal commitment comes from a love of life. I don’t think the idea of foundations, charity, aid is what excites me; they are a means, not an end. It has been a privilege to be on the boards of many organisations, because I meet amazing people who devote their lives to work for the causes they are passionate about. I love meeting these people and learning from them.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: You are a fearless advocate for women’s rights and ask difficult questions around religious strife, marriage and prostitution. Does it ever feel like you are fighting a losing battle?
Surina Narula: It is very difficult to measure success in these areas, but unless we have the courage to question bad practices, how can we start a dialogue? By starting a dialogue, however difficult, we can start the process of change.
LUX: Is that how the Difficult Dialogues initiative came about?
Surina Narula: Difficult Dialogues is part of a wider agenda of regional development which aims to involve the voices of key stakeholders in the process of policy formulation. Policy is eventually what really changes the plight of people, and this process needs to be structured, transparent and more inclusive. We organise events debating ‘difficult’ issues with Government, policy formulators, academics, corporates, NGOs and last mile implementers of policy, before making specific policy recommendations for the area.
LUX: What reforms have your teams been able to effect?
Surina Narula: Thanks to the work of the CSC, we have succeeded in adding a general comment in the UN Rights of the Child, guaranteeing that whenever governments discuss the welfare of children this expressly includes street children. We have also had success with Plan International, where our teams work hard in law reform to support the rights of women and girl children in the UK and India. Through Women and Children First, our teams are effectively reducing the mortality rate in newborn children in parts of Africa.

In 2012 Surina founded the tve Global Sustainability Film Awards. Left to right: Giorgos Lemos, Surina Narula and Nikos Fragos. Producers of, ‘Amerika Square’, the film won the Founder’s Award at the GSFA2018
LUX: Your work is heavily focused on South Asia, as well as the UK. Why is that a priority for you?
Surina Narula: I believe it’s best to start with what you know. South Asia is closer to the language and culture I grew up in. I learned about South Asia through western writers in English. I also read Thomas Hardy and Shakespeare. They were great, of course, but I grew up imagining I was Hardy’s Tess, not Vikram Seth’s Lata. Now, I am much clearer about my own identity and have learned so much about people in our region.
LUX: Was this the motivation behind the DSC Prize for South Asian Literature?
Surina Narula: Yes, it’s about sharing the cultural richness and diversity of South Asia, and bringing our literary talents to a global audience. We encourage a wide range of entrants: the Prize is open to writers from anywhere in the world provided they write about our region. Over the last decade, it has become the definitive international prize focused on South Asian fiction writing.
Read more: Philanthropy: James Chen on providing vision for all
LUX: How do you develop such nuanced conversations across a region with so much diversity?
Surina Narula: If you know this region, it’s clear there is great diversity in language and dress. The Prize is focused on nine South Asian countries which include India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, Maldives and Afghanistan. Translation has helped capture the nuance of conversations; we also celebrate our diversity by physically presenting the award in different countries by rotation.
LUX: How does neo-colonialism intersect with the storytelling of that region?
Surina Narula: Every nation in the South Asian region has suffered through our shared colonial history, as well as civil and religious conflict. The entire region is connected in this way. Before Independence, English literature and the English language were prevalent because of colonialism: we were forced to speak and write in the language of the conqueror. So the DSC Prize brings to the English-speaking world a deeper understanding of the vibrancy and richness of South Asian culture.
LUX: The TVE Global Sustainability Film Awards celebrates a different kind of creativity. Tell us more about that.
Surina Narula: Television for Environment (TVE) has been at the forefront of amplifying messages around sustainability for the last 36 years. My journey with them began ten years ago, when I was introduced to them as a fundraiser. The organic natural next step for us was to give awards for well-made environmental films, leading to the conception of the annual TVE Global Sustainability Film Awards. The awards are unique because film submissions are judged not only on the quality of their content but on their message and impact. Our greatest success was when we highlighted the film My Octopus Teacher at the TVE GSFA 2020 and won the Oscar for the best documentary.
LUX: How would you like to see the next generation taking forward your legacy?
Surina Narula: One of the greatest Sikh Gurus, Guru Gobind Singh, once said, ‘Shiva, grant me this boon! May I never, ever shirk from doing good deeds!’. He acknowledged how hard it is always to do the right thing. This is because life is all about choices: we are always trying to make choices that help us enjoy our lives to the full and to fulfil our personal responsibilities. I think the next generation has a lot going for it [in this sense]. Access to technology and economic independence makes young people more capable. If they can develop and remain compassionate, the world will be a better place.
Find out more: jaipurliteraturefestival.org
As with all of our philanthropists, readers who have their own foundations and philanthropic interests are encouraged to reach out to our interview subjects and their institutions directly.

Helga Piaget, Founder of Passion Sea
Helga Piaget is the founder of the Monaco-based non-profit organisation Passion Sea, which reaches out to schools around the world with educational and artistic initiatives around ocean conservation. Here, Piaget speaks to LUX about pushing ocean conservation to the top of the youth agenda and the role of art
If passion could save the oceans, Helga Piaget would have done the job already. An engaging mix of fire and focus, she is sitting with LUX at the Yacht Club de Monaco, speaking about her programme to bring awareness of ocean issues to the younger generation through her art programmes at her non-profit organisation Passion Sea. Born in Germany and based in Monaco, Piaget spends much of her time engaging with schools to try to create a new generation who understand the issues facing the oceans, and the routes to resolution.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Our location is not a coincidence: Monaco’s Prince Albert is one of the most significant high-profile supporters of ocean causes, something in the DNA of the principality with the celebrated Oceanographic Museum and Prince Albert II of Monaco Foundation, as well as being the President of the Yacht Club itself.
LUX: Passion Sea strives to engage young children in the conservation debate. Why?
Helga Piaget: Education is huge. Children are the future – the next adults, and the next leaders. So, if you educate them in the right way, they might be able to make a change. I specialise with younger children because they are sponges. They educate others: when they play, they ask the other kids, ‘Why did you throw that [litter] on the ground?’ Then, they often go home and realise how much trash and plastic is in their households, and the parents learn, too. I think they know even more than us sometimes.

Passion Sea runs educational programs across the globe
LUX: Explain the role of art in Passion Sea’s efforts.
Helga Piaget: We educate through art, because when children paint something, or they have to do poetry, it stays in their brain. You have to get it anchored in their brain, and [the best way to do] that is through art. It makes them happy, too, learning in a happy way. We did a book with artworks from around the world [in 2017], but for the last two years we have been working on [producing] big flags with schools worldwide, with one from each country. It’s really something to be proud of. I’m waiting to do an exhibition on it, but for the moment it’s not the right time. We already have 25 countries, and beautiful works which are all related to the topic of water. A whole class of children [produces] each work: that’s what’s beautiful. When it’s ready, I often go to the school and have a wonderful event with the mayor and the parents. Normally the schools do other programmes afterwards for conservation in their area. It never stops with us.
Read more: James Chen on providing vision for all
LUX: So, for Passion Sea, creativity is a form of activism?
Helga Piaget: Yes. It’s a snowball system, from one [project] to the other. We find one school, and we meet with the directors and teachers who are willing to participate. Then, through the locals, we find the next connection to the next school. If you start in one good point, you get the connections afterwards, and they start working with you. I am very lucky because I have travelled nearly the whole world with Piaget, so I have good connections in most countries. Now I live in Monaco, which I am a citizen of, so I am very well-connected there. Our prince [Albert of Monaco] does a lot there. It’s very important to have people like him, who have a name, in my book. If you don’t have names, people are less interested. They like heroes, someone they can follow. It makes them listen more.

Piaget with Paris Baloumis, Oceanco’s marketing director
LUX: How difficult has it been to incentivise those in the high net worth community to care about the oceans? Does it ever feel like you like you are fighting a losing battle?
Helga Piaget: Some days it does feel like that. It’s very difficult, but if you have one or two people who understand, it gives you the energy to continue. Two years ago, I was at the Monaco Yacht Show and I was the only one who was speaking about sustainability; everyone [else] was just thinking about money. But the biggest luxury is water, and fresh air. If the water is not clean, who can sell boats? People won’t go to dirty lakes or seas. Everyone has to work together. So I said, ‘The money is in the water.’ Ever since, we have been contacting marinas and boat owners to give them flags for the boats. The flag means they are respecting and protecting the waters. [It’s a way of getting people to] think about how they live, to not to buy too much throwaway material, and to use better products when they clean their boats. A year later there were four, five, six events in construction technology, and everyone was cleaning with these new products. I was delighted. I am really just trying to make people aware. When people see me now, they always ask questions about the topics of nature. They say I am the mother of the oceans!
LUX: What is the nature of philanthropy?
Helga Piaget: Giving the time and energy to make something positive happen. It doesn’t need to be worldwide. Even if it’s small – it can be next door, in the community – it is amazing to see something happen. For me, it’s water and the environment. There is so much being done, but there is still so much to do. Water connects us all, with our body, with our whole planet. It’s important. You must feel where your heart goes – for you need a big passion and you need a lot of time – then think as big as you want.
Find out more: passionsea.com
As with all of our philanthropists, readers who have their own foundations and philanthropic interests are encouraged to reach out to our interview subjects and their institutions directly.

Ebinehita Iyere, founder of charitable youth organisation Milk Honey Bees
Milk Honey Bees celebrates and empowers Black girls and young women by providing a safe space for creative expression and healing. Here, the organisation’s 28-year-old founder Ebinehita Iyere discusses her personal journey, the impact of violence on women and the importance of putting ‘HER’ first
LUX: What’s your earliest memory of wanting to be involved in youth work?
Ebinehita Iyere: Youth work has always been a significant part of my life. My earliest memory of wanting to be involved was at the latchkey after school club I attended in primary school, supported by some amazing youth workers. I naturally started applying those skills to other young people around me.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
As I got older I really realised the impact that those youth workers had on me. When I left home aged 15, I became a youth worker without even knowing it, providing peer support to other young people like me. I was living in a hostel, so I created a youth work space in my small hostel room and everyone would come to my place. The community always had an impact on me and how I viewed society because people didn’t understand us, but the community did, the youth workers in the community understood us.
LUX: What inspired you to set up Milk Honey Bees?
Ebinehita Iyere: The work I was doing centred around young men. I was raised to believe that most issues in the community predominantly affect young Black men. That’s all I knew. Then, after a very tragic event affected me deeply, I realised that there weren’t any spaces for girls and young women to process the things they had experienced. I thought, when an incident happens in the community, where do the girls go?
Milk Honey Bees started with me, working on myself. My traumas had forced me to grow up far too quickly. So, there was a long process I had to go through to heal my own inner child, and through that important work I saw what I could do with other Black girls.
I had always used reading as an escape and when I read Milk & Honey by Rupi Kaur it was the first book that I felt in a long time really connected with me, so I shared it with a few girls, and essentially, with and for them Milk Honey Bees was created.
No one had ever asked these girls what they needed. My whole view on the needs of girls changed. Through creativity and putting ‘HER’ (Healing, Empowerment, Resilience) first, we were able to create a safe space for girls, where they could finally put themselves first, celebrate themselves and be visible.
LUX: How has the organisation evolved since its inception?
Ebinehita Iyere: The organisation has evolved in many ways and continues to do so. Milk Honey Bees began as a project that sat under my full-time job at Juvenis, where I work as a Therapeutic Diversion Practitioner. Through Juvenis we quickly found that the intersection of race and gender is incredibly important, and as a result Milk Honey Bees has evolved into something far bigger than we ever thought it would be – a space for Black and Mixed Girls to be themselves – which means we’ve been able to reach and support more girls than I could have imagined.
We’ve been able to take our time to develop our presence: who we are, what we want to achieve. Black girls are forever evolving so as an organisation we must grow with and for them. We have built and sustained more relationships with the community, schools, parents, and professionals. Some of the girls came to me at 17 now they’re in their early twenties – we’ve all been growing and evolving together.
Read more: The artistic legacy of Valmont’s Didier Guillon
Before the pandemic, we were doing creative projects and most of our work was done face-to-face. So, we set up online spaces where the girls could just chill and be still, feel empowered and vent about things. We also used creativity to stay connected which has led to us being able to reach and impact many more young lives.
Through the pandemic we actually evolved to become more sustainable and more visible, and are emerging with enormous energy and exciting plans for the future, both on and offline which led to being supported by the likes of major brands like Barbie, Sony Music, PR agency DH-PR and Adwoa Aboah’s media platform the ‘Gurls Talk’ podcast.

Milk Honey Bees’ partnership with Barbie aims to instil Black girls with the belief that they can do anything
LUX: Can you tell us more about the concept of H.E.R and how it works in practice?
Ebinehita Iyere: The concept is about putting ‘H.E.R’ first because Black and mixed race girls typically have to wear an armour. They have to mobilise in their families and communities and tend to be denied the time and space for healing themselves.
H.E.R stands for Healing, Empowerment and Resilience. It works in practice through helping the girls learn how to navigate themselves, and in turn, how they can navigate within the sisterhood and the wider world. Essentially, it teaches them to understand whilst being understood.
Healing comes first, and we use creative expression to do much of this work because people need to feel safe and comfortable to express how they feel. We use tools like play, art and healing circles, which allow the girls to be vulnerable in a supportive expressive environment.
Empowerment is about the reclaiming of power. So, taking back the power they felt they’d lost through their negative experiences. We do this by doing things the girls were told they couldn’t do. Black girls are often told they can’t or shouldn’t do certain things, but we empower them to do whatever they want, through raising aspirations through giving them amazing opportunities, such as new educational opportunities, writing for magazines like Grazia, and working with exciting brands like Barbie and Sony Music. It’s important to show the world the power the girls have, so they in turn feel self-empowered.
Resilience is about building on what the girls already naturally possess – and they possess a lot of it – especially with this generation dealing with the pandemic and social media pressures for example. Milk Honey Bees shine a light on various forms of resilience and support our girls to build it within and beyond the community. We also focus heavily on the fact that it’s OK not to be OK, and even just articulating this is a form of resilience. We show ourselves that we don’t always have to be strong or present a certain way. You have put HER first!
LUX: Why is it so important to enable and support creative expression amongst young Black women?
Ebinehita Iyere: As I mentioned before, creative expression is really important for healing. You can feel a sense of both strength and vulnerability through creativity in all its forms. It comes from within – plus, creative potential is limitless.
It’s particularly important for Black girls, who have long been the pioneers of creativity – yet are rarely credited for it. We support them to take ownership of it. Creative expression also determines how your internal feelings are shown and embraced by the world. For Black girls and young women, it’s so important, so that the world doesn’t continue to only see one side of them. Our one-to-one and group sessions often lead into social action projects. Their creativity fuels their voice and visibility.
LUX: Are the girls you work with referred or do they tend to reach out directly?
Ebinehita Iyere: Both! We have a referral system in place through Juvenis, which is our parent charity. We also get referrals from social care, education, mental health partners and sometimes local institutions like the police.
We are really strong on encouraging and facilitating peer-to-peer support, which means that girls can reach out to us directly – they often refer their friends or refer themselves. We even have boys referring girls to Milk Honey Bees! Young men who see the work we do sometimes refer their sisters or girlfriends to us, which is great. We also get a lot of parents coming to us.
LUX: How do you ensure you’re meeting the needs of the individual within the collective?
Ebinehita Iyere: Before anyone is put in a group, our work always begins with a one-to-one session. I always start by asking the girls how they are, who they want to be and what they need, and we co-design an individual support plan.
The next step is the group process. We spend time getting to know each other and ourselves as individuals. Within the group, everyone has a role, or ownership/leadership of something. Everyone is individually celebrated, even within a group.
We create a space free of judgement and rooted in the celebration of Black girlhood. We work to the ethos of: “I am my sister’s keeper, while I’m keeping myself.”

Milk Honey Bees organises creative workshops and projects based on what the girls want to do, see and learn
LUX: You’ve said before that “people need to start seeing Black girls and stop putting them in the same category as women”. Can you explain what you mean by that?
Ebinehita Iyere: A lot of the time Black girls are judged as adults when they are still children. One of the key barriers to the intersecting needs of Black girls and young women being centred by services is the manifestation of adultification bias, where notions of innocence and vulnerability are not afforded to certain children due to racial prejudgement. They are held to greater levels of responsibility due to being treated as though they are more mature, with their rights often being diminished or overlooked.
For example, research has found that adultification contributed to the perceptions amongst those in authoritative positions view Black girls and young women are less innocent, which influences a greater use of force, harsher punishments, and decreased protection and support from services in comparison to white girls. This can have further damaging impacts on how they view themselves, their mental health, as well as negative experiences and interactions with various professionals across so many systems, including education, justice, health, and social care.
If society views Black girls as Black women they are essentially taking away their childhood. There’s an erasure of innocence because of this assumption. We need to allow Black girls to thrive and fail in their girlhood, in order to become the best women they can be.
It’s easy for others to try and write you off and label you as an “angry Black woman” without even knowing who you really are or based on your expressions. I know this stigma first-hand from teachers, to social workers and even previous managers. It affected me deeply. I don’t want any more girls to have to go through that as girls or women.
LUX: As a young founder, what challenges did you face in setting up the organisation and how did you overcome them?
Ebinehita Iyere: Initially, my biggest challenge was me and not being able to process myself. I realised very early on that I had to work on myself first before I could really help anyone else. So, I learned to look after myself while trying to look after others. Now I allow myself to process my feelings and sit with my emotions. They are valid.
You’re allowed to cry, rest, be happy, feel confused – you’re allowed to ask for help. There is amazing strength and power in helping others, but you have to love and take care of yourself first before you can do that for anyone else. I’ve learned how to embrace my vulnerability and turn it into great strength, by speaking up for myself when it matters and allowing myself to be vulnerable with others, knowing it’s more than OK.
Your experiences do not define you; they will only allow you to learn, grow and become the best version of yourself for you. My experiences have not allowed me to grow personally and professionally.
Read more: Juanita Ingram on empowering women in the workplace
Outside of my personal life, my transition to a founder was as a result of most of my work being with boys in the community, but I started to realise that there was a real lack of understanding when it came to creating safe spaces for Black girls to express themselves in the community after incidents happened, or even spaces that celebrated Black girl joy. Creating safe spaces for girls is something I assumed people would understand, but they didn’t. People couldn’t understand what I was doing.
Being supported by my passion, family and a core group of people in the youth sector who understood my vision (Jenni Steele, Winston Goode and Whitney Iles), and receiving funding and recognition through awards and press also helped my journey to ensure that no matter the challenge I could overcome it.
LUX: How do you think education systems can better support young people? Are there any skills, for example, which you think schools should be teaching?
Ebinehita Iyere: I think education systems can provide better support by allowing young people to be creative. Life, career, and success – none of these are linear. Thinking creatively helps young people navigate these things.
I also think schools should be teaching more life skills – processing emotions, managing money, and mindfulness for example – to prepare young people for the highs and lows of the working world.
Schools should have a four-day teaching week with one day set aside for play, mental health, life skills, pastoral care etc – for both staff and students – plus engaging with families. Showing that it’s OK for them to express themselves because without expression you can’t function. We saw it in the pandemic – imagine if adults had had the personal tools to have been able to support kids more during the pandemic?
LUX: What impact does the exclusion of women from conversations around violence have on individuals and communities?
Ebinehita Iyere: For every experience of violence whether it’s structural violence, domestic violence or youth violence, there’s always a woman on the end of it – whether that’s on the side of the perpetrator or victim. Violence is not just the act itself. It’s the aftermath. Instead of grieving and healing, girls have to wear this armour and protect boys and men. In other words, girls are spending more time mobilising for others than healing themselves.
Excluding women from these conversations leads to overwhelming feelings of invisibility, not feeling like our voices are heard, and erasure from our experiences. We are more than just a hashtag, we should not only be visible when being mourned but also while living. We should not be excluded from conversations about our safety in fact we should be safe.
Even when we are included in these conversations we aren’t leading them. The impact is really bad. Giving the women of tomorrow the skills, language and tools to be able to have these conversations in their spaces and beyond is essential in my opinion.

Iyere at the Veuve Clicquot Bold Woman of the Year Awards 2021 in London. Photo by David M. Benett/Getty Images for Veuve Clicquot
LUX: What upcoming projects are you looking forward to?
Ebinehita Iyere: We have so much coming up for us and essentially everything is led and developed by the girls. We are developing a new schools based project for teen girls and have just launched our project with Barbie for 5-10 year olds.
We are super excited for the launch of Creative Connection, our a brand-new project in partnership with Sony Music UK. I’m really looking forward to this because it’s an incredible chance for young women to navigate the industry they want to be in – and an amazing chance for the inspirational businesses and creatives they engage with to learn from the girls.
Creative Connection is a 8-week mentoring project purposed with empowering Black/Mixed Black young women, who have an interest in getting into the music and wider creative industry, through a series of introductory workshops and sessions. In collaboration with Sony Music UK, Milk Honey Bees have curated a unique curriculum supporting a selected group of 10 Black/Mixed Black female creatives aged 18-23, by offering them creative mentoring and work placements. Being able to fuse creativity, work and wellbeing together to all work hand in hand is really exciting, and the ten young women who are selected will be the first of their kind.
LUX: And finally, you were recently nominated for the Veuve Clicquot Bold Future award. What does that mean to you personally and to your organisation?
Ebinehita Iyere: It was so amazing to be recognised by Veuve Clicquot, mainly because it’s so rare to see that kind of visibility for people like me. Even though I didn’t win the actual award, I am still a winner!
My name, Ebinehita, means ‘my destiny’. My journey fluctuated from not feeling like I had a destiny to fulfilling my density. I’ve worked so hard to create one for myself through hard work and self love, so to be recognised by such a prestigious brand made me so proud. For every woman who fought to get where you are: continue to be bold because you are the future.
Find out more: milkhoneybees.co.uk
Follow Ebineita Iyere on Instagram: @ebinehitaiyere_

Didier Guillon with his son Maxence who will take over leadership of Fondation Valmont in 2022
artnet’s Vice President Sophie Neuendorf speaks with the founder of the Valmont group and one of the most important philanthropists and collectors in the art world: Didier Guillon
Over the years, French-Swiss entrepreneur and philanthropist Didier Guillon has built a cosmetics imperium, arts foundation, and expansive collection. The Valmont group has become a great family success story thanks to not only his creative genius and passion for art, but also in large part to his wife Sophie who’s able to anticipate women’s desires and needs by combining luxurious ingredients and advanced technologies in Valmont’s high-end range of cosmetics.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Ahead of a major new thematic exhibition opening at Palazzo Bonvicini – a historic palace which is also home to Fondation Valmont in Venice – which will bring together artists Isao, Stephanie Blake and Silvano Rubino with the art students of Publicolor (a New York-based non-profit organisation that helps marginalised youth reintegrate into society through the use of art as an expressive therapy), Guillon discusses family business, his philanthropic projects and the value of generosity.
Sophie Neuendorf: What’s it like working alongside your wife?
Didier Guillon: It’s a truly inspiring peer-to-peer relationship. There’s no domination of one to the other. Sometimes, we have differences of opinion, but that usually leads to an even better solution. She’s a new Helena Rubinstein! Although I’m more involved in the collection and Fondation, she’s always interested in my passions and projects.
I’m also excited to reveal that we will open a Maison Valmont in Madrid very soon, which combines both my passion for fine art and her work ethic. We’ll have a retail space as well as a secret space for our VIP clients where we will exhibit fine art. It’s like showing a new world to our clients, which is very important for us.

Sophie Neuendorf: Are your children keen to follow your footsteps in terms of collecting and philanthropy?
Didier Guillon: I’m certain that they will. They understand the value of generosity and of philanthropy as I’ve instilled it in them for many years.
Read more: Umberta Beretta on fund-raising for the arts
Sophie Neuendorf: There are many family businesses within the art world, where savoir-faire is passed from one generation to the next. Are you working closely with your children to ensure the transfer of the foundation into the future?
Didier Guillon: We’re really at the beginning of the process. My son will lead Fondation Valmont starting in 2022. He will be primarily responsible for discovering emerging artists for an exhibition we’re launching in Venice for the 2024 Biennale. The theme will be the concept of travel. For my son, it’s a true immersion into the art world.
In terms of the business, it will take much longer to decide if and when my children will join the Valmont Group. Perhaps, they would like to have some other experiences first, which to be honest, I believe is in their best interest. However, we all have to protect the concept of heritage, in terms of art but also of family businesses and values. It’s very important to transmit one’s values to the next generation. For me, that means being known for one’s generosity in all its different facets! Not for being rich, for example. I would be horrified to appear on any “rich lists”!

Villa Valentina on the Greek island of Hydra, where Fondation Valmont hosts artist residencies
Sophie Neuendorf: How do you choose the artists you work with?
Didier Guillon: The absolute objective is to have a deep connection with the artists. For example, I offer our artists the opportunity to travel to Hydra for a four-day workshop and artist residency. It’s a feeling of generosity in terms of spirit and knowledge. It’s important to me that our artists know and embrace the fact that charity is a big part of our ethos and will be part of any exhibition.
I work closely with my son in the decision making process. Neither of us wants to buy work for speculative purposes. We buy for passion and to support the artists. That’s also why we created the “DM” art fund: to raise money to support young artists, which is especially important now, in the wake of the pandemic.
Sophie Neuendorf: What would you like your legacy to be?
Didier Guillon: The notion of generosity in thought and deed. It’s very important to me and it’s what I would like to transmit to the next generation.
Read more: Gaggenau’s Jörg Neuner on embodying the traditional avant-garde
Sophie Neuendorf: If you could have dinner with any three artists, living or dead, who would you choose?
Didier Guillon: Francis Bacon because he was the first artist I saw with my father at a big solo show in Paris. Sol LeWitt because he’s the opposite. Cecily Brown because she has a funny eroticism in her paintings. For me, the way she paints is absolutely fantastic. She’s the new Gerhard Richter.
Sophie Neuendorf: You recently opened a beautiful space in Venice. Why Venice?
Didier Guillon: Venice is an international destination where the art takes possession of the city. Also, it’s a sustainable city because you don’t have cars, which is the same as Hydra, for example, where there are only donkeys. The city also represents the fragility of humanity, seeing as its constructed on poles.
We opened the space few years ago as a place to invite some of our many valued clients and friends. We truly enjoy showing them the beauty – known and secret – of Venice, as well as introducing them to our fragrances. I really want to welcome our guests into the Valmont world.

The grand interiors of Palazzo Bonvicini in Venice
Sophie Neuendorf: What is luxury for you?
Didier Guillon: Luxury, for me, is having the time and money to dedicate, imagine, and create things for those that are disadvantaged. I want to leave a better world for our children and grandchildren. Charity should be a global endeavour. We all have to do our part.
Sophie Neuendorf: The pandemic has been tough for the art world. How did you experience it?
Didier Guillon: We were very fortunate to be together as a family during those few months of lockdown. For me, it was occasion to develop my own artistic creations, all of which were sold to support our art fund.
Sophie Neuendorf: Do you think ESG is important for the art world? What, if anything, are you doing in those terms?
Didier Guillon: Living and creating sustainably is very important. We only use glass for our products, for example. To be honest, it’s a very big challenge to combat climate change. We feel it’s very important to do our part for the environment, but we work more closely in helping disadvantaged children because children are our future.
Find out more: lamaisonvalmont.com
Follow Sophie Neuendorf on Instagram: @sophieneuendorf

Bellini’s Pietà at the Museo Poldi Pezzoli, which Beretta helped restore
The role of philanthropy has never been more urgent, and is reflected in our ongoing online series. Here, Umberta Beretta outlines her work around women’s rights and art for the many
Beretta was born into a family of prominent industrialists in northern Italy and is married to Franco Beretta, who leads the famed gunmakers. For the past two decades she has been active in fund-raising for numerous non-profit organisations and foundations with a focus on art, including her work for the Italian pavilion at the 2017 Venice Biennale and the Museo Poldi Pezzoli in Milan; medical charities, including cancer research through the Fondazione Beretta, of which she is a board member, and the Essere Bambino foundation; and on social causes such as campaigning against violence against women. The Beretta family’s involvement in art is notable also for Christo’s 2016 project The Floating Piers, which connected the shore of Lake Iseo with the island of San Paolo, owned by the Berettas, with fabric-covered walkways.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Where did your interest in philanthropy in the arts come from?
Umberta Beretta: I have always had an interest in the arts. My father Giorgio Gnutti often took me to museums or when visiting artists’ studios. My grandmother (on my mother’s side) pushed me to do volunteer work. Art is my passion and the time I dedicate to less fortunate people or causes is my way of giving back.

Umberta Beretta photographed by Lady Tarin
LUX: Which art projects are exciting you?
Umberta Beretta: The past year has been very complicated and frustrating, but I very much look forward to the Venice Biennale [due to take place 23 April to 27 November 2022] curated by Cecilia Alemani. I admire women who do well in the arts. My hometown of Brescia and Bergamo will be Italian Capital of Culture in 2023, so we are planning a series of cultural activities and that’s quite exciting.
LUX: How important are private and philanthropic support for the arts?
Umberta Beretta: They’re both crucial. In Italy this still has yet to be fully understood. Individuals should be given more tax incentives [to donate]. But it is in our culture to promote beauty so against all odds I think Italy will always be a motor for the arts.

Beretta with the Ghanaian artist Ibrahim Mahama
LUX: How has the pandemic affected the arts in Italy?
Umberta Beretta: Tourists will always come to visit our museums. What concerns me most is the impact the pandemic will have on young, lesser-known artists, whose opportunities have frozen. And the same can be said for emerging fashion designers.
Read more: Meet the new generation of artisanal producers
LUX: What else can be done to support women’s rights?
Umberta Beretta: We can start by educating our children. I try with my son every day. All boys should be taught to respect women and all girls should be taught to demand respect. Women have the right to express themselves freely like men. In the art world, for example, women should be free to express their views on sexuality without scaring the public away. In everyday life they should be able to be mothers and have a career at the same time.

Beretta with the artist Christo in his New York studio
LUX: What project has pleased you most?
Umberta Beretta: Definitely Christo’s Floating Piers. Winning the Montblanc de la Culture Arts Patronage Award in 2015 for Italy. Restoring some of the masterpieces of the Museo Poldi Pezzoli through the Restoration Club… I could go on.
For more information, visit: umbertagnuttiberetta.com
This article was originally published in the Summer 2021 Issue.

Manfredi Catella, CEO of COIMA and president of the Riccardo Catella Foundation
Manfredi Catella is the CEO of COIMA, the real estate company behind Porta Nuova in Milan, one of the most important real estate developments in Europe. He is also president of the Riccardo Catella Foundation which aims to promote sustainable and responsible urban development by improving and animating public spaces. Here, Catella discusses transforming urban environments, mixing business with philanthropy and how technology advances sustainability efforts
LUX: The Riccardo Catella Foundation has had an interest in promoting sustainability long before sustainability became a buzzword, how did this come about?
Manfredi Catella: The Riccardo Catella Foundation was established in 2005 in honour of my father, the entrepreneur Riccardo Catella. At the time, not many entities were focused on promoting ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance), or impact indicators in investments, and we felt it could be our contribution to set up a non-profit organisation committed to promoting sustainable territorial development. We also have the ambition to educate communities about the effects of climate change and what actions need to be taken to fight and prevent this phenomenon. We do this through a citizen engagement program of civic-cultural projects within the realm of green and public spaces in the city of Milan. We believe it is important to listen to citizens in order to understand their vision for the urban space surrounding their homes and integrate programs and services that can improve their quality of daily life.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: What is the most exciting philanthropic project you are currently working on and why?
Manfredi Catella: At the moment, the philanthropic project where we are dedicating a lot of our energy to is The Riccardo Catella Foundation’s management of Milan’s third largest park, BAM (Biblioteca degli Alberi Milano), which we undertook together with COIMA on behalf of the Municipality of Milan. It is the first public private partnership in Italy that allows a private foundation to manage such a vast public and green space in the city centre. The 10 hectares of the botanical garden, which was developed by COIMA as part of its Porta Nuova development, is a ground-breaking project that aims to involve companies, non-profit sector, and citizens (BAMFriends) in the management of a public area. In addition, we animate the park through a cultural program based on four pillars: open-air culture, education, wellness and nature.

BAM (Biblioteca degli Alberi Milano) is Milan’s third largest park, managed by The Riccardo Catella Foundation
Ensuring the safety of the local community in the outside spaces has been particularly important since the start of the pandemic. We have been increasing services to enable greater green mobility over the past year. The changes are visible to park visitors. In outdoor areas, new bike racks have been set up, with information on anti Covid-19 measures, sanitising gel dispensers and continuous sanitisation services for floors, children’s playgrounds and communal areas. Safety is the starting point for a series of inclusive initiatives such as Wi-Fi enhancement and the launch of the Porta Nuova Milano app, which is designed to book events and services in the area.
LUX: Please explain your workings in neighbourhood community management?
Manfredi Catella: COIMA believes that the only way for the built environment to help fight climate change and to promote diversity is to integrate them into the basic economic, social and environmental model of every real estate development and by setting measurable objectives and transparently reporting on those objectives. We believe in placing nature and humans at the centre of all real estate development and urban regeneration schemes. In Porta Nuova, we have created a thriving urban environment that enables constant interaction between nature and architecture. There are walkways, green spaces, and piazzas with spaces created for exercise, relaxation, and socialising, all of which welcomes 10 million people every year. It includes Biblioteca Degli Alberi Milano (BAM), an innovative urban park and botanical garden, which plays host to a diverse programme of cultural events and activities for residents, workers, and visitors alike.
Read more: Michelin-starred high altitude dining in Andermatt
LUX: Why do you think it is important to mix business with philanthropy?
Manfredi Catella: In general, the corporate approach to philanthropy has really evolved, and over the last ten years in particular, there has been a shift towards a model of collaboration and sustainable, long-term initiatives. It is important to mix business with philanthropy because corporations have a highly influential role on the social and natural world in which we live. It is also important as sustainable business models have a strong track record of delivering superior returns. Corporate philanthropy is no longer about simply giving money and walking away. By using the skills, tools, and approach of our business, we can continuously monitor the impact of our work and ensure it is having the best possible outcome for those who need it.
The pandemic has highlighted the fragile nature of our world and we believe that business has a duty to create positive change and a sustainable future as we recovery economically from Covid. This led us to establish the COIMA ESG City Impact Fund in 2020; an investment fund focused on sustainable urban regeneration. We aim to use this fund to redesign new physical and social models for housing, tourism and urban regeneration of neighbourhoods and believe that sustainable real estate can play a central role in a post Covid recovery. As responsible managers of institutional capitol from all over the world, we believe can help shape the future.

Bosco Verticale was designed by Boeri Studio, and built and managed by COIMA as part of the Porta Nuova development
LUX: Apart from sustainability projects, are there any other philanthropic causes you have a particular interest in?
Manfredi Catella: Since 2018, we have been promoting an important social inclusion project through the Riccardo Catella Foundation, together with the Dynamo Camp association, called the Porta Nuova Smart Camp. It is an inclusive and innovative project for children both with and without serious pathologies and disabilities. Nature, sustainable architecture, and technological innovation are topics at the centre of the camp’s activities, along with incorporating the values of the Foundation and the community of COIMA’s Porta Nuova development.
LUX: How has working closely with local communities over the last 10 years changed your outlook on real estate development?
Manfredi Catella: We are recognised as a sustainable real estate company because it has long been our goal to create projects with a strong positive social and environmental impact on its community. The past year has reaffirmed that we all need to continue conducting our business and investing in a responsible way. The past ten years has taught us that it is essential to always look at the bigger picture. For us, this means that we look at a neighbourhood scale instead of a single building. By doing this, we can effectively redevelop urban spaces and provide a selection of amenities to better serve a variety of city users. For example, the COIMA ESG City Impact Fund has just acquired the railway yard of Porta Romana in Milan, together with Covivio and Prada, and we are very excited about exploring this neighbourhood scale development.
Read more: Alia Al-Senussi on art as a catalyst for change
Through our passion and experience, we have also developed our own sustainable vision called COIMA Roots which focuses on driving sustainable, economic, and social performance across our developments. COIMA Roots has been created in line with our belief that humans and nature should sit at the heart of all urban regeneration and development. To accomplish this, our set of values, or roots, are nature, beauty, affordability, human, happiness, ethics, service, and knowledge.
LUX: What were your principal goals when creating the Riccardo Catella Foundation?
Manfredi Catella: When we started the Riccardo Catella Foundation, our goal was to actively support the local economy and to promote the culture of sustainability and innovation in territorial development. We also wanted to make sure we were improving the quality of urban life and public green spaces through the foundation’s cultural projects. I feel that the challenge to create a place of nature, inclusion and growth in the heart of the city at the BAM park will be one of our challenges over the coming years. We are working to create a park that engages the community through a rich cultural programme inspired by sustainability but at the same time would like to create a sustainable business model that could be replicable for other parks in other cities around the world.
A street art project at BAM in Milan
LUX: The Riccardo Catella Foundation has been around for almost 15 years. What has been the most significant change in sustainability during this time?
Manfredi Catella: Two main drivers: awareness and technology. When we began the foundation, sustainability and climate change was not a common topic as it is today. In recent years, we have witnessed a major shift and an increased awareness and now all players, from the public administrations to corporate to citizens, are recognising the need for urgent concrete action. Also, today, we have technological solutions that before were not available and it is fundamental to stay at the forefront of these technologies to continue to push the bar in integrating these solutions in development.
LUX: Which regeneration projects by others have particularly impressed or even inspired your philanthropic efforts?
Manfredi Catella: When we began working on the proposal for the management of BAM, we visited many parks around the world, including The High Line in New York and Millennium Park in Chicago. Then we worked on creating our own interpretation that would integrate well into the city of Milan.
LUX: Is there a major difference in approach between European, Asian and American organisations involved in philanthropic urban regeneration programmes?
Manfredi Catella: Across Europe, philanthropic engagement is an integral part of corporate social responsibility and reinforces related strategies. More and more companies of all sizes are dedicating financial resources, products, knowledge, and time to the common good. The world of philanthropy is renewing itself and dated foundations are starting to make way for a new approach to charity that incorporates social purpose and sustainability through impact investing. We believe that impact investing will become mainstream and that the positive environmental and social contribution will be integrated into traditional investments. We are dedicated and are working actively in that direction.
Find out more: coima.com

Lady Edwina Grosvenor. Photograph by Roo Kendall at Pencil Agency
Lady Edwina Grosvenor is the daughter of Britain’s richest landowner, the Duke of Westminster, and a passionate advocate for prison reform. She is the founder and chair of One Small Thing, an organisation that works with prisoners and staff in both male and female prisons, and a founding investor and ambassador of the Clink Restaurant chain, which trains prisoners for work in the catering industry. As part of our ongoing philanthropy series, she speaks to Samantha Welsh about her early work with prisons across the globe, the importance of training officers and her vision for the future
LUX: What are your earliest memories of wanting to give to make a difference?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: I was about 12 when my mother and father decided to take me and my older sister to a drug-rehabilitation centre on Hope Street in Liverpool to meet two heroin addicts, to understand about drugs and addiction. It was a pivotal moment. I remember realising there are reasons why people become addicts, and so my interest in human behaviour began. Years later, I realised I had money to give and there was a big internal wrestle with what that meant, what I was going to do with it, how I was going to do it, what would be the appropriate way. Then, at 15, I worked in a homeless shelter called Save the Family where mothers went with their children as a last-ditch attempt to prevent the children from being removed into care. The mothers were taught how to be parents. If you’ve never been parented yourself, how could you be expected to do it? I found that really hard-hitting as some fathers were either in prison, others had left, or they were dead. The mothers all had trauma-histories. I was the same age as some of the children that were there, they knew who I was and they challenged my family background. It made me think.
Working with Save the Family and visiting the two heroin addicts on Hope Street are the two really big moments in my life and both those happened before I was 16. From then on, I was always thinking, how is that fair, why have I got all this when others have so little?
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: When were you drawn to advocate for justice through prison reform?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: I travelled alone to Nepal when I was 18 to work as a prison’s assistant missionary in Central Jail, Kathmandu. I was going into prison to remove innocent children serving time alongside their parents. I remember the first four boys were all under the age of five. They’d never seen a white person, and they’d never been in a car. They were violently sick throughout the five hour trip from high in the remote Himalayas down to the flatlands of Nepal. It was just utter chaos, but wonderful chaos and I was doing something that other people don’t do.
LUX: So from the start, you knew you had go into prisons to be sure of making a difference?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: Yes. It only became obvious when I went into women’s prisons in the UK. The case studies were part of my graduate dissertation on children growing up in prisons. I found that government legislation and the prison system were not responding to the reality of what was happening in prisons. After graduating in Criminology and Sociology & Criminal Behaviour, I started working with women offenders and their children. I also started to understand how the law works by working in the House of Lords. So with this, my passion and resources, I could hopefully approach this problem from every angle and be effective.

Lady Edwina Grosvenor speaking at a conference
LUX: What characteristics are shared by the worst prisons you have visited?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: Overcrowding is a big problem, infections spread faster, it’s harder to manage prisoners effectively, it’s harder for staff to do their jobs well and its harder to run a good, clean, safe regime. Also, bad leadership. You can go to prisons that look grim but the leadership is outstanding, there’s great staff morale from the governor down to the officers on the wing and the prisoners have a sense of hope. As in business, there has to be good leadership top down through every pay grade.
LUX: How does understanding offenders’ past trauma help in reforming behaviour?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: I set up One Small Thing to understand trauma through a gender-lens. My organisation provides training for prison officers and at the end of the course, we emphasise one small thing: it’s about changing the question from ‘what’s wrong with you?’ to ‘what’s happened to you?’ The way men generally tend to deal with their violence is to externalise it whereas women often internalise it. For example, women are usually abused by the person to whom they say, “I love you” which is why they suffer more with mental health problems. If a prisoner tells you what happened to them, you stand a chance of understanding who they are, why they are behaving the way they are and then you can work with them more effectively.
Read more: New residences at hot selling Andermatt Swiss Alps
LUX: Is it possible to change the way that correctional institutions approach rehabilitation?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: It absolutely is – that is why I never get too downbeat about things because it is entirely possible. Negative culture can become very strong in some prisons and you can feel it. With One Small Thing, over six years we have been working across all the women’s prisons and the long-term high secure male estate, which is 17 prisons. We have been training the officers, putting interventions in for the prisoners and working with the leadership down through the ranks to bring about that cultural shift.
LUX: So changing the culture ‘inside’ increases the probability prisoners who have served their sentences do not reoffend once they are ‘outside’; the press has reported widely on the success of the Clink restaurants here. Can you tell us more?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: We have a five-step integrated approach at the Clink: recruitment to the programme, training, support, employment, mentoring. A lot of organisations can do one thing really well, but to be successful you have to do it all for someone not to reoffend. The mentoring is critical as it supports the hard work done whilst the person has been inside the prison training. Do you have a suit to go to your interview? Do you have a flat? Is it furnished? Do you have anyone to talk to? Maybe they can’t see their friends and family because they are part of their old life and they do not want to reoffend. It is painful.
LUX: How do you think academics and other professionals draw on your experience here?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: Our trauma work was adopted into policy and written into the Female Offender Strategy, published in July 2018 by the Secretary of State for Justice. The Clink restaurant chain has just announced its expansion in partnership with the MOJ across 70 more prisons.
LUX: Why have you had to contribute financial resources alongside your professional work?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: I think this is an interesting thing when it comes to the role of philanthropy, and the public sector. I decided not to set up a foundation so that I could give to things that weren’t registered charities. When you’re trying to bring about a system change, and do things that have never been done before, you have to do things entirely differently from the beginning. For example, the training that we put across the prisons came from California, and the author of the work is a lady called Dr Stephanie Covington. I was able to bring her from California over to England to start training the prison officers. We were then able to put her curriculum into the prisons, but none of that could have been done if I had a foundation because she’s not a registered charity; she’s a professional expert, consultant and author. The conversation I had with the head of the prison service was along the lines of “I’ve seen this amazing thing in California, we really need this across our women’s prisons.” He said, “Edwina, there’s no money.” So I said that I would pay for it and he said, “Edwina, there’s no one to organise it’. So I said that I would organise and he agreed. It worked so well that it has now gone into the male estate.
LUX: What upcoming projects are you looking forward to?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: I am working on a big five year pilot project called Hope Street. I am redesigning the justice system for women and their children in the community in the hope that we will prove concept and then it will be rolled out nationally across England and Wales. Hope Street is about offering a safe space for women to serve their sentences in the community alongside their children. There are fewer than 4,000 women in prison in this country in12 women’s prisons, many of whom are perversely sent there for their own safety. Most women are inside for non-violent crimes, the large majority are in for very short sentences. Their children get removed from them, this is about 17,000 children per year. Hope Street will sit across the county of Hampshire. The county boundary is relevant because you have the local police, the local probation, the local services and commissioning routes. We’ve designed Hope Street to fit into that local landscape. It’s designed to be replicable and scalable so that it could be rolled out nationally.

An imagined render of Hope Street. Photograph by EnAim
LUX: How does Hope Street work?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: Hope Street will reduce the number of women being sentenced to prison in Hampshire by being the safe and healing community alternative. Women and their children will be able to access holistic, wrap around support in one place. At Hope Street there will be flats for the women and children, intervention rooms, workshops and training facilities where the women will do the work the courts prescribe. It’s a real life, open community with a café for the public as well as the women themselves, a crèche, and a garden. When it’s time for individuals to move on to a less supported environment, Hope Street will provide move on accommodation and continued support through outreach workers. It’s been four years’ in the planning and development, construction has begun and we open in Q2 2022.
Read more: Tasting with sustainable Napa wine producer Beth Novak Milliken
LUX: What advice would you offer someone else with personal resources who wants to make an impactful difference?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: I think people who have a lot should be conscious of it, and think about what they might or might not like to do with it. Wealth can be an incredibly powerful and amazing thing but it can become toxic to manage. I’ve managed to think about my philanthropy firstly, as a career and secondly, as a hobby to be enjoyed. Even on holiday in Sri Lanka last year, I found a prison opposite our hotel and managed to get in. Dan, my husband said: “Have you noticed the prison’s there?” and I said, “Of course I’ve noticed the prison’s there!”
LUX: What is the most memorable moment of your philanthropic journey?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: A big impactful one for me was visiting twelve prisoners in the Secure Housing Unit (segregation) within Pelican Bay prison, a State Male Supermax prison in northern California. In this prison the officers had guns, riots were common place, alarm bells rang; it was a chaotic, violent place. I needed to see and understand the work that the men were doing to address the trauma that they had suffered and to see how it may fit back in our English system. These men were never going to see the light of day again, however, I heard them describe their compulsion for violence as a physical fire in the stomach that they could not stop “but what I can do now is recognise it, breathe through it, and I know I can control it now.” For the first time they were being given words to be able to articulate and therefore address and process some of the horrific things they had been through. The only two things the prisoners felt were wrong with the programme were that it should be expanded to the whole prison and the teaching should be in a classroom not a cage.
LUX: What are your next big challenges?
Lady Edwina Grosvenor: Getting Hope Street fully funded and open. We have £6 million left to raise of £26.2m in order to fully fund the five year Hope Street pilot. I would love to hear from people who would like to support us.
Find out more: onesmallthing.org.uk/hopestreet
Samantha Welsh is a contributing editor of LUX with a special focus on philanthropy.

Philanthropist and businessman Etienne d’Arenberg
Etienne d’Arenberg hails from one of Europe’s oldest families and is treasurer of the Arenberg Foundation, whose mission is the promotion of the understanding of European history and culture. He is a partner of family-owned Swiss private bank Mirabaud. He is also President of the Menuhin Competition Trust, and Trustee of several Swiss and UK charities. He speaks to LUX about European values, and the evolving perspectives and expectations of the next generation
LUX: Has the nature of philanthropy changed in the last two decades?
Etienne d’Arenberg: Both from my private banking experience at Mirabaud as well as from various circle of donors I belong to, I feel that there is a clear evolution in philanthropic practices. Firstly, there is an increasing involvement in philanthropic areas outside the traditional non-profit sector with growing interest from both governments and companies to partner with individual donors on specific issues. Secondly, and this is probably the consequence of the first point, there is an increasing focus on systemic change and transformative grant-making approaches that achieve greater leverage. Lastly, and this can become challenging for smaller institutions, there is a growing expectation for impact measurement and focus on KPIs.
Another trend that I see emerging in large donors’ circles – often business-owning families – is the need to align business and family platforms. The time where your company was polluting the rivers while at the same time your family foundation was giving to the WWF is over. There is a search for coherence between the different activities with a growing alignment between the business, the investment vehicle(s) and the philanthropic foundation. Interestingly, private banks in Geneva such as Mirabaud have been at the forefront of this trend with their founding families being very active in local communities, while at the same time promoting a company’s approach to addressing the most pressing social and environmental issues.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Tell us more about your last point – are people being judged by different criteria?
Etienne d’Arenberg: We are faced with issues of huge magnitude, both on the societal and environmental front and this is especially true in times of COVID-19. If you combine this with growing access to information, I do feel that there is a real demand from the public for more sustainable business practices and generally speaking pressure for accountability. I see this pressure mounting, especially from a new generation of customers and employees.
If you run a company that is active in socially or environmentally damaging activities, the issue is that you will not be able to shift your business focus overnight. Our role as investors – and this is what we do at Mirabaud – is to accept companies that may not yet be there, but which are able to demonstrate a forward-looking vision including a clear strategy to transition to clean, circular and inclusive business models. For a family-owned or family-controlled company such as Mirabaud, this is also a wonderful opportunity to reconnect with purpose and long-holding family values.

The Arenberg Foundation organises concerts in the remote village of Lauenen, in central Switzerland.
LUX: Is inclusion and bringing people together an important element of philanthropy?
Etienne d’Arenberg: Inclusion is about embracing people irrespective of their difference, whether that’s race, ethnicity gender, sexual orientation or identification, religion or economic circumstances, and providing them with equal opportunities. This is where philanthropy plays an important role as inclusion often starts with access to education, healthcare or basic needs.
But inclusion is also about getting rid of bias, the “us versus them” old way thinking, and embracing the fact that our difference is something positive: this goes far beyond the tropic of philanthropy. I come from quite a traditional background, but I am proud to say that I do not feel threatened by a society that changes. Quite to the contrary and under the impulsion of my daughters, we have been revisiting family values and behaviours, making sure not to pigeon-hole people and being particularly mindful not to impose suffering by raw reflexes of exclusion.
Mirabaud has also committed itself to diversity and inclusion, making sure, for example, that we create an optimal workplace for women. The fact that we were one of the first Geneva private bank to welcome a female managing partner helped us to develop a solid framework for gender equality practices. This has nothing to do with tokenism as it is based on the strong conviction that a forward-looking institution needs different perspectives and experiences.
Read more: Sophie Neuendorf on building a more sustainable art world
LUX: With the demands that are ever growing on the state sector, does the private sector need to step in more to support the cultural and charitable activities that were previously more supported by the state?
Etienne d’Arenberg: I don’t want to be a judge of the private sector being ‘not enough’, because whatever comes is already something and some individual donors are immensely generous. As I was mentioning before, there is an increasing need for approaches that achieve greater leverage and I believe that public-private partnership will play a greater role in addressing the need for systemic change.
The private sector can also act as a catalyst for change, raising awareness on specific issue and campaigning direct governmental support. I have been following the work of a UK charity which focuses on children food poverty: this is a very good example of an initially privately funded charity, who is actively campaigning for legislative change and working in close collaboration with government on food delivery. I am sure that we will see more on this in the future.

The Bol d’Or Mirabaud regatta on Lake Geneva
LUX: Does the next generation of wealth owners have different priorities for philanthropy?
Etienne d’Arenberg: Traditionally, family businesses or wealth owners have been quite active in their communities, and Mirabaud is no exception, both at the bank and at the partners’ level. Ask many Geneva-based NGOs, charities, cultural or sport institutions and they will tell you about its commitment.
I feel that the type of issues Generation Z cares about are a little bit different and I see this with my daughters. Their preoccupations are centred around inclusion, mental health, environment and racial equity. They will tell you bluntly that they are not prepared to work for a company that does not match their ethics or values, even if that means foregoing a number of lucrative jobs. To my view, this is quite representative of a generation that is much open to a new set of issues.
What is also changing is the active role they are ready to take. I think that the generation of philanthropists who will just sign a check is slowly over, and we will see a new generation of individuals who will want to take a much active role, starting earlier in life as volunteers, advocates or activists, and using a wider range of engagement tools.
As I said, Mirabaud has demonstrated a 200-year-old interest in the communities in which it operates and I sense that as a bank we are particularly interested in understanding this new generation, not only because they are our future clients and employees, but also because they are shaping the future we will be operating in, as a company.
Read more: Lamberto Frescobaldi on 1000 years of tradition and wine
LUX: Do Mirabaud’s philanthropic contributions focus on culture and the arts?
Etienne d’Arenberg: First and foremost, concerning contemporary art, in recent years we’ve been sponsors of FIAC in Paris among various other renowned institutions. We’ve also sponsored the Zurich Art weekend, which is, in a way, the pre-Art Basel event, in a more intimate setting. Even if we are an institution that celebrated its 200th birthday in 2019 (so we are 202 years old now) our motto is always “to be prepared for now”. As in, immediately at your service, to sponsor and to be interested in today’s world and that’s why we are interested in contemporary art. We know the value of looking into the past, and taking lessons into the future.
The second thing to remember is that culture is not something which always pertains to art. If you look at the enthusiasm of the public, art is not always the biggest thing, sports, for example, are part of the culture of a nation. We are sponsors of the largest inland regatta competition in the world, the Bol d’Or Mirabaud on Lake Geneva, and it’s a fascinating competition, because the lake has very particular wind conditions that are ever-changing, it is not a one-sided Caribbean type wind that comes constantly from one side and doesn’t change that often. Here again our motto “prepared for now” completely makes sense.
LUX: The concept of Europe is an important one for your family foundation. Why?
Etienne d’Arenberg: When we think about Europe, our family thinks of the continent which includes Switzerland and the United Kingdom, not only the European Union. The concept of Europe is indeed very important for our family, as it includes a set of value that are dear to our heart: human dignity, rule of law, equality and democracy to name a few. This sounds wonderful and noble, but the truth is that it is quite vague in practice.
What we have been trying to do with our family foundation is to revisit these values in the light of today’s challenges and explore new ways to shape our common future.
I am personally convinced that Europe has a key role to play in shaping the post-COVID recovery, and building a new social contract based on these long-lasting European values and at a very modest level, we are trying to be part of this conversation.
Etienne d’Arenberg is limited partner of family-owned Swiss private bank Mirabaud and is Head Wealth Management United Kingdom.
Find out more: arenbergfoundation.eu, mirabaud.com

A colourful neon installation by Jason Rhoades in the home of German art dealer David Zwirner
Art collector and author Tiqui Atencio is the founder and chair of the Tate Latin America Acquisition Committee and a trustee of the Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation amongst numerous other philanthropic arts and culture organisations. As part of our ongoing philanthropy series, she discusses her latest book, the importance of collecting art and her efforts to promote Latin American artists

Tiqui Atencio
LUX: How did you come up with your idea for your book For Art’s Sake?
Tiqui Atencio: The idea for my second book, For Art’s Sake was born whilst I was writing my first book, Could Have, Would Have, Should Have. For me, it was a natural progression. After visiting the homes of the collectors that I interviewed, I decided I wanted to write a book with photos about art dealers. I wanted to see how they lived in their homes with the artists they represent and collect. I wanted it to reflect their passions, motivations, pursuits, adventures, and personal choices.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: ‘Heroic commitment’ or ‘crazy silliness’ – how is collecting art different from buying art?
Tiqui Atencio: Buying art can be different from collecting if the intention of the person buying the work is different from buying to form a collection, or increase one. Motivations and objectives are very varied. Some are committed collectors that go the extra mile to get what they want, others are not as passionate or dedicated. I would never describe it as silliness or craziness; it’s more like a steadfast passion.

The cover of For Art’s Sake by Tiqui Atencio, published by Rizzoli New York
LUX: How do you gain the trust to access these private homes with the team?
Tiqui Atencio: Most of the dealers I approached and interviewed were either trusted friends or people I had met through the art world at different occasions over the years, sometimes having bought from them myself.
Read more: Lamberto Frescobaldi on 1000 years of tradition and wine
LUX: From your interviews, what essential principles guide an architect or designer in showcasing a collection?
Tiqui Atencio: I believe that a good designer or architect will take into consideration the taste of their client in art, their collecting patterns, and preferences in lifestyle and choices in home living.
LUX: Among the homes you have visited, do you have any personal favourites?
Tiqui Atencio: Every home and collection had a certain angle of attraction, and I can’t say I had a favourite one, but being originally Latin American I could have moved in Luisa Strina’s home in São Paulo with only a toothbrush.

Lucian Freud’s Annie, a painting of the artist’s eldest daughter from 1962, hangs above a sofa upholstered in William Morris “Acanthus” print in Iwan and Manuela Wirth’s home in the Scottish Highlands
LUX: How do you think your own approach to collecting has changed over the years?
Tiqui Atencio: At the beginning, when I was very young, I was buying what I liked without too much information. With time and experience, I buy with more caution and research, but still following my heart and instincts.
LUX: For Art’s Sake integrates with your other roles within art philanthropy, what are you most proud to have achieved with its publication?
Tiqui Atencio: I am very proud to inform the readers of my books about the sense of sharing, giving and philanthropic commitment to the art world that most collectors, through their collecting practices have given to humanity. Their sense of responsibility, their generosity and their role in promoting art and culture.
Read more: How women artists are reshaping art history
LUX: What inspired you to become Chair of the Tate Latin American Acquisition?
Tiqui Atencio: I was part of an effort to increase the holdings of Latin American Art for the Tate. The intention was to promote the art and artists from the region of the world where I was born. So, I came up with the idea of forming a committee who would be willing to support this initiative, and that is how the Latin American Committee for Tate came to life.

Platypus, 2009 by Amy Sillman in the home of British art dealer and collector Ivor Braka
LUX: Have you found that the pandemic has affected art buyers’ attitudes?
Tiqui Atencio: Yes, personally I am buying less. I am longing to go back to the fairs and auctions of the past to see and feel the emotions and excitement of falling for a work of art. I have bought online, but not often and I can’t say it’s the same experience.
LUX: Do you think the pandemic has affected fine artists’ creativity?
Tiqui Atencio: I believe the pandemic has affected us all in some way – positively and/or negatively. With time, it will be interesting to see what comes out of this challenging moment. I am a positive thinker and I do believe we will come out better than we think – same with artists!
LUX: What is your favourite period of art?
Tiqui Atencio: I confess it’s mid-century Latin American Art, but my taste is very eclectic and varied and in my collection, there are many periods and styles.
Find out more: tiquiatencio.com

Durjoy Rahman is an art patron and collector, and the founder of Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation
Art collector and patron Durjoy Rahman founded the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation in 2018 to promote South Asian art and artists to global audiences by hosting exhibitions, commissioning new works and facilitating cross-cultural residencies. As part of our ongoing philanthropy series, he discusses the business of art philanthropy and why artistic narratives play an essential role in documenting history
LUX: How does giving fit with your beliefs?
Durjoy Rahman: Giving has been engrained in me since childhood. My parents instilled the importance of money management by giving me an allowance from a very early age. I was always told to save, use and give from that amount. It’s something I teach my children. The gift of knowledge is often held in high esteem in Asian culture more so over monetary ones. Due to limited availability of wealth to majority of the people and the long history of colonialism, the patronage of the arts and culture was very scarce and I wanted to contribute in a meaningful way. I feel privileged to be able to promote artistic endeavours from southeast Asia.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Why were you compelled to collect art as opposed to another valuable asset type?
Durjoy Rahman: I started collecting by chance not by a scheduled plan. We received a beautiful painting as a wedding present from a prominent artist. I wanted a few more paintings for my walls, so I started to visit galleries to find things I liked. Then I started reading more about the artists whose works spoke to me. I collected pieces that were notable and told stories about their artistic journey. Most pieces were passion buys just because I loved them. The inherent value of art lies in the pleasure of acquiring it and holding on to it. If one goes in with the mindset of building assets, the fun of collecting evaporates in entirely. Of course, the collection is valuable not because of its market value but because many were done by artists who introduced new techniques in Bangladesh and played an integral part of our art history. Many works were destroyed due to lack of preservation so not many notable works remain.
LUX: What triggered your decision to advocate for South East Asian artists?
Durjoy Rahman: South Asia has a rich cultural heritage. Art, music, and dance are a part of our daily life, but because of the long history of colonialism, artistic patronage was scarce. After independence, more and more art institutes were established and art movements were started. Now, the world is becoming more connected and the traditional hubs of art in Europe are also encouraging more diversity. This has made the global art scene very interesting and not limited to only European schools. The South Asian art scene is becoming more established with the growing number of art events and institutions, but still the artists need a lot of support to be able to establish themselves internationally. Patronage is essential for art to thrive and survive. Our artists are very talented and I hope that the individual like myself can contribute to introducing these artists to an international audience.

Joydeb Roaja, The Right to Relief, 2020 – one of the artworks included in Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation’s 2020 online exhibition Future of Hope
LUX: Western narrative discourse about South East Asia is dominated by tragedy, conflict, schism, floods, famine, genocide. What is the relevance of art in crisis?
Durjoy Rahman: South Asia was under colonial domination for centuries. The postcolonial period has been plagued by border and religious conflicts. Conflict, famine, tragedy has happened in every country in the world; the Great Depression in the United States, Europe after World War I and II. Every country has experienced suffering but the Western narrative about our region was most remembered because of globally televised news that emerged in the 60s and 70s that established these stereotypes for South Asia. All crises always inspired the creative community. It’s their narrative that makes us understand human suffering better. Otherwise, it’s just historical information. The birth of Bangladesh in the 70s was followed by a famine. Many artists depicted horror with their artworks. I think these artworks depicted suffering for generations to come and understand what the country went through. Only humans can create beautiful things out of a painful experience. The narrative creates history.
Read more: Jewellery designer Tessa Packard on charity & creative thinking
LUX: Where will the voice of truth and art tell the history in these dark times in Myanmar?
Durjoy Rahman: It is said the history is often written by victors but it is little relevant now due to global access of information to everyone. Every narrative is available and it is up to reader to draw their own conclusions. Documentation and witnesses about Rohingya plight made the world change their views. The sufferings are established fact result from the autocratic activity by the ruling regime. The quarter that caused these past miseries have solidify their position with the new situation that recently unfolded in Myanmar.
Artworks and tapestries created by Rohingya women and children depicting the horrors they endured will always be a part of history; they have cast aside the “official” narrative .

Mong Mong Sho, Songs Of Covid 19, 2020 from the Future of Hope exhibition
LUX: Why did you headquarter DB Foundation in Dhaka and Berlin?
Durjoy Rahman: Berlin and Dhaka are both thriving art cities filled with many talented artists. DB Foundation aims to be a conduit for art and artists across Europe and South Asia. Berlin is an international city for art and design and a perfect place to build greater awareness for South Asian artists on the global stage while Dhaka remains DBF’s epic centre for activity.
LUX: Your focus is ‘to promote art from South East Asia and beyond in a critical, international art context.’ Which countries particularly?
Durjoy Rahman: Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
LUX: Are there examples from this rich art heritage you are excited to have introduced to the West?
Durjoy Rahman: Bengal has thousands of years of heritage in art and craft. Textiles were one of the wonders from this region and played a dominant role in our glorious past. Historically, the intricate weaving in Muslin fabric from Bengal received an appreciation from the West and also became a sign of superior craftsmanship in many European royal courts.
Through the DBF’s outreach program and artist residency program, we aim to show the world once again the skill and creativity of Bengal. I have the privilege of donating a work by Mithu Sen from West Bengal, India to the Kunstmuseum Wolfsburg, Germany. Her work is based on a collection of memorabilia that people normally collect as souvenirs. It was a great accomplishment to help bring Mithu’s work to the western audience according to the Museum press release the first work of a female contemporary artist collected by a major public institution in Germany.
Currently, we are working on a project that will tell the story of displaced elephants due to the Rohinga crisis where the artist used sustainable material like bamboo and quilt making skills to tell a story about this plight of humans and animals caused by conflict. The work will be displayed internationally with the support and initiative from DBF.
LUX: Your archive of artists, past and present is acclaimed and you mentor emerging artists. What was the game-changer for DB Foundation in a critical sense?
Durjoy Rahman: The real challenge for us has been to find a niche in the global art events and to make a meaningful contribution to the artist community. We adopted the model of a residency program centred around an idea or a burning issue. Artists from different parts of the world interpret the central theme. For two weeks the artists live and work together. For artists in southeast Asia, it’s a unique opportunity. For artists from Europe, this is also an experience to work with the brilliant artists from Asia and understand their perspective. So I would say our Majhi Art Residency program is a game-changer for DBF foundation which we have been hosting since 2019 and plan to continue for the next ten years.

Sujan Chowdhury, Wings of Hope, 2020 from the Future of Hope exhibition
LUX: How did the pandemic affect upcoming exhibitions, commissions and residencies?
Durjoy Rahman: We have ventured alternate art space to exhibit art on a limited scale while major public exhibition spaces were closed. We continued our International Art Residency in Berlin during Berlin Art Week 2020 despite pandemic and to maintain consistency of the continuation of our supported projects internationally. However, the pandemic has really brought forward the need to use technology in every aspect of our lives and the focus has shifted to connecting virtually. We too are focusing on remote initiatives and found the many ways one can connect to a greater audience. We still tried to engage artists and marginalised artisans during the pandemic while observing safety protocols. Last year, at the peak of the pandemic, many craftsmen and their families in Bangladesh were greatly affected due to the economic downturn and low tourism activity. We created an initiative to support traditional craftsmen and their families by offering practical and financial support so that they can continue the creative process.
Read more: Alia Al-Senussi on art as a catalyst for change
LUX: Circularity could be said to future-proof giving. How can business support art philanthropy at the level of helping people help themselves as opposed to funding them top down?
Durjoy Rahman: The business of art philanthropy has been historically top-down going back to how art and crafts were supported by royal and affluent patrons in the Europe, Americas and Asia. I think that to create a more sustainable and self-sufficient model, the public needs to get involved and be motivated. While I think that the top-down approach will always be a critical part of art philanthropy, businesses can create public demand by creating programs for the public (especially virtual events) meant to keep the public engaged and inspired. As long as this demand exists and businesses are meeting it, they will become partially self-sustained in funding channels.
LUX: 2020 was Covid-dominated, hopeless, until the point of vaccines’ licensing, as will be seen when lexicographers list the vocabulary we used most. What can art philanthropy offer in a wider sense to humankind?
Durjoy Rahman: The Covid pandemic has really focused the public on the importance of one’s mental health. Creativity, art, and culture are the ultimate mind healers, and art philanthropy supports that. Being a cultural foundation DBF were probably the first organisation in Bangladesh got involved with front line workers to equip them for better safety and serve people more confidently.
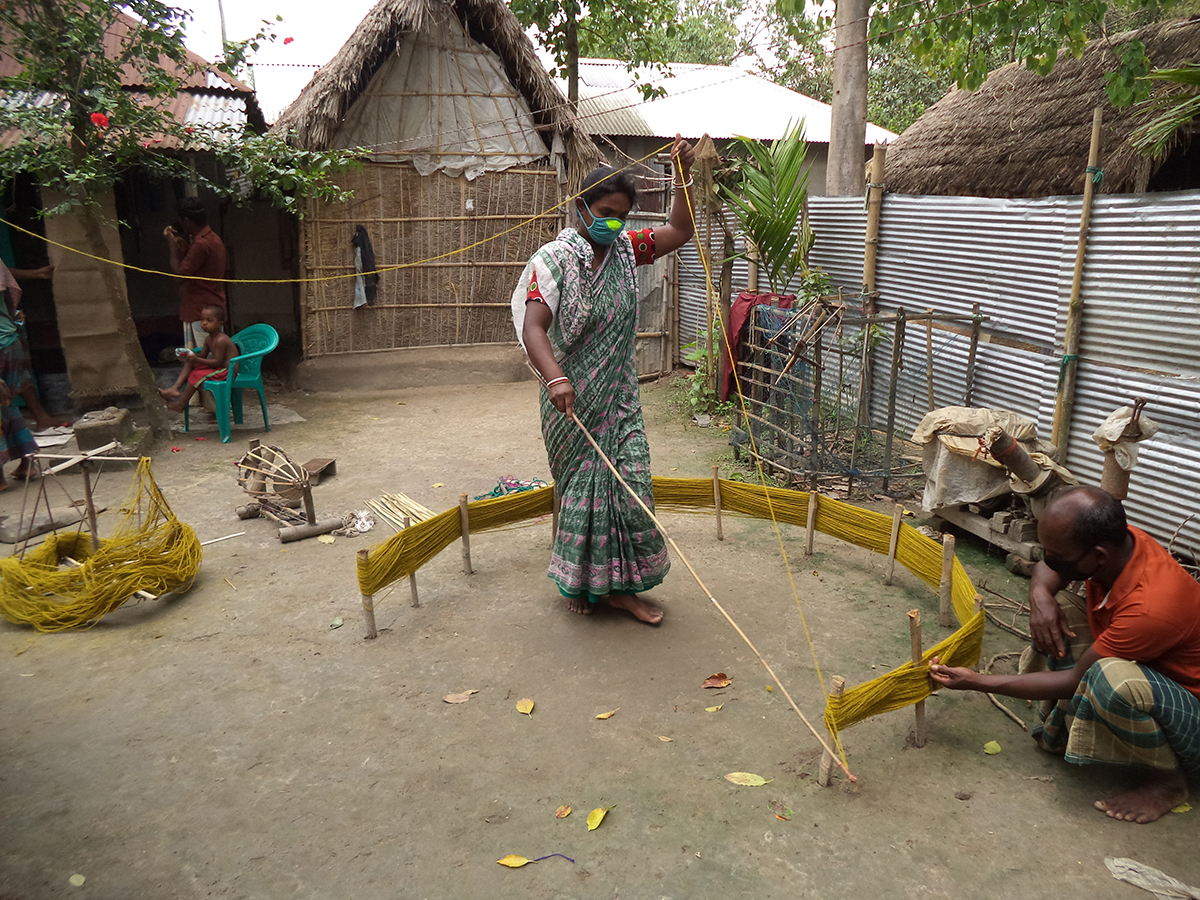


Here & above: Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation launched its philanthropic project “Bhumi” in 2020 to support rural creative communities in Bangladesh. Courtesy Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation and Gidree Bawlee Foundation of Art
LUX: Your passion to connect extends to activism through your support of satirists and the rights of minorities. What do you feel was particularly relevant to defend in 2020?
Durjoy Rahman: Migration, displacement, and supporting minorities. We focused our activities with minorities in 2020 through one of our major initiatives “Bhumi”, where we worked with artists and craftsmen from a marginalised ethnic group. We are currently working with Rohingya refugees and the environmental consequences of this mass migration. We are trying to build awareness among the international community about the plight of this ethnic group and its impact on the fragile hills of our border and the already dwindling elephant herd which inhabit that area.
LUX: Where has DB Foundation facilitated public discourse and created the climate for political change?
Durjoy Rahman: Diversity has been at the centre of the creative field, especially now. We have done several initiatives across Europe and Asia aimed towards actively facilitating our activity in the arts and culture from South Asia. Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation wants to bring representation to these artists, give them the recognition they deserve, and bring their voices into the art conversation, so they are heard. Our initiative “Future of Hope” has also highlighted a key word “hope” during the early break of pandemic. Now, “hope” has become a global slogan.
LUX: What one piece of advice should an art philanthropist share with the next generation?
Durjoy Rahman: Be generous when thinking of art and culture – a small contribution can make a significant impact on the art and artist.
Find out more: durjoybangladesh.org

Jewellery designer and philanthropist Tessa Packard
Tessa Packard is the founder of her eponymous fine jewellery brand, and a business mentor for several youth and education-focused charities. As part of our ongoing philanthropy series, she speaks to Samantha Welsh about charitable giving amongst younger generations, the influence of social media and why successful philanthropy requires creative thinking
LUX: How did you first get involved in philanthropy?
Tessa Packard: I grew up in a very philanthropically orientated family. Charity was a forward theme in our household, and because my parents were so passionate about it, my sister and I adopted an interest in the concept of ‘giving back’ at quite a young age.
It wasn’t until I was eighteen, however, that I really understood what charity work actually meant. At my father’s suggestion, I agreed to a three-month volunteer placement at the Amelia Trust Farm in Wales, which is a grassroots charity supporting youngsters who have largely been excluded from mainstream education at the hands of abuse, neglect or neurodevelopment disorders. It was a complete baptism of fire. Despite everything I had been taught by my parents about the ‘real world’, experiencing it first hand was somewhat different. True reality was infinitely more gritty, unfair, shocking, brutal and humbling all in one mouthful. I still consider this experience to be one of my most formative.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Who has been your greatest influence?
Tessa Packard: With regards to philanthropy, my father and my great-grandfather (who I never met, but was instrumental in shaping my own father’s beliefs in charitable giving).
LUX: What sector are you passionate about?
Tessa Packard: Most of my philanthropic involvement to date has revolved around the theme of education and systemic change. Education has always seemed to me to be a sensible place to invest my energy, whatever the end goal. Whether you are looking to eliminate polio or save the rainforest, all roads tend to lead back to education.


Here and above: In collaboration with Lyndsey Ingram Gallery, Tessa Packard and her team created a mural based on Frances Hodgson Burnett’s book The Secret Garden which was later installed in Honeypot House, a children’s charitable home in Hampshire
LUX: Do you think there are any parallels in being a creative and being a philanthropist?
Tessa Packard: Interesting question. I think that successful philanthropy requires creative thinking. It can be a challenge to communicate successfully with your audience, and more often than not, the answer to solving any human-socio-economic problem on a long-term, systemic level is complex. The philanthropist must be willing to take risks in order to bridge the void between sectors – a task that is far too frequently overlooked – and this requires out-of-the-box tactics and a fertile imagination. You have to believe that even the most impossible outcome is possible, and generally speaking creatives are quite good at doing that because their job is to always think about the ‘new’.
Read more: An interview with Brazilian artist Maxwell Alexandre
LUX: At what stage of someone’s life have you seen intervention make the most difference?
Tessa Packard: If you were to approach philanthropy like a business deal, then investing in people at an early age generally yields better results in the long term. In practice, however, it isn’t quite so simplistic. Creating systemic change in any sector requires all the wheels of progress to turn at the same time, and that means transforming everyone and everything connected to the supply chain in unison.

Tessa Packard’s crab earrings from her Secret Garden collection
LUX: What success story has made you particularly happy?
Tessa Packard: I’m extremely excited about the work of Emmanuel Akpan-Inwang, who is currently building a new generation of children care homes in the UK. The existing model is embarrassingly inadequate and I really think Emmanuel is about to revolutionise a very important sector.
LUX: How do generations Y/Z give compared with generations X and the Baby Boomers?
Tessa Packard: I am by no means an expert here, but Baby Boomers generally tend to have much more prescriptive attitudes to philanthropy. They might begin to think about ‘giving back’ only when they are comfortably installed in steady, well-paid jobs and / or with a little more time on their hands. Baby Boomers also like to be able to justify their philanthropic investments – if you look closely, most of them tend to donate to causes that they personally understand or have experience of. They also tend to be less hands on and more cheque book-forward.
Read more: How women artists are reshaping art history
Generation X philanthropists are a mix of the old and the new. Whilst they also see philanthropy as something to enjoy in their more settled or mature years, they are often less partisan or dogmatic in outlook, meaning the manner in which they look at philanthropy is often more creative than the Baby Boomers. This generation can be credited as the originators of a number of entrepreneurial social programmes, and although Generation X are more hands on, they are generally so in two specific ways. The first is in a visionary capacity, as the founder, trustee or leader of a charity or charitable programme; or physically, by raising money organising or taking part in fundraising challenges, such as marathon running or mountain climbing.
Generation Y or Z philanthropists are probably the most hands on of the groups to date. They tend to be the more likely of the three to actually volunteer or spend time with grassroots organisations. There is often a desire to have a direct, personal relationship with the charities or individuals they support, as this direct line to the charity is integral to the experience of authentic ‘giving’. Giving back, for them, needs to be itself an experience – handing over a cheque is not fulfilling enough. Generation Y / Z philanthropists also tend to be concerned with, or involved with, charities and organisations that deal with large, macro-level problems such as global deforestation, ocean plastics or refugees. Unlike the Baby Boomers, these themes are not chosen as a result of lived experience – they are a reflection of the concerns of the here and now.

‘Forest Glade’ earrings by Tessa Packard
LUX: What issues come up most frequently in conversations about giving that you are having with your network?
Tessa Packard: There are a large number of adults in their 20s and 30s who have the means and energy to fund or support grassroots charities across the globe, yet have no idea where to start or who to fund. They want to be authentically connected to these charities (they like the idea of working with smaller organisations as they can track the impact of their donations or expertise more easily), but also want to feel part of something bigger. Time and time again the question we ask ourselves is how to best connect these dots.
LUX: Does the impact of social media change how things are done or how well they are done?
Tessa Packard: In general, I think charitable organisations have a lot to learn when it comes to making the most of social media. It’s not surprising to be honest – I can barely keep up to speed with it myself when it comes to my own business, and imagine if you are a grassroots charity with limited funding and even less free time… I certainly think a few free branding or marketing tutorials by big agencies for small charities would be a helpful start. The exchange of knowledge and expertise is often one of the most valuable donations a larger organisation can make to those in the charity sector.
LUX: Social impact entrepreneurialism or outsourcing to a third party manager – how do you choose?
Tessa Packard: The best kind of philanthropy is the one that is considered, and encourages the philanthropist to keep giving. Whichever route you choose, I would always start with the same question: what do I want to fix, and what is preventing this problem being fixed now? From there you can do a deep dive to identify where you need to go in the sector to create systemic change, and how best to do it. Sometimes the answer is to create your own vehicle to combat change, and sometimes it is best to support an existing vehicle that knows the ropes and is ready to expand.
LUX: Can you offer some ideas to a teenager wanting to start on their lifetime journey of giving?
Tessa Packard: Do a three-month volunteer placement at a grassroots charity. You might question your sanity at points, but you’ll never regret it.
LUX: What is one thing they should not forget?
Tessa Packard: My great-grandfather used to say: ‘Don’t carve your name in dark and gloomy places; carve your name with pride for all the world to see.’ I think that’s a pretty important lesson: whatever you decide to do with your life, make sure it’s something that you are proud to be remembered by.
Find out more: tessapackard.com, @tessapackardlondon
Samantha Welsh is a contributing editor of LUX with a special focus on philanthropy.

Alexandre Mars is the Founder & CEO of non-profit foundation Epic and the Founder of Paris-based VC fund blisce/. Image courtesy of Epic
French entrepreneur, author and philanthropist Alexandre Mars founded nonprofit organisation Epic in 2014 to help change the lives of disadvantaged young people around the world through individual and corporate donors as well as partnerships with other social organisations. As part of our ongoing philanthropy series, he speaks to Samantha Welsh about the importance of encouraging people to give more often, building a strong team and putting in the hours to achieve success
LUX: When did you start your first business and what made you do it?
Alexandre Mars: I started my first business at 17 years old by organising concerts at my high school. While I didn’t have the natural ability to become a professional athlete or movie star, something about entrepreneurship resonated with me.
The goal was never just to make money. It was about what to do with that money – a means to an end. Growing up with a mother that instilled values of altruism and solidarity in me from a young age, I knew that I wanted to give myself the necessary resources to protect my loved ones and then help others in need around the world. This first business was a first step toward realising that mission. I earned enough money to buy my first computers and that’s how my career as a tech entrepreneur was born.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Why did you pivot from serial entrepreneur to successful philanthropist?
Alexandre Mars: I’d actually consider that it was more of a continuation than a pivot. As I mentioned before, it was always my goal to help those less fortunate. It just took me a bit longer than expected to generate the means of being able to do so on the scale I hoped.
When I was ready to create Epic, my foundation, I still came at it from a very entrepreneurial perspective. In fact, a close friend of mine asked me an essential question as I embarked on this new venture: ‘What’s your uniqueness?’ In other words, how could I help others in ways that someone else couldn’t. Entrepreneurship is what I know best, so I built Epic like my previous startups, methodically and always with market needs in mind.
Working with young people can make for the most measurable outcomes. We know empirically that intervening early on is the most effective way to change life trajectories. That’s why we’ve decided to specialise in helping children and young people aged 0 to 29 years old.
Disadvantaged youths can come from anywhere, whether it be halfway across the world or in our own neighbourhoods. While the specific issues may vary from physical safety and job prospects to education and healthcare access, the overarching injustice remains the same: no one should be denied the opportunity to live their life to its full potential just because of the circumstances of their birth.

Alexandre Mars in Mumbai. Image courtesy of Epic
LUX: Tell us about Epic.
Alexandre Mars: Epic is the culmination of deep market research into the philanthropic sector and the solution to three major obstacles to charitable giving: lack of knowledge (about who to give to), lack of trust (that the funds would be put to good use) and lack of time (to do the necessary research).
Our vision is a world in which every child and youth has access to safety, empowerment and equal opportunity. Our mission is to find, select, back and monitor high impact charitable organisations in order to catalyse their impact on underserved children and youth, and the systems affecting their lives. We are able to effectively fund them thanks to our donors who pool their resources together via our platform.
There are currently 26 organisations in the Epic portfolio worldwide, working on essential issues like access to healthcare, employment, education and physical safety. To date, we have raised $30 million.
What sets Epic apart is the robustness of our methodology that promotes transparency and accountability. From the outset, Epic has had a rigorous selection process to ensure trust and confidence. We curate a portfolio of high-impact, mid-size organisations addressing the complexity of issues affecting children and youth in a select number of countries, through a thorough and cutting-edge sourcing, vetting and monitoring process.
Another important factor is timing. We intervene at a stage in these organisations’ development when our support is the most transformative, allowing them to scale and have an even greater impact on children and youth.
Read more: Alia Al-Senussi on art as a catalyst for change
LUX: You are the enfant terrible disrupting traditional philanthropy, yet you build great teams. How do you go about that?
Alexandre Mars: Whether at Epic or any other startup I’ve founded, an undeniable key to success has been building the right team. And it starts with humility: you need to evaluate your strengths as well as your weaknesses, and hire for those needs.
For example, I built my career in the tech space, but I don’t know how to code. I surrounded myself with talented, passionate people. But it’s not enough to hire them. You need to have trust and give them autonomy to do their best work. It sounds like a simple formula, but it really works.
LUX: What issues around methodology come up most frequently in conversations between your NGOs?
Alexandre Mars: One of the interesting things that comes up often is how we measure success. We have been working hand in hand with our portfolio organisations to define a specific set of KPIs that they report on and that are tailored to their issues areas and strategy, for example: academic success rates or job placements. It’s a very interesting data-driven process that enables Epic to understand organisations’ performance in the context of their own success metrics as well as in the context of our centrally defined framework.
LUX: You have ‘skin in the game’ and pay all operating administration costs yourself – what are your expectations of companies and individuals who give and outsource to Epic?
Alexandre Mars: Two words: involvement and trust. We make sure that donors are very engaged throughout the giving process and that they’re able to follow their impact. Thanks to our thorough monitoring that brings accountability, our donors are more likely to continue giving. It’s a virtuous circle. This relationship of mutual confidence keeps our donors coming back year after year.
I also ask our donors to move away from certain outdated views on philanthropy, and to understand that impact and success cannot always be boiled down into quantitative terms like the number of children served per euro spent. Our organisations are dealing with a complex set of issues, and change takes time, as well as precise methods of measuring and understanding those outcomes. But you are right, I do have a lot of skin in the game so that 100% of all donations are sure to go directly toward changing lives.

Image courtesy of Broadsoft
LUX: How has your approach guided your selection of partners in diverse regions and cultures?
Alexandre Mars: Our methodology takes into account 45 criteria in three categories: governance, impact and operations. It was developed by our team that draws on experience from both the non-profit and private sectors. For example, we’ve integrated best practices from the venture capital sector and evaluate organisations as if we were investing in a tech startup, looking at factors like growth potential, the quality of the leadership and most importantly, the organisation’s ability to create changes in the lives of the children and young people they serve.
The principles of our selection process drive at an understanding of how an organisation fares against an objective set of criteria. By looking through the lens of each organisation’s internal and external contexts, we are able to look at a worldwide set of organisations operating on vastly different issues and across varying social, financial, operational contexts. Interestingly, we do observe a certain universality, to an extent, in these organisations’ frameworks.
LUX: What corporate structures are most open to outsourcing their philanthropy to optimise returns?
Alexandre Mars: We work with corporates, but also foundations and individuals. One of the most frequent reasons they choose Epic is because we address three major obstacles in charitable giving: lack of trust, time, and resources. This is especially true when it comes to funding organisations that are in other countries than where the donor is located. We are a sort of one-stop-shop that they can trust.
Furthermore, I believe that people go through Epic to support children and youth because they have confidence in our model that focuses on strategic philanthropy. We look for impact and have developed a cutting-edge selection and monitoring methodology to ensure a certain return on investment, to borrow a term from the business world. It’s quite innovative, which explains why Harvard University did a case study on the Epic model in 2019.
Read more: Michelin-starred high altitude dining in Andermatt
LUX: To the average person, charities want to get more people to give, whereas you want people to give more often. Why?
Alexandre Mars: Our experience has shown that charitable organisations benefit from having a stable source of funding, rather than volatile ups and downs throughout the year. It allows them to more effectively plan and allocate resources to those they serve. That’s why our model is centred on multi-year unrestricted funding, giving organisations the stability and autonomy to do what they do best. We encourage companies and individuals to make giving a habitual action and embed the social good in a way that fits seamlessly with their personal situation or business model.
The form this solidarity takes will vary from case to case. For example, we’ve worked with Société Générale on a simple yet innovative solution that allows the bank’s corporate clients to round-up foreign exchange transactions and donate to Epic. And for entrepreneurs, we created the Epic Pledge whereby they commit to donating a percentage from the future sale of their company.
You are mission-driven, so how do you control social media to deliver success?
LUX: How does blisce/ fit into your current vision?
Alexandre Mars: At my growth stage venture capital fund, blisce/, we support mission-driven entrepreneurs to build global consumer technology companies like Spotify, Pinterest, Headspace and Too Good To Go. So we’re approaching social impact from another angle, but it’s absolutely core to our collective vision.
Finance can be a powerful tool and, if yielded responsibly, can be a force for good. That’s why we’re committed to working with our portfolio companies to improve their (and our own) environmental, social and corporate governance measures. For example, our term sheet includes two non-negotiable clauses for ventures: an agreement to carry out an ongoing ESG evaluation every 12-18 months, as well as a commitment to interview at least one diverse profile for every open senior leadership position. Our team has committed to donating 20% of its carried interest revenues to Epic, so it’s really a virtuous circle between my investment and philanthropic activities.
As a testament to these engagements, we’re very proud that blisce/ recently became the first B Corp certified growth stage VC fund in the E.U.
LUX: How has this vision developed and what projects are you looking forward to over the medium term?
Alexandre Mars: It is my view that solidarity and sharing are going to become increasingly essential, and that we can no longer rely solely on public support if we are to address the challenges we face such as rising inequality, climate change, lack of diversity, gender inequality. We need the participation of the private sector and an engaged citizenry as well.
In the near term, we will be doubling down on our strategies at Epic and at blisce/ to identify and support exceptional social organisations and mission-driven companies that positively contribute to our communities and planet. I’m thrilled by all of the determined social entrepreneurs I meet on a daily basis, and look forward to announcing those that we’ll be backing soon.
LUX: Has Covid accelerated how you do things?
Alexandre Mars: In my opinion, Covid has accelerated a trend that has been building for the past several years. I’m old enough to remember how different the world was just 20 years ago. People viewed success differently: it was about the number of zeros in your bank account, about having a corner office and a company car. Today that’s all changed, especially with the arrival of the millennials and Gen Z. Today, we know that real fulfilment and purpose comes when you put that material success toward realising your mission, whatever it may be.
Covid has only reinforced this evolution, as it has given many of us time to pause and reflect while also exposing the ever-widening rifts in our societies. So in terms of how it’s changed things for us at Epic and blisce/, I can’t recall a time when we’ve seen such an outpouring of support from across the board, or so many entrepreneurs for whom combining purpose and performance is an automatic must-have. It gives me reason to believe in the work we’ve been doing and to be optimistic about the future.

Image by T.G. Herrington
LUX: What lesson did you learn with a start-up as a teenager that you will share with your own kids?
Alexandre Mars: Entrepreneurship, including my first venture, has taught me so many lessons over the years. That’s part of the reason I wanted to write my recent book on the subject (it’s out in French now under the title OSE ! Tout le monde peut devenir entrepreneur, and the English translation is coming soon).
If I had to pick just one piece of advice, I’d emphasise the importance and necessity of hard work. Luck and natural ability only account for a small fraction of success. What will set you apart is outworking the competition, which will inevitably require sacrificing other activities such as going to the movies, coffee breaks, and weekends with friends. You won’t be able to do everything and work hard at the same time. That’s the harsh reality of it.
In my book I talk about Canadian journalist Malcolm Gladwell and the 10,000 hour theory he popularised. He explains how, in any discipline, 10,000 hours of practice is required to achieve the level of world-class mastery. This theory is based on the experience of three psychologists in observing violin students at the prestigious Berlin Academy of Music. The results were surprising: future international maestros each had reached 10,000 hours of practice; good violinists reached 8,000 hours, and future music teachers did not exceed 4,000 hours.
To take another example: when the Beatles were successful in 1964, supposedly coming out of nowhere and taking the world by storm, in reality they had exceeded 12,000 hours of rehearsals and concerts. They didn’t just appear overnight.
And as a last piece of related advice, I always remind my children about the importance of having a mission. In the end, having a sense of purpose is what brings true satisfaction, plus it will sustain you on your arduous but rewarding entrepreneurial journey. When you wake up in the morning with something bigger than yourself on your mind, you’ll find the motivation you need to succeed.
Find out more: epic.foundation
Samantha Welsh is a contributing editor of LUX with a special focus on philanthropy.

Alia Al-Senussi is an academic and global arts patron. Photograph by Anton Corbijn
Alia Al-Senussi grew up between Egypt, South Dakota, and Minnesota, and is now based in London where she works as a cultural strategist with a special focus on young patronage and culture within the Middle East. She is the Art Basel Representative for the UK and MENA, a senior advisor to the Ministry of Culture of Saudi Arabia and a guest lecturer at institutions such as Brown University and Sotheby’s Institute. Here, Al-Senussi discusses her philanthropic efforts, work in Saudi Arabia and belief in art as a catalyst for social change
LUX: What forms the basis of your passion for art and culture? When did this interest begin?
Alia Al-Senussi: I am passionate about contemporary art and supporting living artists. I focus mostly on Middle Eastern art and artists as this is close to my heart and my heritage. I very much hope I see the day when more artists of Middle Eastern origin are integrated in to the wider art world, and society looks past myopic views of political systems and embraces people, and the change they are trying to bring.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
The first time I really understood what contemporary meant in the context of art was visiting Tate Modern in January 2004, and experiencing the life-changing work by Olafur Eliasson The Weather Project. It felt like an overwhelming moment: to gaze into this vast space and to see people treating a museum like a social space rather than a temple to worship art. In this way, art could change the way we see and the way we act—I became a believer.
Art provides an alternative discourse by which we can solve problems, promote heritage and instil a sense of national pride. My hope has been that by educating artists and patrons we can then educate the wider population on the benefits that art can bring to their everyday lives, not only beautifying the communities where we live, but also promoting more creative ways to solve problems, bridge differences and build community sentiment and strength.

H.R.H Alia, 2016, Hassan Hajjaj. Courtesy the artist
LUX: What is it about certain contemporary artists such as Manal Al Dowayan that so inspire you to champion them?
Alia Al-Senussi: In Saudi artists and patrons I see this deep commitment to art as a cornerstone of an evolving society. I am proud to be a part of this fascinating art world, and to help introduce more and more of my friends to Saudi culture, and to artists like Manal AlDowayan, Dana Awartani and Maha Malluh. These pioneers, of all ages, have been the voice of their society, as well as patriot activists. They are change-makers as well as cheerleaders, leading us all in to a brave new world.
Phil Tinari, a dear friend, and brilliant cultural leader, visited Saudi Arabia at my invitation in September 2019, and immediately understood what was unfolding. He has since agreed to work with me and our team at the Ministry of Culture, as the curator for the inaugural Ad-Diriyah Biennale. Collaborating with Phil has been a sustaining (and guiding) light in this year of uncertainty amidst Covid-19. Phil sent me this message the night he arrived to Riyadh, illustrating just how quickly he grasped the changes afoot – it is a quote from Václav Havel’s 1994 speech The Need for Transcendence in the Post-Modern World:
“Today, this state of mind or of the human world is called postmodernism. For me, a symbol of that state is a Bedouin mounted on a camel and clad in traditional robes under which he is wearing jeans, with a transistor radio in his hands and an ad for Coca-Cola on the camel’s back. I am not ridiculing this, nor am I shedding an intellectual tear over the commercial expansion of the West that destroys alien cultures. I see it rather as a typical expression of this multicultural era, a signal that an amalgamation of cultures is taking place. I see it as proof that something is happening, something is being born, that we are in a phase when one age is succeeding another, when everything is possible. Yes, everything is possible, because our civilisation does not have its own unified style, its own spirit, it’s own aesthetic.”

Al-Senussi with friends at Roden Crater. Photo courtesy Alia Al-Senussi.
LUX: The world is watching the next generation of Saudis and there is an optimistic outlook for women’s voices to be heard – how have you found your passion for politics, power and patronage is received among educated women of influence in Saudi?
Alia Al-Senussi: My work in Saudi Arabia has been multifaceted, as I have been part of the moment when this cultural community came together and continued to evolve. I was lucky to have been introduced to Saudi through family, and then friends, and to have been there at the first moments of a cultural reawakening almost two decades ago, helping to make connections amongst members of the community within and outside of the Kingdom. Women were then, and still are, at the forefront of culture and are change-makers at every level.
Read more: Life coach Simon Hodges on how to thrive in uncertainty
The idea that culture can change a community was instilled in me throughout my life, but never more so than through my work with Art Basel. I have been able to translate this to so many parts of my personal and professional lives. My colleagues at Art Basel and in Saudi embrace the belief that culture has power; that it is at the nexus of change and positive evolution.
LUX: You are renowned not only for your intellect, but also for your drive. How much of your time does chairing or founding patron groups take up?
Alia Al-Senussi: I actually think I fried brain cells rather than grew them getting my PhD! It certainly was an intellectual exercise, and one that made me realise how important it is to continuously exercise one’s mind, as well as emotions. My mother instilled in me a sense of honesty, integrity and work ethic. She taught me that one must not rest on history or title, but one’s own value and contributions to society. My maternal grandfather often discussed the value of “being a productive member of society.” I have taken these values to heart and strive to make a contribution, big or small, in any way I can through the work I do.
Most of my personal and professional time is taken up with activities in art and culture. I am fortunate that many of my friends are also intimately involved in the art world so I can share these fantastic and special experiences with them. It makes it a lot easier to keep busy with work when you do it with people you love and admire!

Al-Senussi at Mada’in Salih, an archaeological site located in the area of AlUla within Al Madinah Region in the Hejaz, Saudi Arabia. Photo courtesy Alia Al-Senussi.
LUX: What exactly is your role as Chair of the Tate Young Patrons, and how do you ensure you get optimum results?
Alia Al-Senussi: I served as Chair of the Tate Young Patrons for 5 years, and now sit on the Director- and Board- appointed Tate Modern Advisory Council as well as being a founding member of the Art Now Supporters Circle (Tate Britain). The Tate holds a very special place in my heart. It was one of the first institutions I got involved with in London, through the Young Patrons. Then the Middle East and North African Acquisitions Committee was launching and I was one of the first people on board. One thing led to another and I was asked to be a Young Patrons Ambassador, and also to represent the Young Patrons on the advisory board of the Tate. I feel like the Tate is family and also that I have a responsibility to help it evolve and grow, not just in London, but in the Middle East also, and in terms of its role in society, particularly at this fractious time.
LUX: Can you tell us a little about your work with Delfina Foundation?
Alia Al-Senussi: ‘A rising tide lifts all boats’ – that is my motto, and one that I see embodied in the work of Aaron Cezar in his role as Director of Delfina Foundation. Aaron, and the foundation, are unlike any other. Delfina is a home, not just at its physical space in London, but also throughout the world whenever you come across residents (artists, curators and collectors). Delfina Foundation is a safe haven, and Aaron is the ultimate angel, providing solace and shepherding our entire community to embrace new concepts while breaking down the intellectual barriers that keep us apart.
Read more: Juanita Ingram on empowering women in the workplace
LUX: What are your proudest achievements?
Alia Al-Senussi: I discovered my passion for art and the art world by chance. Upon graduating with my MsC from LSE, some friends recommended that I meet Michael Hue-Williams to work on a project he had created in Siwa, Egypt, with the world-renowned artists Ilya and Emilia Kabakov.
I had never worked in the arts, but as I had an interest for non-governmental organisations working in the Middle East, I thought this would be an interesting first job for me. Also, the fact that Siwa bordered Libya was particularly poignant.
In the end, it was fate and I fell in love with art, the art world and everything about it. I saw it as being a perfect way for me to balance my interest in political science, international relations and the history of the Middle East with a “softer” way of approaching the difficult issues facing the region.
My entire life is shaped by this first art world experience, and by the belief that an international cosmopolitan world is a better one. Every time I make an introduction, conceive a project or bring people somewhere new, I feel a deep sense of pride – the world shrinks that tiny bit more and we learn more about our neighbours and about humanity.
LUX: How will COVID-19 affect what do you do?
Alia Al-Senussi: I hope, and fervently believe, that people will realise the importance of culture in this new and renewed world. Of course things are moving online in the short term, and I believe that this means we can share our shows and messages with a wider audience and hopefully make them want to come see things in real life. Art Basel provided me, and so many, with an online community, but this was not a substitute for the thrill of interacting with people, swapping stories, having fun and experiences in Hong Kong, Miami and Basel.

Al-Senussi at The Lightning Field.
LUX: We know you have been passionately engaged with the US election process and we would love you to share with us a few ways you think the result will benefit the work of your partners over the next four years.
Alia Al-Senussi: I have decided to embrace beauty. I also have committed myself to art and artists that reflect my values, and who work to effect positive change in their worlds, and in mine.
A large part of my Libyan identity was actually shaped by my mother, an American of Scandinavian-German origin who grew up in Worthington, Minnesota. My mother studied International History for her Bachelor’s degree in Minnesota. She fell in love with Middle Eastern culture so upon graduating decided to pursue a Master’s at the American University of Cairo. It was in Cairo that she met my father.
My American identity is inextricably linked to my Libyan heritage, to my belief in an international cosmopolitan world, and to the life I have built for myself in London, the Middle East and Asia. Everything I held dear was shattered in 2016, by others’ small-minded desire to isolate ourselves from the “other” in the US and the UK. I couldn’t imagine that was the world I was living in. How could my community reject the essence of me in such a way? My friends bundled me up, helped me to heal and gave me my marching orders (literally!). Going to the Women’s March in Washington was a therapeutic moment, and now four years later I see the change again, and I am hopeful we can rebuild and evolve by making a world that is more equitable and by embracing the ideals that I hold dear.
LUX: Any other advice for our readers who might be considering going into art philanthropy?
Alia Al-Senussi: Artists, collectors and institutions are becoming more aware, and truly taking ownership of their ability to be change-makers. I applaud institutions like the Tate that are working to accurately reflect our world in their galleries—a global cosmopolitan world.
Fill yourself with passion, surround yourself with people you admire and embrace the idea of what is right, rejecting what is wrong. As mentioned before, a rising tide lifts all boats, so make sure your community rises with you.
Follow Ali Al-Senussi on LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/alia-al-senussi

Keith Breslauer congratulating a wounded British veteran during The Veteran Games
Keith Breslauer is the founder and Managing Director of private equity company Patron Capital, and a trustee and donor to numerous charities including the Royal Marines Charity and the Prince’s Teaching Institute. As part of our ongoing philanthropy series, he speaks to LUX about building bridges between charities and the corporate world, his work with disabled veterans and how philanthropy differs in the US and the UK

Keith Breslauer
LUX: What inspired your interest in philanthropy?
Keith Breslauer: I was brought up to believe that giving what you can is the biggest triumph in life. I took this belief and inspiration from my parents and religion into my career and to help create a platform to give what I can to those who need it, enable others to do the same and make a lasting difference.
LUX: Why did you decide to support the Royal Marines?
Keith Breslauer: I’m from the US where veterans are celebrated on both a public and personal level. However, when I moved to the UK twenty seven years ago, I was disappointed to learn that British war veterans often receive marginal public support. That is why I started ventures that manifested as fundraising for all veterans with a focus on volunteering for the Royal Marines Charity (RMA-TRMC).
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: What led you to create Patron Capital?
Keith Breslauer: Lehman Brothers allowed me to come to Europe and work on distressed assets, which was a niche sector of real estate at the time. I loved being in the UK – everyone said ‘Breslauer is a New Yorker, he’ll never stay’ – but I love that on a typical Friday night (pre-Covid) I have five-plus cultures and languages at my table. So, when Lehman Brothers asked me to go back to New York, I decided to stay and took the leap to start our business with a great team of partners and the rest is history.

Keith with Royal Marines and a team from the Royal Navy on a riverbank during their re-creation of Operation Frankton, which was sponsored by Patron
LUX: What are the principle benefits of a business involving itself in charity?
Keith Breslauer: We’ve worked hard for Patron Capital to be positioned as a leader of successful commercial business while also available for charitable good – rather than just donating funds. As a team we’ve built the business to be a bridge between charities like the Royal Marines and the corporate world. We can offer them everything from business plans, employment advice, office space, secretarial services, to our business contacts and expertise.
We also utilise our business to give a voice to the extraordinary people we raise money for. In 2017, we established The Greatness Lectures, a forum to inspire, educate and create opportunities through Patron’s extensive business network. Through education, The Greatness Lectures can involve every member of the audience and ensure everyone has a part to play in the Patron value of ‘creating a positive change whenever and wherever required’.
LUX: How does philanthropy differ in the US and the UK?
Keith Breslauer: The key differences between the US and the UK lie in the construct of giving, the perception of philanthropy and the landscape of donors. In the US, it is not just tax-deductible, but also a status symbol for many and there are significant givers across the spectrum. However, while in the UK, it is a tax credit and the dynamic of it being a status symbol is far less prevalent – instead, there is much more grassroots support where individuals across the country might not give a huge amount, but they donate what they can on a regular basis.
Read more: Katrina Aleksa Ryemill on helping women in the arts
LUX: Is there anyone in particular who inspires you philanthropically?
Keith Breslauer: There are so many people, but I will always be inspired by Harvey Krueger, an early boss of mine at Lehman Brothers who is known for being the first banker to bring Israel, really, to the international capital markets. He embodied what it means to me to give as he gave a lot of his time and limited resources but remained focused on the primary objective of how to help those who needed it.
LUX: What feels more rewarding: enabling people to get involved in charity, or simply giving?
Keith Breslauer: I am a big believer in doing more than just giving. If you don’t immerse yourself in the act of charity, then you can only help on a superficial level and you will never understand the satisfaction of knowing what a difference you’ve made. To understand what a charity stands for – getting under the skin of why you’re trying to raise money – you need to endure some sort of hardship to help. You need to get know the people you are helping. At Patron, we encourage employees to take part in fundraising events that help people push their own preconceived limits. For example, in 2019, Patron sponsored Rock2Recovery’s flagship fundraising event – a sponsored climb of Ben Nevis in Scotland – and we were really proud to see an all-female team from Patron join the 140 climbers taking part. In total circa £26,000 was raised for the charity.


Keith (top) with his youngest daughter Samantha on Mont Blanc Massif, and at the summit of Pointe Percée
LUX: How has your religious background influenced your charitable work?
Keith Breslauer: My religious background is incredibly important to my approach to charity and giving – it’s the core of it really. For a start, a principle of the Jewish faith is to give away about 10% of what you earn, and I adhere to this with my time and money. Next, there is the concept of ‘tikkun olam’ which comes from Mishnah, a body of classical rabbinic teachings, and is defined by acts of kindness performed to perfect or repair the world. This is key to how I was raised and how I try to live my life; if you have the ability to make a difference then you should whenever and wherever you can.
LUX: What is the biggest lesson you have learnt in your lifetime?
Keith Breslauer: I have learned so much throughout my life and I am still learning, but one of the biggest lessons that has stayed with me comes from the late Lord Rabbi Sacks, and that is about working hard and seeing the possible where others see the improbable. We can achieve more than we think we can if we try.
Read more: Entrepreneur Wendy Yu on creativity & charity
LUX: How has Covid-19 affected your philanthropic efforts?
Keith Breslauer: In the first few months of lockdown, it was really difficult for everyone as no one knew what the future would hold – everyone suffered. We tried to stick to a routine at Patron and this is why we took the Greatness Lectures, a forum to educate and inspire the Patron team, our friends, and partners, online. This included “Reports from the COVID-19 Frontline” with Dr Seb Vandermolen and Nurse Laura Pinches, who had both been working on adult COVID-19 wards at St Thomas’ and St Bartholomew’s hospitals respectively.
Alongside our efforts to establish The Women In Safe Homes Fund, believed to be the world’s first gender lens property impact investment fund being launched as a solution to the lack of affordable, safe and secure homes across the UK for women and their children, who are experiencing homelessness or who are at risk, I’ve made a personal commitment of £1 million to demonstrate how important this fund really is. We’ve also organised a Greatness Lecture with Chloe McCardel and Jane Jutsum to share different perspectives on domestic violence and providing help and inspiration to its survivors. Chloe is an elite athlete whose love of marathon swimming helped her recover from post-traumatic stress disorder, and she holds the world record for the longest non-stop ocean swim – 124km. Jane Jutsum is Director of Business Development at Solace, a charity that exists to end the harm done through violence against women and girls.
All of our charities have suffered this year; the Royal Marines Charity (RMA-TRMC) alone needs £1.5 million of vital funds. We’re always looking for ways of raising money and connecting those who wish to help with any one of our 30 charities.
LUX: What has been the most surprising discovery in your philanthropic activities?
Keith Breslauer: The most surprising thing for me to discover is the significant impact we can have through the multiplier effect of dedicating both time and money, rather than just one or the other. Our initiatives focus on funding projects and events with the potential to harness a multiplier effect either driving further donations, raising awareness, or helping deserving individuals who have suffered injury, illness or disadvantage achieve personal goals and build self-esteem.

Keith with the in-house climbing wall at Patron Capital
LUX: What are your passions outside of business?
Keith Breslauer: I’m obsessed with mountain sports, especially skiing, and climbing. I even had a climbing wall fitted in our office. When I first moved to the UK, I was introduced to European mountaineering through a trip to Mont Blanc. My wife told me I was only allowed one trip, but I’ve been addicted ever since and have now climbed, notably; Old Man of Hoy, Denali and various summits and routes in the Mont Blanc Massif. I also strive to incorporate social impact into everything and anything I do. And, last but not least, my family – they are everything to me.
LUX: How have you combined those interests with charity work?
Keith Breslauer: My personal philosophy on life and in business is to lead by example. Through working with the Royal Marines Charity (RMA-TRMC), I’ve been able to share this approach undertake challenges with some extraordinary individuals that also raise awareness and funds for those in need. For example, in 2017, we sponsored The Royal Marines’ recreation of Operation Frankton, an 85-mile paddle and a 100-mile run described as the most courageous raid of World War II. This commemorated the 75th anniversary of the legendary feat which was immortalised in the 1955 film ‘The Cockleshell Heroes’ and raised money and awareness for the charity. I joined the team as we retraced the route of 10 commandos who paddled up the Gironde estuary in December 1942 to attack enemy German ships moored at the port of Bordeaux in occupied France, before making the 100-mile journey on foot to rendezvous with the French Resistance in Ruffec. Only two men survived to tell the tale – the others succumbed to hypothermia or were executed by the Germans – but the operation’s significance reportedly led Winston Churchill to say he believed the raid could have shortened the war by six months. For me, our re-enactment was a once-in-a-lifetime experience.
LUX: Should we expect to hear of any upcoming projects?
Keith Breslauer: I’m looking forward to working with disabled veterans as they take on new challenges, including in the near future with a disabled veteran Mark Bower. More generally, we have a range of both adventure projects and practical projects with different charities to drive reach and penetration where charities have lost traditional channels of outreach and fundraising due to the pandemic.
Find out more: patroncapital.com

Wendy Yu on her trip to Rwanda with Women For Women International charity
Fashion entrepreneur Wendy Yu is the founder and CEO of Yu Holdings, an international ambassador for the French Fédération de la Haute Couture et de la Mode, and a supporter of The Metropolitan Museum of Arts, BAFTA and numerous other charitable foundations. As part of our ongoing philanthropy series, LUX speaks to Yu about her long-standing commitment to the arts, female empowerment and children’s education
LUX: As well as supporting the Costume Institute at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, when did you first have the idea to set up a China program and why?
Wendy Yu: Having spent many years residing in London, travelling for business and working with international organisations, upon returning to Shanghai to live a few years ago, I felt an immediate sense of responsibility to my country in terms of helping to shape the creative and cultural space and provide a bridge between East and West.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
This is why conversations about China with The Met were initiated. Having been fortunate enough to spend some time with Andrew Bolton, I wanted to give the design community in China the opportunity to meet him and understand more about his work at The Costume Institute. The Met has such a big following in China, but mostly because of the Met Gala, and yet there is so much more to know and learn.
I invited Andrew to China in 2017, where he and Angelica Cheung co-hosted an event to meet emerging Chinese designers. I’m passionate about providing a platform for creative and cultural exchange.

Wendy Yu at The Met Gala
LUX: Have you always been passionate about costume?
Wendy Yu: I’ve always been passionate about fashion as part of the wider creative industry. Fashion and costume are so intrinsically linked to a sense of identity, emotion, stories, a moment in time and culture. It’s also provides us with an opportunity to dream, and further nowadays, share our voice as our wardrobe is beginning to say something about our values.
LUX: Is there anyone the philanthropy world who particularly inspires you?
Wendy Yu: Amal Clooney, and Queen Rania.
LUX: What exactly does the Women For Women International charity do, and how do you ensure your support is optimal?
Wendy Yu: Supporting women is one of my priorities and I have loved to support Women For Women International as they are a wonderful charity dedicated to helping women, who are living in areas of conflict and are often marginalised. I travelled with Women For Women to Rwanda a few years ago to meet some of these women, and it was one of the most enlightening and heartfelt experiences of my life. It was incredible to see how these women had benefited from Women For Women’s training program, which provides them with the necessary skills to become financially independent and support their families.

Wendy with some of the women helped by the Women For Women International charity in Rwanda
LUX: Do you think that the role of private philanthropy is becoming more important, with increasing limitations on government funding?
Wendy Yu: Absolutely, particularly for the creative industry and especially at the moment, where much of government funding is having to be redirected due towards the pandemic. With philanthropy comes a true personal passion and commitment, often deriving from a special relationship that goes beyond financial support and can be truly game-changing for the people and organisations on the receiving end.
Read more: Why The Alpina Gstaad is top of our travel wish list
LUX: In terms of your support for the educational prospects of China’s children, is there anything that concerns you about the path ahead for Teach for China, and what made you decide to launch an art fund?
Wendy Yu: I believe in the importance of creativity in enhancing our lives and particularly that of children. Teach For China does an incredible job at providing education and facilities for children living in rural areas of China. What I felt I could bring to the table as one of their committee members was to provide the means for them to integrate art in their program, a subject that can often get sidelined when there is a lack of funding. Together we established an art fund, which would see the funding of art teachers and the necessary materials for schools in rural areas.

Wendy working in one of Teach For China’s classrooms
LUX: Do you enjoy collaborating with Teach for China?
Wendy Yu: Very much so. Working with Teach For China has given me the opportunity to meet and spend time with the children who are benefiting from the art fund, as well as integrate their artwork in some of my own projects, including a clutch for a collaboration I did with Olympia Le-Tan where we used an artwork created by one of the students.
LUX: How will COVID-19 affect what do you do?
Wendy Yu: Covid hasn’t impacted my interests and what kind of initiatives I am directing my energy to; the causes I am committed to continue to be the arts, female empowerment and children’s education. That said not being able to travel means that at the moment any activity is by default mostly China centric.
Read more: Montegrappa’s CEO Giuseppe Aquila on personalised luxury
We have just launched the Yu Prize, which is an annual award and incubator program to support promising emerging fashion designers from China. The CFDA, the BFC, Camera Moda and FHCM are so good at championing creativity and providing a support system for their rising stars; this is something that is lacking in China and yet we have a burgeoning fashion community of very talented designers. I’m excited and want to nurture this generation of designers, who compared with their predecessors, have mostly studied abroad (CSM, LCF, Parsons) and so are more globally minded. They marry this with a sense of pride of their cultural roots, and from this a new wave of creativity and confidence is born, which serves to reposition “Made in China”. Huishan Zhang, Guo Pei and Caroline Hu craft many, if not all, of their demi-couture pieces locally in China to an international standard.

Wendy Yu (middle) with Anna Wintour and Andrew Bolton
LUX: Do you often get to personally experience the difference you have made to a foundation or group?
Wendy Yu: My philanthropy has always stemmed from a personal relationship and a special connection that I have felt with a cause and therefore my involvement tends to be hands-on. It’s incredibly grounding and rewarding to be close to the people whose lives and/or careers are being transformed. Equally working with organisations that are specialised, and have the power and platform to make a difference is very inspiring. In today’s world and coming from a position of privilege, I believe in the importance of doing good as part of a wider definition of success.
LUX: Any other advice for our readers who might be considering going into the sector?
Wendy Yu: Follow your passion. Have in mind a wider sense of impact that you would like to make to a particular sector or area of interest, and then cultivate specific objectives and tangible projects that can be brought to fruition. Work closely with professional organisations that align with your vision and from whom you can learn more and gain access, however don’t be afraid also to champion people on a more personal level.
Find out more about Wendy Yu’s work: wendy-yu.com
Activist José Soares dos Santos on environmental responsibility

José Soares dos Santos outside the Lisbon Oceanarium
Through his Oceano Azul Foundation and game-changing Oceanário de Lisboa, Portuguese business leader and activist José Soares dos Santos is one of the foremost forces in Europe driving ocean conservation. LUX meets him to find out how he inspires politicians and his fellow philanthropists, business leaders and scientists to create a more sustainable future. By Andrew Saunders
DEUTSCHE BANK WEALTH MANAGEMENT x LUX
We have a responsibility to look after the oceans better, because the oceans look after us. That, in a nutshell, is the reason marine biologist and lifelong ocean-conservation activist José Soares dos Santos established the Oceano Azul Foundation in Lisbon, aiming to look at sustainability “from the ocean’s point of view”, as the foundation’s motto has it.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Whether it is the huge volumes of plastic that threaten marine life of all kinds, unsustainable fishing or the dangers of climate change-related ocean warming and acidification, dos Santos believes the marine environment is under pressure like never before. However, the crisis does not get the international attention and action that it deserves; it is time for businesses, investors, society and science to get together and spread the word.
“The fact is that the planet is a system, and if we don’t take care of the system there will be no businesses, no families and no proper life as we know it,” he says. “This is a responsibility we have and we had better do something about it.”

The central aquarium at Lisbon Oceanarium. Image by Pedro Pina
As executive director of one of Portugal’s largest and most successful business groups – whose Jerónimo Martins food distribution and retail business, chaired by his brother Pedro Soares dos Santos, had approximately €19bn in sales in 2019, with 115,000 employees and more than 4,400 stores – he used his commercial nous and network plus his marine biology training to bring together a group of experts, academics and businesses in 2014 to set up the Oceano Azul Foundation.
Read more: OceanX founders Ray & Mark Dalio on ocean awareness
“Together with my brother, we are at the head of our family group. We are the fourth generation of a very hard-working family,” dos Santos explains.“We have capital to deploy and we can call in interesting people with very good information. We have the means, and we also believe that we have the obligation to act.”
Why focus on the ocean? Portugal does of course have a long and illustrious maritime heritage, but dos Santos is motivated by his concern that the public lacks an awareness of the vital role that oceans play in sustaining life on earth. Even though the oceans cover 70 per cent of the world’s surface, the threats they are facing are poorly understood outside the scientific community. “We are talking about the oceans because there is a lot of curiosity about them. People often ask me questions about the oceans, but I am extremely surprised how little people know about them.”

King Philippe of Belgium and Queen Mathilde at the Oceanarium during their official visit to Portugal, 2018. Image by João Maria Catarino
Dos Santos points out that the oceans are not only home to 15 per cent of all known living species, but also produce over half of all the world’s oxygen, and, in the long term, has the capacity to absorb 50 times more carbon dioxide than the atmosphere. They also act as a massive heat sink to slow down the impact of global warming. They are an important source of food, resources and jobs – the OECD estimates that the blue economy could be worth $3 trillion by 2030, double its 2010 value. Human beings may live on land, but we are highly dependent on healthy, productive and sustainable oceans to enable us to do so.
Hence the foundation’s successful initiative, RISE UP – A Blue Call to Action. This is a joint initiative involving everyone from local fishing communities, foundations, indigenous people’s organisations and conservation groups, such as Ocean Unite and Environmental Defense Fund. Its campaign agenda was launched in May 2019 and presented to UN Secretary General António Guterres in February this year.

José Soares dos Santos announcing the donation of nautical equipment to the Portuguese National School Sports network by the Oceano Azul Foundation, 2019
Dos Santos was determined that the Oceano Azul Foundation would not be just another politically motivated pressure group pursuing its own narrow agenda, but instead a collaborative platform uniting marine conservationists, science, academia, business and society, as the collaborative and partnership-based RISE UP campaign, with over 400 organisations signed on in support. “We must keep science inside the foundation,” he says, “because we are not politicians and we cannot drift into politics. If we do that, we will be exactly the same as many other foundations and pressure groups. The world needs something different, not just another one of those.”
In particular, his view on the primacy of business and private investment in building a strong and self-sufficient culture of ocean stewardship marks out the Oceano Azul approach to sustainability as something out of the ordinary. “Our philosophy is not to donate money but to invest it. We believe that it is very important to take care of the planet but that we shouldn’t just give all that responsibility to the government.” He continues, “I find it very hypocritical when people say it is up to the government to change things. No! We elect the government, and we should say what we want.”
Read more: Nadezda Foundation’s Nadya Abela on running a children’s charity
Oceano Azul has also teamed up with the Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation to develop the Blue Bio Value business programme, an accelerator scheme to help new and sustainable blue-economy business ideas to grow faster and more effectively. A vibrant blue economy provides jobs and generates returns that can in turn be used to protect the ocean environment. “We believe in investing to create jobs, create value and to create social value,” he points out.
The programme, now in its third year, helps innovative marine biology-based businesses to scale up. Applicants undergo a rigorous due-diligence process that can lead to a prize corresponding to €45,000 awarded to the best start-up or start-ups, as well as access to coaching and mentoring services and valuable business networking opportunities. So far, 28 businesses from 15 countries have benefitted from the programme, ranging from Biosolvit, a specialist in offshore clean-up materials made from discarded biomass, to sustainable aquaculture engineering start-up SEAentia.

The Lisbon Oceanarium studies vulnerable and endangered ocean-dwelling species, including birds such as this Atlantic puffin. Image by Pedro Pina
At the heart of dos Santos’s mission to provide better information and education about the role of the ocean in maintaining a healthy planet lies the Oceanário de Lisboa. The newly refurbished facility is the largest indoor oceanarium in Europe and one of the city’s major attractions. Home to large collections of marine life, it had 1.4 million visitors in 2019.
“The Oceanário de Lisboa is at the heart of what we do,” he explains. “People go there and the effect on them is fantastic. They can see that below the surface of the water, the ocean is a place full of life that we have a responsibility to protect.”
Read more: British artist Petroc Sesti on his nature-inspired artworks
When he is not chairing the Oceano Azul Foundation, dos Santos is heavily involved in the family business. It’s no surprise that he is a staunch advocate of the ability of business owners to move the dial on ocean sustainability. “Business owners can change this,” he says. “I am a great believer in owners because they have a longer term perspective than financial markets.” He is at pains to point out that while he fully appreciates the importance of the financial markets, he is also aware that the long-term view required for sustainability can be at odds with short-term market expectations of publicly owned companies. “You need courage to do this; it’s not always good for your short-term share price,” he says.

José Soares dos Santos with the UN Secretary-General António Guterres at the opening of an exhibition at the Oceanarium, 2020. Image by Pedro Pina
As an example, he cites his family’s decision to remove all plastic from its businesses’ supply chains. “This is a huge transformation. It will cost a lot and take many years.” A publicly owned firm would struggle not only with the complexities of executing such a decision, but also with shareholders and hedge funds that prioritise short-term profitability. Consequently, such businesses may want to do the right thing, but be unable to follow through, he says.
By contrast, successful privately held family businesses are often built on long-term investment strategies. They appreciate the win-win of sustainable investing, but in turn often lack good quality information about what to invest in. This, too, is where the Oceano Azul Foundation has a role to play. “When we talk to owners, we can see they are worried. But they often do not know what to do. This is the bridge we have to cross – I can go out there and explain the issue, but I also have to provide the instruments.”
Read more: Marine biologist Douglas McCauley on environmental philanthropy
Creating the right framework for sustainable blue economy investment is thus crucial, he says, and the Oceano Azul Foundation’s Blue Azores programme is a model for how this can be achieved. The Azores, an autonomous region of Portugal, is an Atlantic archipelago that is home to some highly diverse and under-pressure marine environments and ecosystems. In partnership with the Regional Government of the Azores and Waitt Foundation, the Foundation has run two scientific research expeditions, the result of which was the February 2019 signing of a memorandum of understanding for both the conservation of those environments and the sustainable development of resources and fisheries within the area.
As a result of the memorandum, 15 per cent of the Azores Exclusive Economic Zone will be designated as marine fully protected areas, with comprehensive plans for the sustainable development of resources and fisheries within the zone – in line with the UN’s 2030 sustainable development goals, among others – to follow.

The Oceanarium building, designed by Peter Chermayeff in 1998. Image by Pedro Pina
Blue Azores is a great example of what can be achieved through a marriage of government, society and business investment, says dos Santos. “The Azores government has an outstanding leader who appreciates the need to take political decisions that will go beyond his term of office. It makes the Azores a very good place to invest, because there are programmes there that you can measure, and you can see making a difference. They will be good for the fishing industry, but also for the preservation of the oceans.”
It’s precisely that kind of win-win that dos Santos believes is key to building a stronger, better understood and more resilient approach to marine conservation and development. It’s a big job, but he has faith that it can be done – and more quickly than you might expect. “I am a great believer in humankind – given the right circumstances, we are capable of achieving extraordinary things and really making a difference to the planet.”
Lisbon Oceanarium
Opened in 1998 and designed by architect Peter Chermayeff, who also conceived the design for the Osaka Oceanarium, the spectacular Oceanário de Lisboa is home to some 16,000 marine organisms representing 450 species from across the globe. The attraction’s centrepiece is a vast tank containing five million litres of sea water, in which approximately 100 species – including sharks, rays and a giant sunfish – swim in near-ocean conditions.
The Oceanario is also the base for dedicated teams of experts in education and ocean conservation, including more than 30 highly qualified marine biologists. Its educational outreach programmes reach more than 100,000 school children every year.
Find out more: oceanoazulfoundation.org
This article originally appeared in the LUX x Deutsche Bank Wealth Management Blue Economy Special in the Autumn/Winter 2020/2021 Issue.

Nadya Abela is the founder and CEO of the Nadezda Foundation in the Russia and the UK
Philanthropist Nadya Abela established the Nadezda Foundation in her hometown of Tver in Russia in 2015 to provide disadvantaged children with much needed medical care and educational support. In 2019, a sister foundation was registered in the UK. In the first of our new philanthropy series, she speaks to Samantha Welsh about her motivations, the process of setting up a children’s charity and the challenges presented by the global pandemic

Nadya Abela
LUX: When did you first have the idea to set up your Nadezda charity fund in Russia and why? What prompted you to also to launch the foundation in UK?
Nadya Abela: When my youngest son was born here in London, I start realising more and more that being a parent is enormous responsibility and hard work. I felt lucky that my boys had good medical and educational infrastructure available for them here in UK. When I start comparing that to what was available back then for children in Tver, Russia, I realised there was a huge gap between the two.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
I flew home in the summer of 2015 and visited a few children’s hospitals, orphanages and educational centres for underprivileged children. Right there and then I decided to set up a foundation that would concentrate on children’s health and education issues in my hometown and other cities in Russia.
A few of my dear girlfriends (who are now on the committee at Nadezda Foundation) and I had been discussing similar issues here in United Kingdom for a long time and so we decided to set up the UK foundation in 2019, which also helps children who also find themselves in difficult life situations.
LUX: Is there anybody in the world of philanthropy and fund raising who inspired you?
Nadya Abela: Regular people, who give their time and money to support causes that are dear to their hearts or families, always inspire me.
LUX: What exactly does Nadezda Foundation do and how do you ensure you get optimum results?
Nadya Abela: Our foundations concentrate on children’s health and education. I believe those two factors are most important in creating positive future for them and for society in general.
LUX: How much of your time does it take?
Nadya Abela: Quite a lot, especially prior to important fundraising events.
LUX: Have you always been passionate about the welfare of underprivileged children and young people?
Nadya Abela: Ever since I started my modelling career at the age of 18, I always wanted to adopt a little boy or a girl, to take them away from life in orphanage and create a safe and healthy environment for them to live in. I have not done it yet, but hope that one day it will be possible. For now our charity foundation and I directly help lots of children, and we know that we change some of their lives for the better.


Some of the children the Nadezda Foundation helps (above), and one of the playgrounds built in Tver, Russia for children with autism.
LUX: Do you think that the role of private philanthropy is becoming more important, with increasing limitations on government funding?
Nadya Abela: Absolutely. It is always very direct because it involves less bureaucracy.
LUX: What are the biggest obstacles and challenges you have faced?
Nadya Abela: In Russia at the beginning, it was difficult to get people and big companies on board with fundraising. People were skeptical, or too busy with their own problems. Now, five years later, the situation has changed completely. I have people calling me directly and asking how and where they can help, which is an achievement on its own.
In UK, the hardest part was legally registering the foundation. It was a lengthy and costly affair, but now everything is fairly straight forward.
Read more: British artist Petroc Sesti on his nature-inspired artworks
LUX: Is there anything that concerns you about the path ahead for your foundation?
Nadya Abela: With Covid and current restrictions it is nearly impossible to do any fundraising so our work and the help we can provide is very limited. It is absolutely devastating and takes us back to square one so many children are not getting help they so urgently need.
LUX: What are your proudest achievements?
Nadya Abela: Seeing my two sons want to help with my charity work and support other boys and girls who are currently living in difficult situations.

Nadya outside EACH (East Anglia Children’s Hospices) for the whom the foundation raised £25,000 in 2019.
LUX: How will Covid-19 affect what you do?
Nadya Abela: Covid does not affect what I do. The ministers who make wrong decisions, kill economy and therefore, affect the wellbeing of whole nation and future of our children.
LUX: Do you enjoy running your foundation?
Nadya Abela: It keeps me grounded and yes, when we see how our work has changed children’s and their families’ lives, it does feel good.
LUX: Do you have specific examples of children or young people who have benefited?
Nadya Abela: There are lots of stories and projects from both of our foundations, which you can see on our websites. They all important, no matter how big or small so I wouldn’t want to single one out.
LUX: How would you encourage people to get more involved in supporting vulnerable children and young people?
Nadya Abela: You can go and visit schools and share your knowledge and experience. All children love to learn and they also love it when they feel that grown ups are interested in what they have to say. Find out what their biggest dream is, and help them to achieve it. We do not always have to raise lots of money to help change a child’s life.
LUX: What would you warn people about who are interested in setting up a charitable foundation?
Nadya Abela: Depending on the cause, it can be very emotional and take up lots of your time especially if it’s something you’re really passionate about, but it’s all worth it!
LUX: Have you any advice for LUX readers who might want to get involved in philanthropy?
Nadya Abela: Just do it and don’t look back!
Find out more: nadezdafoundation.org.uk; fondnadezda.com
Marine biologist Douglas McCauley on environmental philanthropy

The Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary, located off the coast of California. Image by NOAA/Mark Norder
Douglas McCauley directs the Benioff Ocean Initiative, the philanthropic organisation created by billionaire Salesforce founder Marc Benioff and his wife Lynne. McCauley, a marine biologist, says that philanthropists can do much more to save the oceans than simply write a cheque
DEUTSCHE BANK WEALTH MANAGEMENT x LUX

Douglas McCauley. Image by Jonathan Little.
We all have an opportunity and responsibility to do something for ocean health, whatever walk of life we are from. The ocean has paid us some service – and this service can be reciprocated.
I grew up in Los Angeles and if you’ve passed through the Greater Los Angeles area you get a sense that there is a whole lot of concrete and man-made change on land. And then you hit the coast and you have this big, beautiful uninterrupted space. So, for me the first debt of gratitude that I have to the oceans is that they were my escape to a world where I could find wilderness and immerse myself in the beauty of the ocean. And there was the practical side: the ocean provided me with my dinner – it gave me employment and income.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
For most people, the debt that they owe the ocean is different. For some people, such as Marc and Lynne Benioff, their identity has been shaped by ocean places such as San Francisco and Hawaii where they’ve lived and raised kids. The ocean has given them a lot of inspiration and beauty and knowledge. To be in a place that is so ancient and to be part of the majesty of the ocean and to experience such a mindful reset, and then to jump back into life on land and manage it successfully, means that you as an individual have drawn some value from the solitude and exaltation felt when by the ocean.
In the arrangement that we forged, Marc and I are each trying to repay some portion of that debt. As an ocean scientist, I can use the tools, our networks and our laboratories to try to be helpful, and Marc uses his resources, his influence, his network, to help create change. These two worlds together are really powerful.
For many people, the oceans feel very remote from us, making it a harder environment as a philanthropic domain to connect with. But there are some very practical ways that the oceans, even if they are remote, do provide benefits to all of us. The most universal of these is that the ocean, as it lives and breathes, as it aspires and photosynthesizes, produces half of the oxygen on the planet.
That means that whether you’re in seaside Miami or in landlocked Geneva, every other breath that you take comes from the oceans. It is a life-support system and certainly enough reason for us to connect to make sure that it continues to be fully functioning and healthy. When you do actually recognise that you have a debt to repay to the oceans, it is important to return the favour to the sea, to repay that debt.
The numbers of people who have made that reconnection to the oceans and have become champions for the seas are relatively few in the world of philanthropy. Statistics estimate that approximately one per cent of philanthropy is dedicated to the oceans. There are so many important causes on the planet that deserve our attention and investment but for a living place that encompasses two-thirds of our planet and provides us with half of our breaths, perhaps it deserves more from us. Each individual’s philanthropic portfolio matters, because each one incrementally will help us move a little bit further north of that one per cent.

Building partnerships with scientists and science can be powerful and create some symbiotic opportunities. Almost all of us have a relationship with a university, and we might be surprised that there are centres and hubs of ocean excellence in many universities, and not just places on the coast. For example, ETH in Zurich, Switzerland is one such hub of excellence.
Read more: How ethical blue economy investments support ocean conservation
Unfortunately, the problems facing ocean health are so large that there has to be a critical mass. No one single university is going to be able to change things. So a lot of what we are trying to do is create a template by which we can activate our colleagues and peers to demonstrate that we can actually make a difference.
For example, when you’re looking at an issue such as plastic pollution, in which you have more than five trillion pieces of plastic in the global oceans, that is too big an issue for any one organisation to solve. So we are trying to create this model to facilitate change by creating open tools that will not only help and but also become replicable in other places.
That is one reason why working with Marc Benioff has been so successful. He is a problem solver who has built a globally successful company. There is much that we have learned from him about the general mechanics of problem solving, and about the many tools that cross that boundary, such as the ones we use in ocean problem solving that originally were designed for industry and technology.
When we started working with the Benioffs, I had the incorrect assumption that we would have a few starter conversations, they would send us a cheque, and we would be off on our own to try to figure this out. But the most valuable thing that they did for us was not send us the cheque. Instead, the most valuable thing that they did for us was to open up their networks and to share their expertise, and to very usefully help match us with people that could have a part of a solution that we needed.
Find out more: boi.ucsb.edu; labs.eemb.ucsb.edu/mccauley/doug/
This article originally appeared in the LUX x Deutsche Bank Wealth Management Blue Economy Special in the Autumn/Winter 2020/2021 Issue.
Deutsche Bank’s Claudio de Sanctis on investing in the ocean

The Lisbon Oceanarium, Europe’s largest informational and educational space on the oceans, is operated by a foundation launched by Portugal’s Dos Santos family. Image by Paulo Maxim
Claudio de Sanctis, the new Global Head of Wealth Management at Deutsche Bank, has been passionate about the oceans since he was young. He now sees the blue economy – the sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth – as a major and necessary target for investments. LUX speaks with him to discover why
DEUTSCHE BANK WEALTH MANAGEMENT x LUX

Claudio de Sanctis
LUX: How did your interest in ocean conservation arise?
Claudio de Sanctis: It’s something that goes back to my childhood. I was brought up in Italy and school summers there are very long. I spent a good portion of that time in the water snorkelling and skin diving in the Mediterranean and I developed an incredibly strong connection to the sea and the life in it. You carry forward that passion for animals and life in the sea; and then, if you are 47 as I am now and you are still spending your holidays diving in the sea with your family, you witness first-hand the changes that have gone on. You have this passion, you have witnessed this crisis, and there is a part of you that says something needs to be done.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: You have personally noticed the environmental changes in the sea?
Claudio de Sanctis: One hundred per cent. If you don’t dive or spend time underwater, the ocean may seem like a beautiful, big, blue expanse and it’s difficult to perceive how it’s changing; it looks as beautiful now as it did 50 years ago. But if you do actually spend time underwater, you then notice that the Mediterranean, for example, has changed dramatically. In the past 40 years, plastic has replaced fish. There were previously a lot of fish, and now there are far fewer and plastic is popping up more and more so it’s now almost impossible to get underwater without seeing a large amount. Also, tropical fish are being seen in Greece, for example, which is a concern as it suggests a very significant change in temperature. If you go to the tropics, the situation is very similar. I have less than 20 years’ experience diving in the tropics, but even in that time, the situation has deteriorated and reefs have disappeared.
LUX: And this is what inspired your focus on the blue economy, which includes ocean conservation and much more besides.
Claudio de Sanctis: That’s correct. There are two fundamental beliefs informing this. One is that institutions such as Deutsche Bank have a fantastic history, if you realise that, for example, we have invested in young artists for the past 40 years for no other reason than social responsibility. While we are a business for profit, doing things because they are relevant and important for the societies we operate in, and because it’s right to be doing them, is important. In that context, we try to do things that are relevant to our clients. I meet clients on a daily basis and more often than not, the discussion will turn to conservation and particularly ocean conservation, and the strongest message I get is one of interest and one of alarm. “How can I help?”, they ask. And that’s how the blue economy comes into play because I believe that the best way to protect the sea is actually to explain to everybody the extraordinary sustainable, long-term economic value it has. There is a lot we need to explain to the world, such as the fact that we breathe because of the ocean; if we damage the ocean beyond a certain point, we won’t be able to breathe air any more. This is very much where education comes into play. And if you understand how the ocean can produce long-term economic development for low-income, underdeveloped countries, that is very relevant. If it’s properly harnessed, the blue-economy potential for a country such as Indonesia is extraordinary. It can lift hundreds of millions of people out of poverty and give them long-term prospects.
LUX: Are there increasing investment opportunities for the blue economy?
Claudio de Sanctis: There are, but there is so much more to be done, which is why the conference we are holding is so interesting. At the moment it is a very thin market but you essentially have three main drivers. The first one is very wealthy families who set up dedicated foundations, which in turn invest long term in ocean conservation and the blue economy. In that space, education plays a massive role. Secondly, if you don’t want to have a dedicated foundation then you can invest in financial instruments. There are more and more liquid financial instruments starting with blue bonds that allow you to contribute capital with a certain degree of return in order to help these underlying themes. The last element that we need to develop is investing directly in companies as more start up with a blue economy angle.
LUX: Will the blue economy become more important within environmental, social and governance (ESG) investing in general?
Claudio de Sanctis: That’s a very good question. My view is that when it comes to ESG, there is no need to put different sub-themes within ESG into competition. There is so much need for more across the board. I can say that interest in ocean conservation and the blue economy is growing exponentially and the awareness of it is growing extraordinarily fast because it’s tied to very important problems. I mean, science has now led us to understand that the oxygen for two breaths in every three comes from the sea, which is something that, five to ten years ago, very few people knew. So if you pollute the sea to a point that that sort of oxygen production slows down, you have a huge problem, because we’re not going to be replanting a lot of forest in the next 50 years. And planting forest takes a long time. Most of the ESG themes are fundamentally interlinked. For example, ocean conservation, blue economy and climate change all interlock.
Read more: Fashion designer Kevin Germanier’s sustainable glamour
LUX: Do companies who may believe they are not responsible for, say, ocean degradation because they are based far from the sea, need to be made aware of this interlocking, that the ocean is relevant to them?
Claudio de Sanctis: That is a very fundamental point. Awareness is everything and in my view, the awareness we need to create is not so much in the companies as in the end consumer. Everybody needs to understand the relevance of this resource, that the ocean is deteriorating and what the consequences of this are. And then on the positive side, what are the opportunities we can extract from the sea if we actually manage it properly? When we talk of the problem of plastic in the oceans, everyone thinks of the poor albatross found with plastic in its stomach, which is a significant problem. It’s an easier problem to grasp than microplastics, which are less visible. But while plastic bottle and bag waste affects marine mammals and sea birds, it is microplastics that affect fish. And the biggest polluting factor in the plastic problem is our clothing. Every time we wash our clothes in a washing machine, particularly anything that has plastic fibres, we release microplastics into the ocean. This is just an example, and this is why we need education, because there is so much more that we need to know and that we need consumers to know because it is they who ultimately drive politicians and purchasing.
LUX: What would you like to achieve through your blue economy programme?
Claudio de Sanctis: In our business we talk to a number of very significant families about what it means to actually have positive impact. So even if we help a few of these families be more aware of the problems and solutions, that is already gratifying for me personally in terms of helping the cause. From a Deutsche Bank point of view, my aspiration is that in the next two to three years when Wealth Management clients think about oceans, they think about ocean conservation and economic development tied to that. And then they think of Deutsche Bank and pick up the phone and speak to their banker here.
Find out more: deutschewealth.com
This article originally appeared in the LUX x Deutsche Bank Wealth Management Blue Economy Special in the Summer 2020 Issue.

Penélope Cruz at the 2018 Cannes festival wearing Atelier Swarovski jewellery. Courtesy Swarovski.
Penélope Cruz brings her renowned energy to philanthropic and charitable work – and now she is designing jewellery for Swarovski. LUX speaks with the Spanish-born Hollywood superstar
LUX: Where do you call home?
Penélope Cruz: Madrid. I grew up in a place called Alcobendas, a suburb of Madrid, with my sister Mónica and our parents and after with my brother Eduardo. My earliest memories are of being in my home every Sunday, everybody cleaning the house. There was always music, and everybody was dancing. My mother ran a hair salon, and between the ages of five and 12, I would go to the salon and listen to the women. I don’t know why but women in a hair salon share their deepest secrets. They would share everything with everybody. That was the first acting school for me.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: Tell us how your collaboration with Swarovski came about?
Penélope Cruz: The whole process evolved very naturally. I had worn some beautiful Atelier Swarovski pieces at various events. But it was when I met Nadja Swarovski and she spoke in depth about Swarovski’s work with sustainability that I became inspired to work on a collection with her. I really care about having a positive impact on the planet, and Swarovski has a rich history of putting sustainability at the heart of what it does.
LUX: What interested you in working with Swarovski Created Diamonds in particular?
Penélope Cruz: Before speaking with Nadja, I didn’t realise that it was possible to create stones in a lab with a low impact on the environment. As soon as I became aware of Swarovski Created Diamonds and other lab-grown precious stones, I wanted to start designing pieces and use them.

Courtesy Swarovski.
LUX: Your jewellery designs seem to have a vintage Hollywood feel. Have you always been drawn to the aesthetics of the era?
Penélope Cruz: My fine jewellery collection has a classic red-carpet aesthetic and I always go back to that – they are timeless pieces that I would always choose to wear. I think there is something for every woman in what we have created.
Read more: How we created the Ruinart Frieze lounge experience at home
LUX: What is the most important thing you learned from this collaboration about how to bring a design concept to life?
Penélope Cruz: It has been an amazing learning experience. I’m very lucky that Nadja and the team have given me such creative freedom. I begin the design process by pulling together images and references of things I love, and then spend hours with the designers to distil the clippings from movies, novels, paintings, ballet dancers and vintage markets into a jewellery collection that tells the story.

Cruz with Vogue editor Edward Enninful and Nadja Swarovski, 2019. Photograph by Nicholas Harvey
LUX: Would you encourage a young person to pursue a career in acting?
Penélope Cruz: It has been an incredible honour and pleasure to build a career as an actor, and to be surrounded by so many brilliant artists in theatre, film and television. Sometimes it can be a huge challenge, but I would encourage any young person to follow their dreams, listen to their heart, work hard and stay away from drugs – whether that is in the creative industries or beyond.
LUX: When you aren’t working on a film, what personal or creative projects do you focus on?
Penélope Cruz: From the age of seven I loved redesigning the clothing and jewellery from the pages of my favourite fashion magazines. So, working on jewellery design projects is a big passion for me and I have been honoured to have the chance to fulfil my childhood dream with Atelier Swarovski, season after season.
Read more: American artist Rashid Johnson on searching for autonomy
LUX: How does your family help you to stay grounded?
Penélope Cruz: I have always kept my personal and professional lives separate. Being with my family gives me so much happiness and it is my priority.
LUX: What inspired your activism, such as your involvement with the Time’s Up movement?
Penélope Cruz: I feel very strongly about the causes I support, and I have noticed a difference in Hollywood since the Time’s Up movement created a sweeping dialogue about the treatment of women. It is already having an impact on the kind of questions we get asked in interviews. Previously, you would be in a press conference and the women would mainly be asked very rude or superficial questions. People are more careful now. It’s symbolic, but hopefully we are understanding how to treat each other with more respect. And these are issues which affect women in all industries and everywhere in the world. If we don’t all do this together, it’s useless.

Cruz with Antonio Banderas, 2019. Photograph by David M. Benett/Getty Images for Somerset House
LUX: Do you have a dream film or television project you would like to direct yourself?
Penélope Cruz: I’ve always wanted to direct. I have directed commercials and a documentary before but hopefully I will be able to do a full-length feature film someday.
LUX: What is it like working with a director such as Pedro Almodóvar, someone you’ve worked with for years?
Penélope Cruz: Pedro is like family; he is very important to me and holds a special place in my heart because he was the reason why I became an actress. I’m excited that we are making a new movie next year.
LUX: What type of music do you enjoy? Is there a track that makes you want to dance?
Penélope Cruz: I’m a big fan of everything that Pharrell Williams does. He’s an amazing producer and songwriter. I also love Eduardo Cruz’s work. He is my brother and we are very close, but I admire his work as a composer and producer so much. He just did the soundtrack for the film Wasp Network.
LUX: Has the past year changed your outlook on life?
Penélope Cruz: We are experiencing a huge moment of social change and I am still processing the transformations that are occurring around us. However, I believe that the values I hold closest – truth, justice and equality, respect for the planet and kindness towards others – will grow in strength. We truly are all one and we have to commit to creating a better tomorrow.
View Penélope Cruz’s designs for Swarovski: atelierswarovski.com
This article features in the Autumn Issue, which will be published later this month.

Baby pillar coral, being bred in quarantine, at six months. Image by Kristen Marhaver
She is one of the most compelling figures in ocean conservation. Kristen Marhaver, a marine biologist and TED and WEF star, has made coral regeneration sexy. She tells Darius Sanai that rapid scientific advance and philanthropic support are combining to make the idea of regrowing the world’s coral a real prospect
DEUTSCHE BANK WEALTH MANAGEMENT x LUX

Kristen Marhaver. Image by Bret Hartman.
LUX: Why has there been so much positive progress in coral science recently?
Kristen Marhaver: For a long time, nobody knew how corals reproduced. We assumed most corals spat out little swimming baby corals. It was only around 30 or 40 years ago that mass spawning of corals was discovered and that’s because it only happened a few nights a year. If you’re in the water one hour too late or two days too early, you won’t ever see it. We always had in the back of our minds that the more we understood about reproduction, the more we could help promote coral reproduction in the wild.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
When I started my research career, we would watch corals reproduce and collect their eggs and raise them through the first couple of days or weeks of life and that was it. It was extraordinarily difficult to make progress and most of the coral community thought that there was no way that this would ever lead to something you could apply in conservation. All of a sudden, things just started to click and every year we made a little bit more progress – by “we” I mean the hundreds of people around the world working on a thousand coral projects every year – and decoding one more puzzle at a time and getting a little bit further along the path.
Then we realised all of a sudden something that had seemed impossible became fairly possible. Now everything is aligned just right, and there is this gold rush in coral reproduction science to increase the efficiency of their breeding. We know that every year we’re only going to make a couple of steps more before we have to wait 11 months to try again.
It has been exciting to see the field’s potential grow in the past few years, and it makes it even more exciting to dig into the ever more difficult puzzles because we know that the more we solve, the more we can hand over the answers to other groups that can scale it up from there.
LUX: Is it correct to say there is hope that coral reefs can be rebuilt?
Kristen Marhaver: We are slowly accepting that it’s an option, but we are always really careful about the scale and the timeline when we talk about it. Sometimes I think that we are in year 40 of a 200 year project. So, we can’t go and give an island nation an entire new coral reef, but we can grow a handful of species, get them out in the water, give them 10 years, and they will be the size of basketballs. We can do that on a metres to tens of metres to hundreds of metres scale, but it is also true that the more that people get good at this, and the more innovation is applied, the more it will scale up. In the next five to ten years, we will have changed from saying, “this is something we can do” to “this is something that we can scale up confidently”. There is an analogy with orchids. These used to be extraordinarily expensive, but if you go to a supermarket or a florist, you will see an orchid for $10. The reason they are so abundant and cheap is because scientists figured out meristem culture, so instead of waiting for orchids to grow big and then dividing, they just take a tiny sliver of tissue and grow a whole new orchid. That completely changed the availability and propagation of those plants. We are about to see the same kind of thing in coral propagation.”

Juvenile corals, aged 18 months in the aquarium system at CARMABI. Image by Kristen Marahver
LUX: You can recreate coral killed by human activity, but how do you ensure the new coral won’t be killed again?
Kristen Marhaver: That’s a great question. And it’s a huge concern. We have a couple of reasons to be optimistic, one of which is that there’s now a really powerful race amongst the countries to enact not only climate plans, but also marine protected areas and fisheries regulations and sewage system modernisation. There are also some pretty nice examples of places where juvenile corals can do better than the adults could. That’s partly because when we are growing juveniles, there is a tremendous amount of genetic diversity. You have more chances of getting a good hand by putting 20,000 juveniles of all different genetic combinations into a place, as opposed to fragmenting 10 or 20 adults and gluing those pieces back onto a reef.
Read more: How Chelsea Barracks is celebrating contemporary British craft
LUX: You are passionate about making sure philanthropists support the right groups in coral restoration.
Kristen Marhaver: The most powerful groups in coral restoration are in places like Belize and the Dominican Republic and the Philippines. You don’t necessarily hear about them because they don’t have the glossy brochure and the advertising budget and the social media person; they’re just all underwater busting their butts. It is really important to find a group that’s not just flashy and well branded, but one that is honest about what they can do. It’s important for donors and philanthropists to do their homework and find out what’s going on behind the scenes.
LUX: And why is coral important?
Kristen Marhaver: I was interviewed once on a television station and the interviewer asked me why we should care about coral reefs. And I said, “Well, they bring in tourism money, and provide food for a billion people around the world, and they grow these beautiful structures that are art.” Then he asked, “Why should we care?” I said, “If you don’t like money or tourism or art, then I really don’t know what I’m going tell you.” But if you have ever been to a beach in the tropics, or been in a building in the tropics, you may have corals to thank for keeping that beach there, keeping that building up. It’s also cultural heritage, the same way that we care about losing languages or losing monuments or losing art. It’s because it’s the heritage of our earth and the cultures on earth. We owe it to small communities around the world to help them hold on to that cultural value as well.
Dr Kristen Marhaver is a coral reef biologist at the Research Station Carmabi and the founder of Marharver Lab, both in Curaçao.
Find out more: researchstationcarmabi.org; marhaverlab.com
This article originally appeared in the LUX x Deutsche Bank Wealth Management Blue Economy Special in the Summer 2020 Issue.

Aquajenne in Paradise II Elevator Girls (1996) by Miwa Yanagi. Courtesy Deutsche Bank Collection
At the heart of Deutsche Bank’s worldwide art programme is one of the most interesting and diverse corporate contemporary art collections in the world. It is part of the bank’s sponsorship of the Frieze art fairs and instrumental in the bank’s support of this year’s innovative curatorial and philanthropic projects, including a collaboration with London artist Idris Khan. Arsalan Mohammad reports
DEUTSCHE BANK WEALTH MANAGEMENT x LUX
This turbulent year marks not only the 150th anniversary of the founding of Deutsche Bank, but also the 40th birthday of its iconic art collection, one of the most substantial corporate collections of contemporary art in the world. A specialised assortment of works, numbering some 55,000 pieces, the collection spans styles and genres and reflects a global mix of talent, from art megastars to exciting newcomers. The art is predominantly works on paper, as this somewhat neglected medium was considered ripe for collecting and institutionalising when the collection was first initiated by the management board in the late 1970s. The collection is bound by only one other rubric: that the works should provide creative, cultural and intellectual inspiration to the creative, cultural and intellectual inspiration to the bank’s employees, clients, visitors and artists alike.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
The Deutsche Bank Collection, which is part of the bank’s Art, Culture and Sports programme, is based in multiple sites across Germany and in its offices worldwide. It also sits alongside a calendar of art events – the bank is the long-term sponsor of global art fair Frieze, it publishes an acclaimed arts magazine, engages in numerous exhibitions and presentations worldwide, and maintains an active purchase programme that prioritises discovering fresh ideas and idiosyncratic thought from young and older artists around the world. You can witness this for yourself at the bank’s impressive PalaisPopulaire complex, in the heart of downtown Berlin. A purpose-built forum focusing on arts, culture and sports, here one can enjoy works from the permanent collection alongside works on loan, as well as a lively calendar of music, film and cultural happenings.

Molo, Kenya (2008) by Zohra Bensemra. Courtesy Zohra Bensemra/Reuters.
This profound commitment to culture is central to the bank’s ecosystem and is a vital component in its identity. It recalls the pioneering spirit of corporate evolution that began when billionaire philanthropist David Rockefeller began the Chase Manhattan Bank’s art collection back in the 1950s. Since then, the notion of a corporate entity finding inspiration, identity and creativity within art has become standard practice, a means of fulfilling social responsibility, nurturing employees’ potential and attracting clients and business from the world’s wealthiest investors.

The PalaisPopulaire, Berlin. Image by David von Becker
A significant part of this success is due to Deutsche Bank’s Head of Art, curator Friedhelm Hütte, who has managed the collection for more than 25 years. A quiet and learned person, Hütte’s strategy of proactively engaging with, encouraging and supporting new and unexposed talent over the years has given him an appreciation for edgy new art and access to the creative minds behind it. Since beginning at the bank’s cultural division in 1986, he has carefully steered its growth, enriching the bulk of the collection with a knack for spotting talent early. Thus, the bank’s inventory includes early works by Damien Hirst, Gerhard Richter and James Rosenquist, all acquired when the artists were yet to become as famous as they are now. “We always want to discover new artists,” says Hütte, “This doesn’t mean that the artist has to be young – it could be that an artist is older but hasn’t found the success that we feel he or she should have.”
Read more: The market for modern classic Ferraris is hot right now
As well as supporting artists through purchasing work, the bank is also committed to emerging talent via its Artist of the Year prize, which has catapulted artists from around the world at the start of their careers, such as Wangechi Mutu, Yto Barrada, Roman Ondak and Imran Qureshi, into the global limelight. “It’s not simply a prize of a sum of money, it’s really to support the artist, so they can reach a new level,” explains Hütte, who offers the example of how an exhibition by Qureshi led to his being represented by Galerie Thaddaeus Ropac in Paris, “one of the top ten best galleries in the world!”
Detail of Blessings Upon the Land of My Love (2011) by Imran Qureshi. Courtesy Deutsche Bank Collection.
In the summer of 2020, amidst social distancing and other pandemic restrictions, the PalaisPopulaire continued with its planned exhibition of work by artists Christo and Jeanne-Claude. Christo, who died in May 2020, is best remembered in Berlin for his 1995 performance in which he and his wife Jeanne-Claude wrapped the Reichstag in fabric. The plans, blueprints, ephemera and sketches for that mammoth undertaking have been on show as part of a major exhibition entitled ‘Christo and Jeanne-Claude: Projects 1963–2020’. The exhibition features approximately seventy works loaned by Berlin collectors Ingrid and Thomas Jochheim, friends of the artist and catalysts for the show.

Wrapped Reichstag (Project for Berlin) (1987) by Christo. © Christo.
“We showed Christo the [PalaisPopulaire] museum last year,” Ingrid Jochheim recalls. “And he was very fond of it. He had partnered on projects with Deutsche Bank several times in the past, always successfully. Just four weeks before his passing, he wrote to me and asked me to give his compliments to the team there.”
But this being 2020, there are more pressing matters at hand. The reconfiguration of partner Frieze London in the autumn as an online event has afforded Deutsche Bank the opportunity to present a curated selection of works that are relevant to our challenging times. The resulting presentation, curated from the collection by the bank’s international art curator Mary Findlay, gathers a selection of more than 30 artists from around the world, each of whom articulate perspectives inspired by issues such as Black Lives Matter, gender equality and sexuality.
Read more: British artist Marc Quinn on history in the making
Titled ‘Taking a Stand: Art & Society’, the online exhibition will show work by a broad spectrum of artists, including Banksy and Joseph Beuys, Iran’s Shirin Aliabadi and Algeria’s Zohra Bensemra, black American artists such as Kandis Williams and Kara Walker, and well-established artists such as Wolfgang Tillmans, Imran Qureshi and Albanian photographer Adrian Paci.

Black Lives Matter protest, Union Square (2014) by Wolfgang Tillmans. Courtesy Deutsche Bank Collection
At times such as these, Deutsche Bank’s fleet-footed operation means their global team have not only been able to respond rapidly and with creativity to events, to build shows on an online platform for Frieze or cope with physical restrictions on visitors to PalaisPopulaire, but also to build on their one-world progressive ethos and take direct immediate action to address the entrenched problem of diversity in the arts.
In association with Frieze, Deutsche Bank are launching a fellowship, The Frieze & Deutsche Bank Emerging Curators Fellowship, to support curators from black, Asian and ethnic minority backgrounds in the UK. Financing the mentorship and education of a curator is a complex process, but at Deutsche Bank a solution has been found in which one of their prestigious collection artists, Idris Khan, is to design a face mask for sale, based on a design inspired by Vivaldi’s ‘Four Seasons’. The plan is in its final stages of preparation, but the energy and enthusiasm inspired by the chance to make a difference is palpable in conversations between the Frieze and Deutsche Bank staff involved.

Centro di Permanenza temporanea (2007) by Adrian Paci. Courtesy Deutsche Bank Collection.
“The fellowship is about fostering systemic change,” explains Frieze London’s artistic director, Eva Langret, who came up with the idea. “It’s about organisations across the nonprofit and private sectors recognising that diverse programming is not enough, and instead working together to embed more diverse voices within arts institutions and organisations that lead the agenda.” In its first year the fund will be supporting a curatorial fellowship at London’s Chisenhale Gallery and the intention is to inspire an ongoing strategy to empower arts professionals from across communities to make an impact on the country’s art scene.
Read more: Four leading designers on the future of design
Curating change is at the heart of the idea, and at 2020’s Frieze London, we will witness, albeit online, how well this approach fits with the Deutsche Bank Collection. “Where we can, we buy works that make a difference,” says Findlay. “There is this idea about artists using their creative platforms as activism – well, we are buying art to make our offices stand out and look exciting, but in some of those works, we are very much looking at what the artists are trying to articulate. This concept is about us engaging with society and the virtual platform will have all sorts of different types of work. There’s lots of interesting work here. I wish we could put it all on a wall and not online, but there you go!”
While there is every sign that the complex workarounds, compromises and challenges that have come to characterise 2020 will continue into our hazy and uncertain future, in surveying this tapestry of arts from across the globe, we can at least draw solace and wisdom from the world of art to inspire, educate and support our frazzled minds at times of crisis. And with the Deutsche Bank team’s deep-rooted commitment to giving a platform to some of the world’s most urgent and pressing issues, there’s every reason to support and engage with it yourself this autumn.

Idris Khan in his studio. Photograph by Stephen White
Behind the mask
British artist Idris Khan has been asked to make an artwork to help fund the bank’s new fund for emerging curators. Here he talks about his inspiration for the new work.
“During lockdown, my partner Annie and I decided to leave London for the countryside. When we arrived, the trees were bare, everything was brown and black. But over the months, I focused on the changing colours, something I probably wouldn’t have done otherwise. It was almost like watching four seasons within two months!
“I took several copies of Vivaldi’s ‘The Four Seasons’ and decided to paint all those colours that I saw during lockdown.
“The image on the mask is my version of bluebells. First, I watercoloured the sheet music, scanned each page then digitally layered the music on top. It’s like capturing many moments of time of looking intensively and also the time represented in musical notation, so it’s titled Time Past, Time Present. I think that this represents what we’re all going through, hence the reason to wear a mask.
“I think this fund is incredibly vital, as a lot of funding and support has been cut, especially during the pandemic. I believe the fund will give curators the opportunity to make incredible exhibitions and will go on to support diverse exhibitions, so that when this nightmare is over we can all enjoy looking at exceptional art.”
Find out more: db.com/art
This article features in the Autumn Issue, which will be published later this month.

Aqua Shard donates a percentage of the retail price of every Peter Pan Afternoon Tea to Great Ormand Street Hospital
Earlier this month, Aqua Shard in partnership with the Great Ormond Street Hospital Children’s charity GOSH launched a Peter Pan themed Afternoon Tea, inspired by J.M Barrie’s infamous tale. Abigail Hodges experiences the creative menu
Whilst admiring the stunning views over the Thames from the panoramic windows of Aqua Shard, a boat appeared on our table in plumes of billowing smoke. This wondrous craft cradled a creative exhibition of savoury and sweet treats: finger sandwiches wrapped in paper denoting the ‘Lost Boy Rules’, an ‘Enormous Mushroom Chimney’, The ‘Codfish’ Captain Hook cod brandade croquette (named after Peter Pan’s nickname for his nemesis), a Tinker Bell shaped cookie sprinkled with gold fairy dust, a deliciously rich chocolate swirl (representing Peter Pan’s Secret Hollow Tree Entrance) and a chewy Tick-Tock the Crocodile dessert of raspberry and rooibos jelly. We sipped Veuve Clicquot champagne alongside vanilla and rose ‘Darling Tea’, and finished the occasion with warm scones, which came hidden within a special treasure chest, accompanied by sweet apricot marmalade (or ‘mammee-apples’) and a rich coconut clotted cream. A delightful afternoon indeed.
For more information visit: aquashard.co.uk

Traveljar guests can enjoy unique wildlife experiences such as morning walks with the orphaned elephants in Zambia. Imag by Andrew White
Traveljar designs luxurious travel itineraries tailored to guests’ interests and led by industry experts such as scientists, Olympic medalists and award-winning photographers. Chloe Frost-Smith speaks to Libby White, Director of Experiences, and Andrew White, Director of Conservation, about responsible travel, wildlife encounters, and far-flung destinations
1. Conservation is at the heart of your business. What are your top tips on how to travel more sustainably?
Libby: We really try to help our guests to become responsible travellers and learn how their trips can benefit conservation, communities and the environment. My number one tip would be to think about what kind of impact you want to leave behind from your travels. At Traveljar, we have partnered with suppliers who provide ethical and sustainable destinations so our guests are having a positive impact no matter where they choose to stay.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Another top tip is to get involved! We love to help our guests find meaningful ways to give back during their trip. We can arrange a day of learning about rhino conservation in South Africa, visit an elephant orphanage in Zambia, spend the day reading to kids in a rural school in Zambia at our library project or take a tour around your accommodation and the local community to learn more about the sustainable practices that are in place to benefit the area. Traveljar also donates to one of our four NGO partners for every trip booked with us and all of our itineraries show guests how their trip is giving back.

Wilderness Safari, Chitabe Camp in Botswana where guests can stay in sustainable luxury as the camp is 100% solar powered.
2. Where would you send travellers asking for the most off-the-beaten-track destinations?
Andrew: Two places immediately come to mind for me, the first one being Busanga Plains in Zambia. Located in the northern part of the Kafue National Park, this grassy seasonal floodplain is known for some of the best lion viewings in Africa. Because there are only a few lodges operating here and less visitors, you will get a more intimate safari experience, giving you a true remote bush safari away from the crowds.

Lion on the Busanga Plains. Image by Andrew White
The other destination I would recommend is Virunga National Park in the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This is one of only three places in the world to see mountain gorillas and is very much off the beaten track when it comes to a holiday. Responsible tourism has the chance to make a difference to the communities living here. As well as support the conservation efforts in the park like the Senkwekwe Centre for orphaned gorillas and their ranger program which has over 700 male and female rangers who are protecting the park’s wildlife. For the adventurous, you can hike up Mount Nyiragongo, an active volcano, to one of the world’s largest lava lakes.

Mountain Gorilla. Image by Nelis Wolmarans
3. What has been your most memorable wildlife encounter to date?
Libby: Without a doubt for me it was seeing my very first rhino in Pilanesberg National Park (in South Africa) and then taking to the air in a helicopter for an anti-poaching patrol with our partner, Rhino 911. Seeing these gentle giants in their natural habitat for the first time was incredible but then to also get the chance to learn more about the dangers facing rhinos and the people try to protect them, made the experience one I will never forget. It has made me even more committed to doing what I can through Traveljar to try and help Rhino 911 in saving this endangered species.
Andrew: There is something very exciting about getting the opportunity to watch animal behaviour on a safari. One of my most memorable wildlife moments was in South Luangwa National park with two clients, both of whom had never seen African Wild Dogs before. After picking up their tracks, we found the pack sleeping in the long grass. Wild dogs are very playful and social and we got to watch them splashing around in the pools of water. Strengthening social bonds and listening to the chatter between them highlights their intelligence and our guests were amazed by their actions. That afternoon we followed the pack as they moved along the river in search of Impala and watched with interest as the dogs chased the impala across the plans, using incredible teamwork in the diminishing light.

Libby & Andrew White with Rhino 911 in South Africa
4. How do you define experiential travel, and do you have a favourite moment from one of your expeditions?
Libby: For us, experiential travel is travelling with purpose and the ability to show our guest that you can combine a relaxing, luxury holiday while giving back. We believe that when people travel with purpose, that they have the potential to positively impact the communities and wildlife they encounter along their travels, as well as to come home feeling inspired themselves.
My favourite moment so far has been taking guests to help set up a library in a rural school in Zambia as part of our community engagement commitment. It was amazing to be able to watch my clients read and interact with the kids, to see the positive impact it was having on them as well and to know that, together, we had all been a part of providing books for over 600 children to continue developing their reading skills for their future.

Children reading with books donated from Traveljar’s library project in Mfuwe, Zambia. Image by Andrew White
Andrew: My favourite moment from our expeditions is always the chance to take clients on a morning walk with the orphaned elephants at the Lilayi Elephant Orphanage in Zambia. I have personally been involved with Game Rangers International for the last 10 years and being able to help others learn about the work this incredible NGO is doing to rescue, rehabilitate and release these elephants back to the wild is always very special to me.
5. What makes your itineraries ‘once-in-a-lifetime’ trips?
Libby: All of our itineraries are 100% bespoke, making them completely tailored to the client’s travel wishes. We decided to do our trips this way because we felt like what equals the “perfect” trip for one person is not the same for the next. We take the time to really get to know our clients and understand what they are hoping for from their trip. Guests can choose every aspect of their adventure, along with our expert guidance, from the type of accommodation they stay in, to the activities they participate in, down to which partner we make a donation to from their trip. In planning a trip this way, we can create the “perfect” and “once-in-a-lifetime” adventure for each individual.

Elephant at sunset in Botswana’s Chobe National Park by Barbara Eidel
6. What is your favourite image from your photographic safari masterclasses and why?
Andrew: For me, the photographic masterclass is all about helping our clients get their dream photo. By travelling with Nelis Wolmarans or myself, our guests will visit beautiful destinations with incredible wildlife, leading to a number of opportunities to either learn more about wildlife photography for the first time or to work on perfecting their skills or trying out new techniques. One of my favourite pictures from a photographic masterclass trip was a beautiful elephant at sunset photo by our client Barbara Eidel, taken in the Chobe National Park. I had the chance to take her on her first African safari last summer and help her in developing her wildlife photography skills, building confidence and creativity in her work . Having a client at the end of the trip enthusiastically share their photos with you and ask when the next trip is going to be, makes it a very memorable adventure together.
Find out more: travel-jar.com

Shirin Neshat at home in New York City
Shirin Neshat’s devastatingly striking art combines dream, reality and an undercurrent of anger and sadness. As a major retrospective of her work is held in Los Angeles, Millie Walton meets the artist at the launch of her collaboration with celebrated Italian winemaker Ornellaia, famous for its artist labels
Portrait photography of Shirin Neshat at home in New York by Maryam Eisler
Iranian-born filmmaker and artist Shirin Neshat sits demurely drinking a cup of coffee in the palatial breakfast room at Baglioni Hotel Luna in Venice. It’s the morning after the Sotheby’s auction at the Peggy Guggenheim Collection which saw the sale of limited-edition bottles of 2016 Ornellaia wine with Neshat’s label artwork. A total of $312,000 was raised, with all profits going to the Mind’s Eye programme, which was conceived by the Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation to help blind people experience art through the use of other senses.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
The success of Neshat’s collaboration, following that of William Kentridge’s in 2018, was well deserving of late-night celebrations, but the artist is composed and alert, her jet-black hair scraped tightly back from her face, and her dark eyes lined with black kohl. It’s a look that would seem somewhat severe or even theatrical on most, but Neshat wears it with authenticity, grace and a sense of homeliness. She pulls up another chair close to hers so that I can hear what she’s saying over the clamour of the breakfast buffet and tells me that she’s been ordering coffee to her room each morning and is worried that Ornellaia will have to foot the bill. Given the sum raised last night along with Neshat’s status as the world’s most important and widely recognised contemporary Iranian artist, it’s hard not to laugh, but she speaks softly and sincerely, taking time to consider each of her answers and apologising when yet another admirer interrupts for an autograph. She has a lot of fans it seems, yet her politically engaged work continues to generate debate. She admits, “Some people dislike what I do. There are a lot of people who hate my work in Iran, but still it is discussed, so I think I’m relevant.”
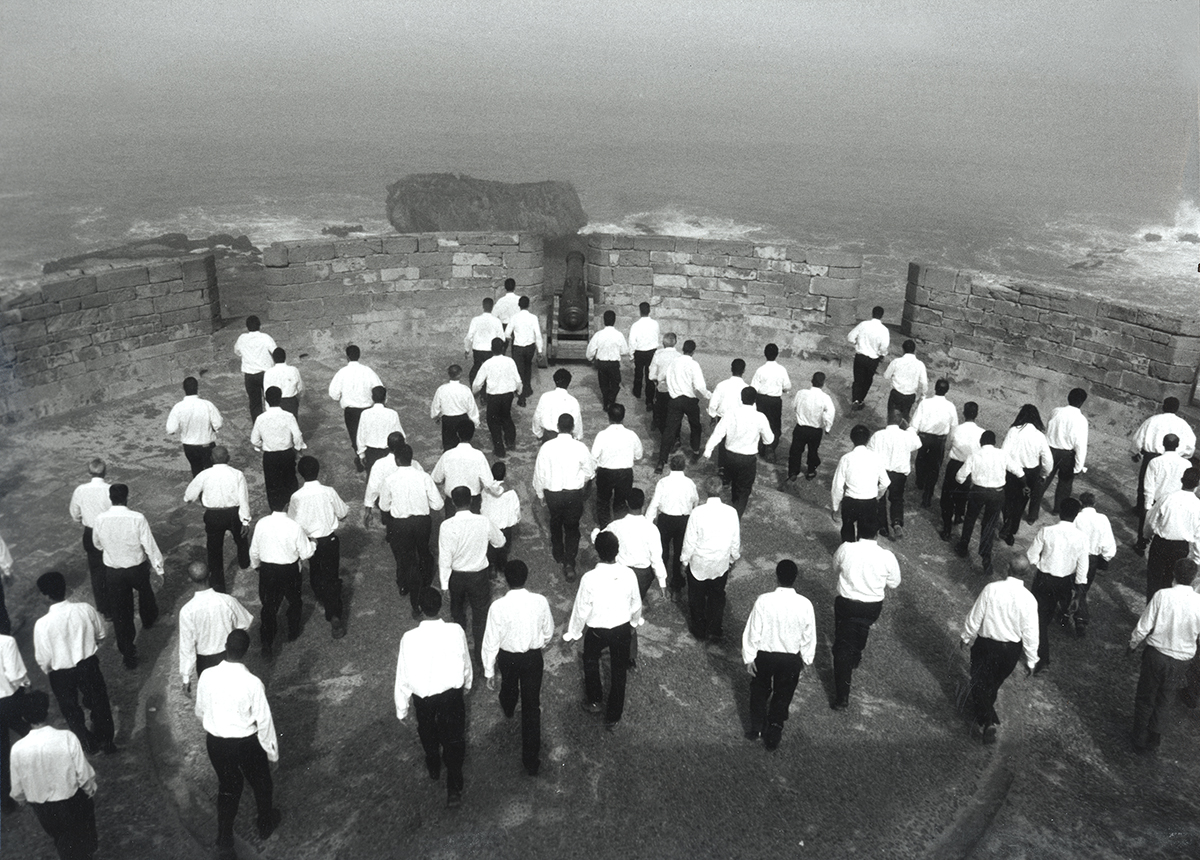
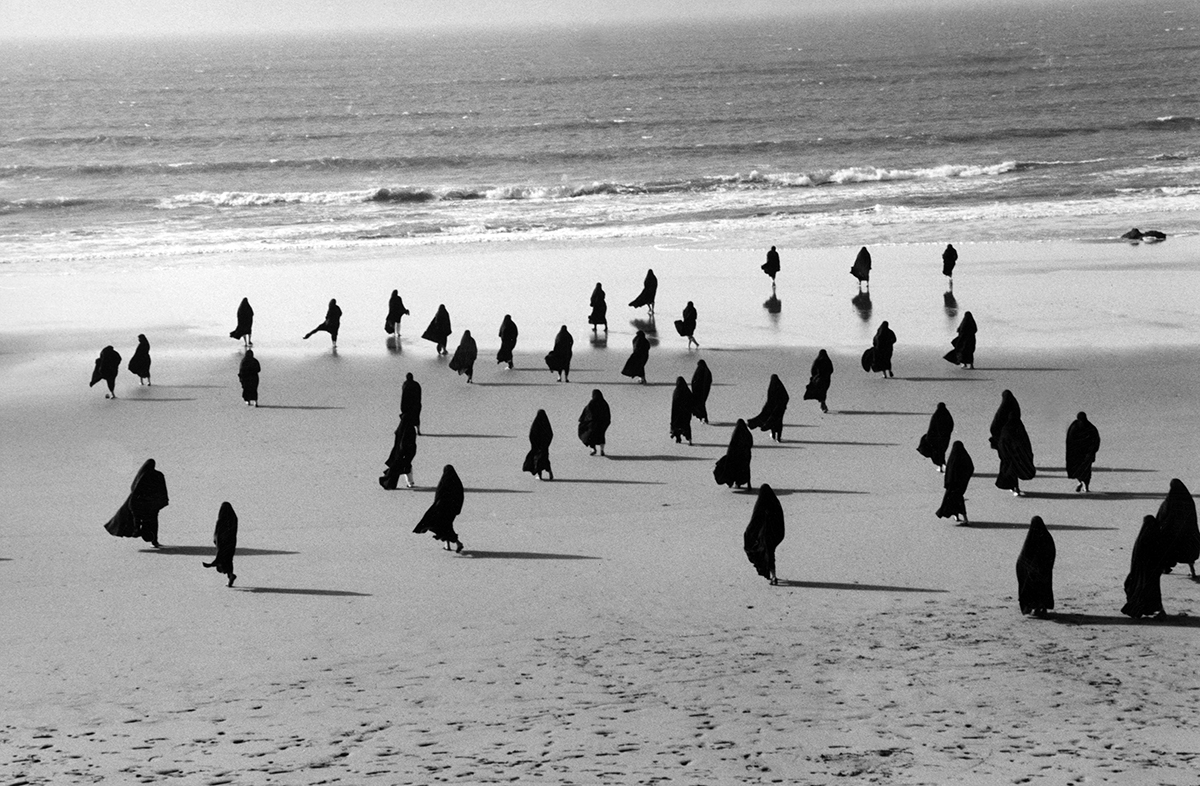


Here and above: stills from Neshat’s video Rapture (1999)
Neshat was born in the city of Qazvin, north-west of Tehran, but left for California at the age of 17 to finish her schooling. Her training as an artist began with her undergraduate and masters degrees in fine art at the University of California, Berkeley. However, she abandoned art-making and moved from Los Angeles to New York in the early 1980s. It was a decade later, through photography first and then film, that she found her artistic vision. She has now been working as an artist for more than 30 years and has won numerous international awards, including the Golden Lion at the 1999 edition of the Venice Biennale for her powerful short film Turbluent, which explores gender roles and social restrictions in Iranian culture. The film plays out on two screens: one shows a male performer singing a love song by the 13th-century Persian poet Rumi to a large audience of men, whilst on the other screen, a veiled woman waits in an empty auditorium, her back turned to the camera. When the man’s performance finishes, the woman begins a wordless song of guttural cries, mournful melodies, panting and animalistic screeching. This film was not only significant in establishing Neshat’s career, but also in paving the way for her succeeding works, which all, in one way or another, deal with the restrictions of female experience. Though embedded in narratives of conflict, Neshat’s work offers a sense of hope in which women find freedom through art in all its various guises.


Neshat’s designs for Ornellaia’s ‘La Tensione’ bottle label

Neshat with Ornellaia’s estate director Axel Heinz
Given these preoccupations, the artist’s decision to collaborate with Tuscan winemaker Ornellaia is somewhat baffling. “In our culture, wine is a way not to escape, but to transcend reality and so [drinking wine] is a sacred, spiritual act,” says Neshat. “But in general, I feel like an occasional step out of your own milieu is actually very positive. For one thing, it puts your work in front of a new audience, but also, for me, [commercial work] is an attractive way of financing my projects. I make work that takes me six years and I make zero money so I think that any patronage that finances your practice and gives you the freedom to do your work is great.” Her series of images for Ornellaia, interpreting the theme ‘La Tensione’ which gives this vintage its name, depict white hands inscribed with Persian script, luminous against a black background. The use of hands, along with literature and monochromatic shades are all typical of Neshat’s aesthetic and imbue the work with a haunting, dreamlike quality. “I’m very interested in the subtlety of body postures and how they can reveal emotion, especially coming from the Islamic tradition and how provocative and problematic the body can be,” she says. “There’s a certain universality about hand gestures.” She places one palm against her chest: “This, for example, could be love”.

Ibrahim (Patriots) from The Book of Kings series (2012) by Shirin Neshat
The work is reminiscent of Neshat’s first series of black-and-white photographs, entitled Women of Allah (1993–97), which was created following the artist’s return to Iran in 1990, her first visit following the 1979 Islamic Revolution. When Neshat arrived back in Iran, it was in the wake of dramatic cultural changes. Women of Allah not only marked the rebirth of her making art, but also her engagement with the country’s political landscape – an engagement which led to her current state of exile. The series focuses on female martyrdom, showing veiled women holding weapons, their faces, hands and feet again inscribed with Farsi poetry, highlighting the revolutionary Iranians’ dual identities as both Persians and radical Islamists, as well as the tension between devotion and violence.
Read more: Introducing the next generation of filmmakers at Frieze LA
Her practice continues to be preoccupied with contrasts, highlighted by the minimalism of black and white, but also with conflict. “There are plenty of artists whose making of art is an aesthetic exercise, which is important because it has intellectual and artistic values of the highest level,” she explains. “But for artists born to a country like Iran, the relationship to art is personal in a way that it cannot be separated from daily realities. I don’t think we have the emotional capability of distancing ourselves from these issues, and it is an incredibly fulfilling process when you make work that is politically conscious. It also means that you have a relationship with an audience that is larger than the [usual] art audience because people are able to identify with the subject matter.”

Despite Neshat’s acute political engagement, her work has a sense of timelessness achieved by incorporating literature and music as well as elements of the surreal. “Music is very existential,” she says. “It sort of neutralizes a political reality, but it also contains all these cultural references and has a strong physical impact. Powerful music affects your heart.” This is perhaps most apparent in Turbulent, which was inspired by a young blind woman who Neshat saw singing on the streets of Istanbul. Many of her works have involved collaborations with composers and musicians as well as writers and cinematographers. “It’s an essential part of my work to collaborate, especially with people who know me and my work well,” she says. “I’m doing a lot of work in media that I never studied. It’s been really interesting to surround myself with people who have the expertise.”

The artist in her studio
Neshat’s artistic ‘family’ is international, but she has gravitated towards other Iranians in New York: “I am sitting on the outside [of Iranian culture], others are by choice and others not; either way, we’re naturally drawn to each other and spend a lot of time helping each other. I do feel integrated in American culture as far as the artwork goes, but I can also see the limitations of not being Western, when your practice is considered to be a little bit outside the box.” Reflecting this duality, Neshat curated ‘A Bridge Between You and Everything’, an exhibition of Iranian women artists held at the High Line Nine Galleries in New York in November 2019.

Raven Brewer-Beltz (2019) by Shirin Neshat
Neshat has called New York her home for many years, but her latest project, Land of Dreams, is the first time that she has directly turned her artistic attention towards the US. The project explores her experiences of being an immigrant, focusing on an Iranian woman who collects dreams that portray American people and takes them back to an Iranian colony for analysis. The project is now being shown for the first time as part of Neshat’s major retrospective ‘I Will Greet the Sun Again’ at The Broad in LA, and one wonders at the colony’s interpretations. “It’s kind of an absurd comedy,” she laughs, “but it was also [about] how to tackle a very important political subject – the antagonism between the two cultures as well as the corruption on both sides – through a human surrealism so that it escapes absolute realism. I want it to be timely, but I don’t want it to have no value in a hundred years’ time.” Are these surreal imaginings ever drawn from Neshat’s own dreams? “Yes, I try to write down my dreams every time I wake up. I like how ephemeral dreams are. My work is like the story that comes after.”
‘Shirin Neshat: I Will Greet the Sun Again’ is on show at The Broad, Los Angeles until 16 February 2020: thebroad.org.
Shirin Neshat ‘Land of Dreams’ opens at the Goodman Gallery in London on 20 February and will run until 28 March 2020. For more information visit: goodman-gallery.com
This article was originally published in the Spring 2020 Issue.

ArtSocial launches art therapy programmes to help disadvantaged children and young people. Image by Justyna Fedec
Alina Uspenskaya is the Founder and Director of ArtSocial, a foundation that supports and establishes arts therapy programmes to help disadvantaged and vulnerable children. Here, Alina tells about the foundation’s vision, annual fundraising gala and plans for the future

Alina Uspenskaya
1. How was the ArtSocial Foundation born?
I started ArtSocial more than 5 years ago because I wanted to combine my passion for art, my love of bringing people together and desire to work for a cause that I care about. During my childhood in an industrial city in the North-West of Russia, arts unlocked a different world for me – a world in which I could dream, and aspire to a full and diverse life. I always wanted to find a way of helping other young people, especially those who are the most vulnerable and to help overcome social, economic or health challenges, using the power of art.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
In the art and fashion worlds of London I met many people and luxury brands who have joined me on this mission. With all of this endorsement, I was able to set up ArtSocial Foundation in 2016 alongside the ArtSocial Patrons Club, which is a philanthropic community supporting the foundation’s work.
2. Have you always been interested in the arts?
Art, music and drama were a huge part of my life. When I was a teenager, music gave me a refuge from the feelings and emotions of a turbulent adolescence. When I moved to London over 10 years ago, I discovered this city through its art and met many like-minded people thanks to the vibrant art world.
I should say, though, that the love of art is not enough to run a charity, even if it is an art-related one. That is why recently, in addition to an Art History degree, I graduated with a Masters in Charity Management from Cass Business School.

3. Which of ArtSocial’s programmes are you most proud of so far?
It has to be the most recent program of art psychotherapy in children’s hospitals that started at St Mary’s Hospital in November and will soon expand into The Royal Brompton Hospital paediatrics department.
Doctors and psychologists agree that art psychotherapy can be very effective in providing an emotional support during hospitalisation, especially for children who cannot always express their feelings with words. I’m excited that this year almost 1000 children and young people who are seriously or chronically ill, or hospitalised will receive much needed emotional support from art therapists funded by ArtSocial.

ArtSocial Patrons Club visit to the studio of artist Hassan Hajjaj
4. How do you become a patron and what does it involve?
ArtSocial Patrons Club is made up of like-minded and diverse people from many backgrounds who share a passion for arts and philanthropy. Throughout the year our patrons enjoy a curated programme of events, including artists’ studios and private collection visits, gallery and art fair tours and bespoke behind-the-scenes visits. In the past, we have visited the studios of artists such as Mary McCartney, Paula Rego and Hassan Hajjaj. This season’s highlights include a backstage tour of The Royal Opera House and a visit to the couture atelier of Ralph & Russo.
An annual patron’s contribution is £1200 and thanks to this support, we can sustainably fund some of our long-term commitments and start new projects. To keep up the community spirit of our Patrons Club, we open up just a few spaces to new members every season. Myself or my team meet with every applicant to ensure he or she receives the best welcome and feels properly involved in what we do.

Actress Sally Phillips was a special guest at the ArtSocial gala and auction 2019
5. Can you tell us about the annual gala event?
In addition to the contributions we receive from patrons, we raise funds at our annual Christmas Gala and Auction. The recent gala brought together 90 people from the worlds of art, fashion and business. Our special guest was Sally Phillips (an actress and a champion for Down’s Syndrome awareness) who gave a touching speech in which she shared how music helps her son Olly (who has Down’s Syndrome) to gain confidence and essential social skills.
Christie’s auctioneer Charlie Foley auctioned a stay at Joali (the Maldives’ first immersive art resort), a luxury experience with Chanel in Paris, a stay at Amanzoe resort in Greece and other luxury experiences.
The atmosphere was very warm and supportive. Thanks to our guests, auction partners and our main partner Faidee jewellery, we raised funds to run all of our projects in 2020.
6. What do you hope to achieve in 2020?
This year, we are celebrating ArtSocial’s 5th anniversary, and the thousands of children and young people who we have reached through the projects we fund and run. Our 2020 focus is on the new hospitals programme, to get it well established and expand to other children’s hospitals in London and in Russia.
We have some exciting events lined up for our patrons in the next few months, and are looking to grow our community and welcome new patrons who would like to join us on our mission. Although, the Christmas season has just passed, I have already started planning for the next Christmas Gala, which will be our biggest yet.
For more information visit: artsocial.uk

A monkey runs across the private pool terrace of the Royal ‘Burra Sahib’ Suite at Sher Bagh. Image by James Houston
Why should I go now?
Thanks to stricter wildlife policies, India’s population of endangered Bengal tigers has increased by 33 percent since 2014, and with 60 tigers roaming 500-square-miles of wilderness, Ranthambore National Park remains the best place to see them.
The park was once the private hunting ground of the Maharajas of Jaipur, and is still home to many ruins of hunting lodges as well as a majestic crumbling fort from the 10th century. The landscape itself is varied with everything from dense jungle to open plains and desert-like areas; each safari jeep is assigned an area on arrival to prevent overcrowding and limit the impact on the habitat.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
The park tends to be quieter at this time of year, making the safari experience especially peaceful and whilst seeing a wild tiger is never guaranteed, it helps to have a knowledgeable guide. SUJÁN Sher Bagh is known to have not just the best guides and trackers, but the luxury group is also committed to conservation, meaning that every guest who stays at the camp is contributing to the group’s philanthropic initiatives.

Sher Bagh’s swimming pool overlooks the wild grasslands. Image by James Houston
What’s the lowdown?
Sher Bagh is a luxury tented camp pitched under a canopy of indigenous trees on the fringes of Ranthambore National Park. There are only 12 tents with the majority arranged in a semi-circle and the royal suite secluded behind mud walls, giving the whole place an intimate, homely atmosphere, emphasised by the warmth of the staff. The place is designed to evoke the romance of old-world travel with wood panelled floors, leather furnishings, vintage trunks, crystal decanters of whiskey and golden oil lamps that light the pathways and hang from the branches come nightfall. The staff are mainly all from the local villages, and everything from the tents to the interior decorations and even the smooth mud surfaces of the pathways are created by local craftspeople, whilst the kitchen uses ingredients grown in the gardens and cultivated on the camp’s farm.

Image by James Houston

Sher Bagh’s staff hang lamps on the trees at every dusk, creating a magical ‘fairy-tale’ atmosphere. Image by James Houston
Breakfast and lunch are generally served in the beautiful grand dining tent with a menu of delicious Anglo-Indian dishes, whilst dinner is traditional Indian cuisine served in a surprise location each evening. The thali and the buttery flaked parathas were amongst the best we’ve ever tasted, and we also loved the selection of canapés served with pre-drinks round the fire every evening, but the bespoke dining experiences were the real highlight. After a morning game drive, our jeep pulled up into the farm yard where a decadent breakfast buffet was laid out underneath the shade of a tree. Before eating, we were given the opportunity to try milking one of the cows and collect eggs from the henhouse, which were then cooked by the chef with fresh herbs and spices. On our final night, we arrived back at our tent to find a table set up on our private pool terrace, surround by hundreds of glowing lanterns.

Breakfast and lunch are generally served in the main dining tent (above), but bespoke experiences can also be arranged. Below: breakfast served on the camp’s farm after an early morning safari. Images by James Houston

The park’s animals naturally wander into the surroundings areas. This is especially the case with the monkeys who, during our stay, swung between the branches overhead, played on the roof of our tent and drank from our pool. In the mornings, the camp naturalist showed us the tracks and trip-camera images of nighttime visitors to the farm, including a leopard, sloth bear and hyena. Understandably guides are required to accompany guests back to the tents after dark, but the real magic of the place comes from not knowing what you might encounter, who might be peeping at you through the branches or sharing the same pathways.
Read more: The must-visit destinations of 2020 by Geoffrey Kent
Indeed, most guests come to Sher Bagh for the wildlife experiences. The camp’s luxury 4×4 vehicles depart for safaris every morning and afternoon, with stops halfway through for drinks and snacks in the jungle. Whilst tigers are the main draw, the park is also home to leopards, sloth bears, deer, mongoose, wild boars, hyenas, jackals, crocodiles and an array of tropical birds. For us, one of the most beautiful experiences was watching the monkeys walking amongst the villagers on their way to morning worship. In between drives, the camp is a very peaceful place to relax, swimming, reading or listening to the hum of the jungle.
Getting horiztonal
We stayed in the largest and most luxurious tent: the Royal ‘Burra Sahib’ Suite. Enclosed behind mud walls, the tent is the most secluded area of the camp with its own private heated swimming pool overlooking the grasslands. The interiors follow the camp’s colonial theme with cream linens, and rosewood and teak furnishings, including a beautiful four-poster bed and two open wardrobes each equipped with a branded safari fleece (the morning drives can be very chilly). There’s a separate sitting room with a curated selection of books, and a spacious bathroom, featuring natural, sustainable bath products. Laundry and ironing are complimentary and the suite comes with a high-tech DSLR camera for guests to borrow on safaris.

Most of the tents are arranged in a semi circle (above), whilst the Royal ‘Burra Sahib’ Suite is secluded behind mud walls (below). Images by James Houston

Flipside
Sher Bagh manages to balance the highest level of luxury with authenticity and honesty. Sustainable practices are integrated into every element of the camp from the homegrown ingredients to the local staff and use of natural materials. The air conditioning units in the rooms and communal areas are the only contradiction to this ethos that we noticed, and although it’s understandably necessary to keep the rooms cool during the hotter months, it seems a shame that these can’t be replaced with a more environmentally friendly option.
Rates: From ₹55,000 for a luxury tent including all meals (approx. £600/€700/ $750)
Book your stay: thesujanlife.com/sher-bagh
Millie Walton

A&K Philanthropy programmes include the Duuma Wajane Bike Shop in Tanzania, where women repair and resell secondhand bikes to support their community
This month, Geoffrey Kent, founder and CEO of Abercrombie & Kent, reports on his industry’s move towards sustainability and why he thinks responsible tourism is the most authentic way to travel

Geoffrey Kent
Working towards sustainable tourism is the travel industry’s duty, and while big airlines and hotels should lead the way, there are still plenty of ways for individuals to make the right decisions. Being a responsible tourist might sound complicated – or lofty – but it does not need to be either. If 7.7 billion people were to make more sustainable choices, the planet would be better off. Think of the influence one individual can have; I have been very inspired by teenage environmental activist Greta Thunberg, whose solitary climate change protest outside the Swedish parliament sparked a youth movement in some 112 countries. It’s often children who are the most aware and passionate. We must live up to their expectations.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Thankfully, the concept of responsible tourism is catching on. It’s true that notions of sustainability, carbon neutrality, animal welfare and cultural sensitivity haven’t always been in sync with the travel industry, but increasingly we find our customers are asking us to book hotels with eco-friendly practices, to support the local communities they’re visiting and to find carbon-neutral ways of making the journey.
A recent study that we commissioned found that 65% of respondents are likely to be more conscious and careful of their own behaviour when travelling and 50% are likely to stay at hotels that contribute positively to the local environment by engaging in behaviours such as sourcing food locally. We’ve found that if our clients are ‘green’ at home, they tend to take those practices on holiday. At Abercrombie & Kent, we can create itineraries for our clients that are both environmentally conscious and culturally sensitive; we were doing this long before responsible tourism was a thing.
Our experience and network of travel partners have taught us that integrating sustainability into your travel arrangements does not mean sacrificing luxury or comfort. When it comes to five-star luxury with serious eco-credentials, the Six Senses group are leading the way with their programmes: energy conservation, water re-use, waste recycling, responsible purchasing and wildlife protection are all part of their policy. There are small groups and properties also committed to the cause: Sanctuary Retreats for example, The Brando in Tahiti, Caiman Ecolodge in Brazil, Mashpi Lodge in Quito and 1 Hotels. Some of the big hotel chains are at it, too; all the properties in the Fairmont Hotel chain are LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certified.

A&K Philanthropy also supports Hansraj Children’s Home in Udaipur, India
It’s not just on land either, A&K operates an annual cruise to Antarctica with James McClintock, an endowed professor of polar and marine biology at the University of Alabama. He shares adventures from more than 30 years of Antarctic research into ocean acidification and how climate change has impacted the food chain, especially penguin rookeries on the Antarctic Peninsula. A&K has worked with Dr McClintock for the past 12 years to support his research, providing more than $350,000 worth of high-tech equipment, from satellite penguin tags to webcams that allow scientists around the world to monitor penguin rookeries.
Our approach to animal welfare issues is uncompromising. Since the company’s inception, I have championed the concept of ‘shoot with a camera, not with a gun’. Our clients travel to Africa to connect with and celebrate its abundant wildlife, diverse landscapes and thrilling experiences. Elsewhere, we follow vigorous animal welfare guidelines developed by the Association of British Travel Agents in conjunction with the Born Free Foundation, a third-party organisation whose mission it is to protect vulnerable animals from abuse.
Read more: ‘Extremis’ by Sassan Behnam-Bakhtiar opens at Setareh Gallery
But there’s more to responsible tourism than getting to your destination and back without wreaking havoc on the community you’ve visited. Imagine a trip that offers you the opportunity to make connections through unique local experiences not found in a guidebook. Travel philanthropy can create the most memorable moments of your holiday. Whenever possible, we ask our clients to take part in our Abercrombie & Kent Philanthropy (AKP) programme.
We founded AKP in 1982 as a non-profit working with communities on education, health care, conservation and enterprise development, in the areas our clients travel to. Simply put, we work with our neighbours. Anywhere there is a Sanctuary lodge or camp, we establish a nearby project. In Uganda that means Bwindi, located beside Sanctuary Gorilla Forest Camp. In Zambia, near Sanctuary Sussi & Chuma, we work with Nakatindi village. It’s vital that these communities should benefit from any influx of tourism into their ancestral homelands. Anywhere there is a Sanctuary boat operating on a waterway, we establish a project at a place where we regularly undertake shore excursions. For example, in Myanmar that’s at Sin Kyun village where we bring education, clean water and hope to a small remote village on the Irrawaddy river.
AKP has full-time community development professionals on staff around the world. Our philanthropy co-ordinators meet with communities to identify local issues and establish where we can have the greatest impact. We never just have a great year, write a cheque and walk away. At Nakatindi, we heard from tribal elders that their highest concern was mother-to-child HIV transmission, so we established a new maternity ward to provide a clean birth environment. These decisions are made in consultation with our community partners, government officials and departments and sometimes other non-profits in the area.
In 2017 and 2018, our guests gave most significantly to education and healthcare, but contributions come thanks to inspiration, never solicitation. Our female teenage guests are often the drivers. They visit a programme with their families and have the empathy and persistence to inspire their families to be philanthropic. I can’t tell you how many phone calls I’ve had from the parents of teenage girls, who say, “She keeps mentioning the programme we visited and we’ve got to do something about it.”
I believe responsible tourism is a more authentic way to travel. Our guests define luxury as having an authentic experience, an encounter that is true to the place and its traditions, incorporating elements of the past and reflecting local culture. They want to get out and explore, experiencing traditions that are not akin to their own. What can be more responsible than that? Lives are changed when one is immersed in a different culture, and one reaches a new understanding of how life is lived in another part of the world.
Find out more: abercrombiekent.co.uk
This article was originally published in the Autumn 19 Issue.

Lewa Wildlife Conservancy, Isiolo, Kenya. Image by David Clode
Philanthropists have long played a huge role in wildlife conservation, but now a more holistic approach is needed in a world where humans and nature increasingly live cheek by jowl

Andrew Shirley
Sometimes, to see the bigger picture, you have to turn things inside out. For decades, wildlife conservation, particularly in Africa, has focused on what lies within the boundaries of national parks, reserves and other protected areas, many of which owe their existence to the fortunes of benefactors and donors enthused with a passion for the environment.
But despite their efforts and the hundreds of millions, if not billions of dollars spent, the continent’s wildlife is still in a state of precipitous decline. Now, there is growing recognition that part of the solution is to be found on the other side of the hard and not-so-hard boundaries separating man from nature.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
To many, the conservation battleground in Africa is a war – literally, conducted by both sides with military-grade equipment and planning – against the illegal trade in ivory and rhino horn. And wildlife isn’t the only victim. Paul Milton, founder of the Milton Group, an advisory firm to a number of ultra-high-net- worth families with a combined interest in over 1.5 million acres of conservation lands in Sub-Saharan Africa, has seen evidence of this first-hand. The story from just one community in Mozambique is harrowing. Scores of children orphaned; fathers lost while poaching or through long-term incarceration; mothers forced into prostitution to survive.
Huge sums are spent to thwart poaching, but too little on addressing the reasons that drive people to do it. Having interviewed many poachers, he says, they want just two things: food security and work. Asking someone who already spends millions on conservation to fund employment creation isn’t an easy sell, yet long term, generating local economic value offers a more sustainable means to reduce poaching.
Conservation and the hospitality industry that springs up alongside it does create jobs, but it’s not enough. Park boundaries that ten years ago were relatively devoid of habitation are now marked by informal settlements of hundreds of thousands of people – the fences of some of the world’s most iconic wild spaces are used as washing lines.
Creating buffer zones around parks is one solution, but only increases the sense of dislocation between local people and wildlife. Even the word ‘conservation’ is controversial due to its colonial undertones: high-minded thinking from afar, divorced from the daily realities of existence.
Part of the problem is that very little attention has been paid to how population growth and infrastructure development, such as new transport corridors, increasingly affect the disparate conservation zones scattered across Africa. The base data exists – the world has been comprehensively mapped from space – but nobody has thought to join the dots in Africa. A new initiative between mapping and geographic information system providers ESRI, Nasa and The Peace Parks Foundation, coordinated by Milton Group and the UN, looking at a ten-million-hectare swathe of Botswana, South Africa, Zimbabwe and Mozambique, should act as a framework for a more unified approach to conservation.
The other elephant in the room is that conservation in its current form isn’t financially sustainable over the long term. Since the financial crisis, the NGO model appears to have hit a glass ceiling and even the most deep-pocketed philanthropists don’t wish to leave money pits for future generations.
Tourism was long regarded as the answer, but alone, it is no silver bullet. At the top end of the market, the cost of providing luxuries to attract big-spending visitors to remote areas makes it difficult to generate huge profits. Further down the chain, the volume of guests on more affordable safaris can damage the flora and fauna supposedly being protected.
Read more: Introducing the new age of ink art
Well-resourced individuals and families, however, are looking at new hybrid hospitality models involving impact investment, public/private partnerships and hospitality programmes for their exclusive use. This model is particularly suited to private reserves, however most of Africa’s protected spaces are under a wider umbrella of stewardship. More innovative models are required, that may not be linked to the protection of a species, but to the wider benefits to society, such as carbon sequestration that can mitigate the speed of climate change. The payment for this ‘natural capital’ could come from companies looking to offset their own carbon emissions.
In my role as editor of The Wealth Report I’ve been lucky enough to see first-hand the amazing work being done by philanthropists in Africa, whether conserving existing wild areas or rewilding landscapes given over to agriculture. The success stories are awe-inspiring. But a new narrative is required that accommodates the needs of people as well as wildlife, one that is not imposed on the continent, but works in harmony with it.
For UHNWIs looking to get involved in conservation, there is a unique opportunity now to shape that narrative. Some advice: let your passion drive you, but don’t let it overwhelm your decision making. Work out where your efforts will have most impact; an isolated block of land may be ideal for a private reserve, but somewhere providing a corridor between existing conservation areas may offer longer-term benefits. Visit existing projects, assemble a team of experts, talk to potential partners and don’t look at wildlife in isolation, the local community is an equally important part of the equation. Finally, have a clear vision of how your project will be financed in future to protect your legacy.
Many wealthy individuals have created their fortunes by turning things inside out to create new perspectives. They still have a huge role to play in safeguarding the world’s wildlife.
The Wealth Report, a guide to prime property and wealth trends, is published by Knight Frank. knightfrank.com/wealthreport
This article was originally published in the Autumn 19 Issue.


Model, philanthropist and psychology student Olivia Anakwe. Instagram: @olivia_anakwe
LUX contributing editor and model at Models 1, Charlie Newman continues her online exclusive series, interviewing her peers about their creative pursuits, passions and politics

Charlie Newman
THIS MONTH: 22-year-old Nigerian American model Olivia Anakwe grew up in the small town of Bucks County, Pennsylvania and was scouted whilst studying for a degree Psychology. In her first season, she walked an astounding 40 shows and has since shot for Harpers Bazaar, W Magazine, LOVE and Allure. Fellow Models 1 girl, Charlie speaks to Olivia about balancing time, philanthropy and Michelle Obama.
Charlie Newman: How and when you were first scouted?
Olivia Anakwe: I was scouted in the summer when I was visiting New York for my sister’s graduation. We went out to lunch at Westville and I was scouted right when I walked into the restaurant. I chose to take advantage of the opportunity, transferred from University of Pittsburgh to Pace University and was thrown right into the middle of the hustle and bustle in the Financial District of Manhattan. I am studying Psychology on the Pre-Medical track and will be graduating in Spring of next year – I can’t wait!
Follow LUX on Instagram: the.official.lux.magazine
Charlie Newman: Was modelling something you considered doing when you were younger or did you just fall into it?
Olivia Anakwe: I did a small Target ad and a knitwear catalogue when I was younger which I can’t really remember very well. Growing up, my aunties always made comments about using my height to model but I never took it seriously.
Charlie Newman: How easy have you found the balance between studying and modelling? Is your agency supportive of your studying commitments?
Olivia Anakwe: My agency is super supportive, but I definitely speak up about my studying commitments and exams. To find balance I take advantage of my free time; whether I am in the hair chair, waiting for my flight, or riding the subway, I save documents to my google drive, make it available offline, and whip it out during those spare minutes. I often take pictures of my textbook and read it over. We are in such a technology-driven age, so it’s all about putting our gadgets to positive use.

Instagram: @olivia_anakwe for Kate Spade Pre-Fall ‘19
Charlie Newman: After modelling, how do you hope to use your degree in the future?
Olivia Anakwe: I am drawn to the meaning behind all of our actions so that is why I love Psychology. However, I want to go into Dermatology and use that unconventional background to offer a different perspective in the medical field.
Charlie Newman: Your career has really catapulted in such a short period of time. What do you to do to stay grounded?
Olivia Anakwe: Bikram yoga has been such an important practice in my life; mentally and physically it has kept my body balanced and stronger than ever. I also love going to coffee shops, reading, cooking with friends, and self-care rituals (sheet masks, essential oils, & wine!)
Charlie Newman: What advice would you give to any aspiring young boys or girls wishing to enter the fashion industry?
Olivia Anakwe: Don’t let anyone get in the way of your drive and stay level-headed. It is important to have confidence because you may receive a million “nos” until one person sees something in you and says “yes”. So always believe in yourself!
Charlie Newman: What has been your favourite job thus far and why?
Olivia Anakwe: Shooting the Miu Miu Spring Summer ‘18 Campaign with Alasdair Mclellan in the middle of the desert of Arizona was incredible. To shot alongside industry legends including Adwoa Aboah, Cameron Russell, Jean Campbell and Dakota Fanning was a total honour. It was my first time in Arizona and the whole team made the experience unforgettable.
Charlie Newman: I can see from your Instagram that your passionate about food. Is this something that was instilled within your family home or since moving to New York? What’s your favourite restaurant in the city?
Olivia Anakwe: Yes, I am a total foodie! Coming together for home cooked meals is ingrained in Nigerian culture – our Thanksgiving and Christmas is nothing less than a 20 dish feast. I have been cooking my own dishes since I was young, but was only introduced to healthy eating when I got scouted and moved to New York. Gathering to enjoy a meal is a ritual that I cherish. My favourite takeaway has to be Queen of Falafel, a mediterranean spot with the freshest falafel, pita, and roasted eggplant. For vegan pizza go to Paulie Gee’s – you will not even believe the cheese is vegan, simply mind blowing! For the latest obsession, Thaiholic, for clean Thai food with absolute flavour.
Read more: Where leading scientists and cutting-edge poets meet
Charlie Newman: I read that you did tap dance as a child. Is this something you’ve continued to enjoy? Have you found the movement and the performance elements of dance helpful to your modelling career?
Olivia Anakwe: No, sadly I don’t tap dance anymore but my background in dance has definitely complimented being in front of the camera. I am more aware of my body because movement allows me to flow into various poses and carry myself when walking into castings.
Charlie Newman: If you could wave a magic wand and change something within the fashion industry, what would you choose and why?
Olivia Anakwe: As always, inclusivity and representation. It is so important for people to see themselves in the things that they admire because it reinforces the greatness they can attain.

Instagram: @olivia_anakwe for Mansur Gavriel
Charlie Newman: I really admire the fact that you’re using your profile to promote good causes, such as organising the ‘Shake That Give Back’ event to help collect funds for the the NUWAY foundation and the Women’s Refugee Commission. Where did this idea come from and why did you chose these two specific charities?
Olivia Anakwe: The conversation sparked as we [Olivia and her friend Meghan] were discussing what we could do to give back towards the end of the year. We both love bringing people together so we figured why not combine both of these things into a huge celebration! We each picked a cause that was close to our backgrounds.
As a first generation Nigerian in America, giving back is something that is ingrained in our culture and a value that my mother and father always instilled. Discovering the NUWAY Foundation was particularly special because they are involved in charitable contributions that are quite active and really make a difference for the communities in Nigeria that they work with. Their message of ‘Give H.O.P.E.’ provides: Healthcare, Opportunity, Pure Water, and Educational resources and development.
Meghan chose the Women’s Refugee Commission as she is a child of refugees. Her mother’s family had everything taken from them, escaped Communism in Vietnam via a fishing boat and landed ashore on the Malaysian island of Bidong where they lived in a refugee camp for a little over a year. The Women’s Refugee Commission specifically helps to improve the lives of refugee women within these camps and empower them once they begin the start of their new lives. They provide services of financial education, reproductive health services and also educate other nonprofit organisations in ways to help prevent these dangers that women in the refugee camps may face.
Charlie Newman: Are you involved in anymore charitable projects this year?
Olivia Anakwe: Yes I am and more is to come! I will also be working with the Model Mafia group this year so be sure to follow along on my Instagram and @modelactivist for upcoming events!
Charlie Newman: Lastly who is your role model of the month?
Olivia Anakwe: My role model of the month is Michelle Obama! I just finished her memoir Becoming; it was so eloquently written and inspiring. She is a true powerhouse and a figure who has always stayed true to herself.
Follow Olivia on Instagram: @olivia_anakwe

Lenny Kravitz performs at the 2017 Leonardo DiCaprio Foundation Gala, with DiCaprio (centre) and Madonna (right)
Whether painting, music or immersive experiences, artists – and the art they produce – play a huge role in raising hundreds of millions of dollars for some of the world’s most deserving charities, says art auctioneer and LUX contributing editor Simon de Pury

Simon de Pury
I’ve done the auction for the Leonardo DiCaprio Foundation Gala for the past four years in St. Tropez. It has raised in excess of $100million for environmental issues. You know, we can try to save everything else, but if we don’t have a planet, there’s not much to save, so I find it very surprising that what should be probably our primary, main concern is just so low down the pecking order of people’s preoccupations. But Leo DiCaprio is probably the most important fundraiser for environmental issues in the world. It’s the longest auction of any auction that I do – people arrive at nine o’clock and it goes on till past 2am. So it’s a real marathon, because not only are there top artworks (he’s a very active collector, so all the artists donate their best works), but also experiences. There are once-in-a-lifetime experiences like going to the gym with Madonna or playing tennis with Federer.
Follow LUX on Instagram: the.official.lux.magazine
And the evening is interrupted by little musical intermezzos. So, last year Madonna gave a fantastic concert halfway through, and then the whole thing ended at 2.30am with an incredible concert by Lenny Kravitz. Once that was finished, the after-party kicked in with DJ Cassidy and there was the after-after-party at the home of Dmitry Rybolovlev. We were the first to leave at 7am. But the party was in full swing!
There’s more money in that tent than at any evening in New York. The combination between high-net-worth individuals – Russian oligarchs, people from the Middle East, former Soviet states, Latin America, America, Europe – mixed with top actors and top models, creates an electric, exciting atmosphere.
The other one that is very exciting is the amfAR Gala in Cannes, which always takes place at what I view as possibly the most beautiful hotel in the world: Hotel du Cap-Eden-Roc. The artworks are displayed in an incredible way. Coming out of the hotel, you see an alley leading down to the sea, and at the bottom of the alley is the star work of the auction. One year they had a Damien Hirst, the famous mammoth; another year, a huge sculpture by Jeff Koons. So, you can really show the works in a spectacular way, and once the guests come they all mingle on that beautiful alley.
The artist Joe Bradley – there is a long waiting list for his work, and he had a big show at Gagosian in Geneva – donated a really fantastic work for the auction. And it made €750,000, which is basically the price you have to pay if you’re lucky enough to be given the chance to buy one.
The other highlight of amfAR every year is when Carine Roitfeld curates a fashion show. And this year it was with 31 different designers, and she picks the theme, and she picks the dresses. One year it was all in gold; one year it was multicoloured; one year it was red. And then all these top models come down the stairs and walk up and down the catwalk and the stage with the most unbelievable music, and so it creates a fantastic atmosphere. And then, once all of the models are on stage, I come up and stand in front of them and start the auction. That’s by far my favourite moment as an auctioneer in any auction.

Supermodel Winnie Harlow at amfAR in Cannes this year
This year was the 25th anniversary of amfAR to raise money for Aids. Another Aids-related charity I’ve done auctions for is the Elton John Foundation. He invites 70 or so people to dinner in his home, outside London. It’s very intimate. He usually pairs up with another musician – John Mayer, Annie Lennox, Andrea Bocelli – and then he comes and plays himself. It’s really nice if you’re invited to a private dinner, so people pay a lot of money for their seat there – much more than they would for a larger gathering. During those evenings, we just sell three or possibly four items. So the main way of raising funds is people getting there.
The Elton John Foundation is one of the most effective foundations on the calendar in terms of research for Aids. He has been relentless for years and years with his Foundation, raising funds. It is remarkable just to see what he has done and how much he gives of his own persona, how much he gives of his own funds.
Read more: Behind-the-scenes of Maryam Eisler’s latest book “Voices East London”
For Aids there’s also the MTV RE:DEFINE annual charity auction. I do it every year in Dallas, in cooperation with the Goss-Michael Foundation, founded by George Michael and Kenny Goss. That is also a fun event because you always have each year an artist that is being honoured. This year it was Tracey Emin.
And the Robin Hood Foundation Benefit in New York raises the biggest amounts; you just have all these hedge-funders in the room and they say, ‘Now we’re going to put the numbers there… please put your pledges,’ and then bleep. ‘You’ve just raised $72million dollars, thank you so much.’
In terms of the cancer charities, there is Denise Rich, who founded Gabrielle’s Angels in New York. I do the Angel Ball auction every year. She takes the Cipriani Downtown, 650 people for a seated dinner. She had the whole Kardashian family coming last time – the whole family except Kim – and they are very close to her, which is very rare. One year she had Pharrell Williams performing and suddenly he said to me, “Simon, come on stage. I want to sell a dinner with me!” And all the women became crazy, screaming. Then Usher said, “I’ll join the dinner as well!” And that second impromptu auction raised more than the regular auction.
The Beyeler Foundation Summer Nights Gala in Basel, Switzerland, is the most original of any fundraiser, because director Sam Keller asks one artist to take over the whole museum and transform it for one night, which means that only as a guest do you get to see what the artist has done.
One year it was Olafur Eliasson and you arrived and everything was black and white, as if we were in a black and white movie. We sat down and started eating the food – black and white. It tastes bizarre when you don’t see the colours. Eliasson said, “Now you know what the world looks like without colour.” And then there was a total blackout and he said, “Look under your chair.” And everybody had this little lamp, and he switched a button and suddenly all the colour came back. The food started tasting very, very good the minute you saw the colour. It’s the most bizarre experience ever. He also did artworks just for that night, paintings all in different colours. All this was created just for the night.
I also love doing the New Museum Spring Gala in New York, because of the artists who attend. Very often you sell great art at these events, but you have no artists in the room – maybe one or two. But the New Museum event is carried by the artists. This year were three of my favourites – all women. Julie Mehretu, Cecily Brown and Elizabeth Peyton, who is my favourite portrait artist today. If you had to choose who would be your dream person to do your portrait, she would be top of my list, and the New Museum had shown a mid-career introspective of her. Besides that there was new work from Jeff Koons, from George Condo… there were something like 55 artists in the room.
In terms of the contemporary art world, the New Museum Spring Gala is possibly the most exciting one, because personally I always find that the most rewarding thing in terms of what we do is the contact with the artists themselves. Nothing is more stimulating. They have such a fresh way of looking at everything. And that’s what I love, because, after all, without the artists all the rest is meaningless.
Simon de Pury is an art auctioneer and collector and the founder of de Pury de Pury. Find out more: depurydepury.com


Model and musician Rebeca Marcos. Image courtesy of Models 1
LUX contributing editor and model at Models 1, Charlie Newman continues her online exclusive series, interviewing her peers about their creative pursuits, passions and politics

Charlie Newman
THIS MONTH: Born in Germany and raised in Spain, 25-year-old Rebeca Marcos has achieved a remarkable amount in a quarter of a century. She started modelling at the age of 20 whilst studying for her Undergraduate Degree in Politics at City University and has since starred in campaigns for Whistles, Armani Exchange and The Kooples, and walked for the likes of John Galliano. She also plays music as part of electro-dance duo Park Hotel. Charlie speaks to Rebeca about self-confidence, career highlights and philanthropy
Charlie Newman: What was it like growing up in Spain and how easy was the adjustment moving to the UK?
Rebeca Marcos: My upbringing was wonderful. Family gatherings were always big and long, I was spoiled for food and good weather. We were encouraged to dance and perform for our family and the beach was super close. My neighbours and I used to go exploring the woods as small children and later on, I joined the scouts at school and we used to go to this old watermill that had no electricity or running water and also no parents nearby so that was wonderful.
Follow LUX on Instagram: the.official.lux.magazine
As a teenager Barcelona was a great city to be – very multicultural and beautiful. After school, in the warmer months, we could go to the beach just to hang out and even in winter it’s always sunny. I was a very happy child. I went to a German school from Kindergarten through to the 12th grade, so I grew up in a strange place culturally speaking. They are very opposite cultures in many ways so moving to London didn’t really feel like a cultural shock. I’m quite sensitive and introverted so I think I internalised the British default setting of being reserved and socially awkward quite quickly. I could read the discomfort in peoples faces with the slightest bit of over sharing, but London is also the place where I learnt manners! Either way, I was one of those European teenagers who loved Harry Potter and my graduation gown was of the colours of Gryffindor so I was living the life, plus the music scene [in London] is so much more stimulating than Barcelona’s.

Image by Rob Aparicio via Instagram @rebecamarcosroca
Charlie Newman: You have graced the pages of many high fashion glossies as well as walking for top brands on the runway. What has been your favourite job so far?
Rebeca Marcos: That’s such a hard question! I have had so many nice experiences and been lucky to work with some amazing creative geniuses. Years ago, I did a shoot for Urban Outfitters with Magdalena Wosinska and we just spent days hanging out topless in nature, riding quad bikes at Dave England’s house (a stunt performer in Jackass) and listening to music. It was great fun. But then I also shot the s/s15 campaign for Phillip Lim in Marrakech with Viviane Sassen and that was like a dream. Everything was beautiful, everyone was chill, we shot without hair and make up and then had a day left to go explore the YSL museum and the Souks. The wonderful production team (who had just finished working on Mission Impossible) helped me buy a gorgeous rug which they took to the hotel for me and I still have. The pictures are still some of my favourites and honestly, I think it was one of the most inspiring shoots I’ve ever been a part of. I also really love Christopher Kane both as a human and a designer. Fitting and walking for him is a very graceful experience.
Charlie Newman: If you could shoot with any photographer who would it be and why?
Rebeca Marcos: Carlota Guerrero. She is a brilliant photographer from Barcelona and I love her work and I bet she is a great human to work with.

Instagram @rebecamarcosroca
Charlie Newman: You shot The Kooples S/S15 campaign with your boyfriend – what was that like
Rebeca Marcos: It was a great experience. They are some of the nicest pictures we have together and it’s always wonderful to shoot with your best friend and in Paris. It was also the first time I shot with my guitar on set and in a way it was great to have Kristian there, but it was also a challenging experience which I grew from. He was the musician in the room, he was getting all the attention for that and I didn’t know if it was the fact that I am a model, or the fact that I am a girl in the underrepresented world of female musicians, or if I was being oversensitive and too insecure about my musical side. I really had to pull my pride together and to say: “No, actually I’m going to pull my guitar out as well. Nobody has invited me to do so but I’m not just going to stand here as a hot groupie because I really don’t think I need to.” It was awkward but I am so glad I did. It was a drama that happened exclusively in my head mind you, but still it was a very important experience for me.
Read more: How Los Angeles became a world-class art capital
Charlie Newman: How easy was the transition from modelling to musician? Do you find they compliment one another or do you find you have to prove yourself twice as much?
Rebeca Marcos: Well I don’t think I ever transitioned. Modelling is something I don’t think you can have any control over, it’s something that happens around you while you are “being yourself”. We are like muses for hire. I have done music since before I started modelling and I’m still doing both. There’s always people who think that if you are beautiful you can’t have any skills but who cares? Not me, I’m the one with both. I don’t look in the mirror and go, “shit I’m too beautiful to write some music today.” Who the hell thinks like that? People think they are ugly and stupid, when really their only problem is their self-esteem and binary thinking. I don’t subscribe to the capitalist idea that one has to work hard to be valued. I think if you love yourself then people won’t be distracted by your insecurities and instead pay more attention to whatever you want to express. They’ll figure out your value by themselves. And if they don’t, block them! I work with passion and that is always more productive than trying to prove yourself to imagined strangers. And if I’m supposed to work twice as hard then I’m probably heading for failure. I hope I’m not. Anyway, I definitely think music and fashion go hand-in-hand. They are both informed by and inform culture, and they inspire one another. So in theory it should be easier for me to work in both. We’ll see!
Charlie Newman: So can you tell us a bit about your band Park Hotel?
Rebeca Marcos: Park Hotel is a dance band. We are a duo fronting it, but we are really a great live band of up to 6 musicians: guitars, synths, drums and percussion. The sound has a post-punk feel to it, but it’s hugely influenced by funk, EDM and even disco. But it’s got a bit of a dark vibe too. It’s like a nihilistic party. Me and Tim – the other half of the duo – met 4 years ago. He had been concocting this project in his head for a while and we’ve been gigging for a couple of years now loving life.
Charlie Newman: What music did you grow up listening to? Do you come from a musical family?
Rebeca Marcos: Yes and no. My parents aren’t very musical but my sisters played violin, cello and piano whilst I was growing up. My dad exclusively listened to about 5 different albums of about 4 different bands, the only international ones being Pink Floyd and Santana – great musical taste, just a little limited. My sisters and my mum just liked the radio, and my sisters were hugely into the Spice Girls, Shakira and Britney Spears. It wasn’t until I was a teenager that I got to expand my musical horizons and I found out that Pink Floyd’s early stuff was a whole different kind of psychedelic.

Image courtesy of Models 1
Charlie Newman: In light of the #MeToo movement, is there anything within the fashion and music industry you would like to see change?
Rebeca Marcos: Well, I believe values are stronger and more reliable sources of change than rules. Sure, models shouldn’t be sent to photographers that are predatory and same with producers that never get called out on by money-minded labels. But both industries are becoming more and more saturated, women just need to keep standing up for themselves and getting together, and the roles that are available to be played by individuals of any gender should be more fluid. If people truly focused on being more compassionate and respectful from the get go, these things wouldn’t be hard to understand, no matter how privileged you are.
Charlie Newman: What advice would you give to young models starting out now?
Rebeca Marcos: Be strong, focus on your happiness and try to experience the teenage years of your career as life experiences and not as career building. Young girls shouldn’t be expected to have figured out what type of brand they want to develop, or be pressured into having a stellar career immediately.
Charlie Newman: Are there any philanthropic causes that you are particularly passionate about?
Rebeca Marcos: The charity of *Talk To Your Local Homeless Person* even if you just say: “how is it going?” and spare some change. They need to be humanised and we are all individually responsible for the people who have fallen through the cracks of our society and need help. We don’t have to give change to every single one of them, that is not our responsibility, but at least keep them and their pain in mind, because that is the least we can do.
Follow Rebeca Marcos on Instagram @rebecamarcosrosa and her musical endeavours via @parkhotelband

View from a penthouse in the Parc Du Cap development by the Caudwell Collection
In 2006 British entrepreneur John Caudwell sold his pioneering telecommunications company, the Caudwell Group, which included high-street mobile phone retail giant Phones4U, and turned his attention to property and philanthropy. His luxury residential development company, the Caudwell Collection boasts a portfolio of properties in prime locations across the UK and France whilst Caudwell Children is one of the leading charities in the UK for children’s disabilities. LUX Editor-in-Chief Darius Sanai speaks to the billionaire about real estate, Brexit and building a centre for autistic children

John Caudwell
LUX: You were known in the UK as one of the big mobile telephone entrepreneurs back in the 90s, 2000s, but now you are involved in property development. How did that happen and has high-end property always been one of your passions?
John Caudwell: I wouldn’t say it was a passion because for one thing I would never have had the money to exercise or endorse that passion, but I’ve always had a passion for beautiful things, especially beautiful architecture. So, my factory, for example, the Victorian tile factory, that was completely derelict until we took it over. We completely restored it and made it into a really fabulous headquarters for the business. So I guess I’ve always had that interest but not as a property developer, more in terms of developing properties for my own business use.
Then the crash happened, and it was almost impossible to find anywhere to put your money that was safer than under your bed, so you have mattresses stuffed full of £50 notes everywhere. The world was so fragile that you could not have any confidence that it was going to pull through and that your money was going to hold its value. So I decided to put my money into equities that I thought were resilient to a world collapse.
Follow LUX on Instagram: the.official.lux.magazine
LUX: What kinds of equities?
John Caudwell: So essential commodities and essential items, things that are always going to be there. For example, there’s always going to be farming, there’s always going to be land and water. Not so much oil these days because that’s a thing of the past, but there were items you could recognise that were probably going to be reasonably – not recession proof – but certainly collapse proof because they would always be needed. Of course even those things were fragile because everything took a big hit, but because commercial property had dropped in value enormously, I decided to start buying property that had long lease holds or even in some cases, shorter lease holds that I could develop and try and add extra value to. That’s how I got into property, but it wasn’t aesthetically pleasing or beautiful property, it was was purely to protect myself commercially. And it did quite a good job – I built up quite a good portfolio, it wasn’t meant to make a lot of money, it was meant to be a protectionist measure. But from that, agents who were having a tough time as you can imagine, came to us with various properties and people came to us with properties that I was actually interested in, things of beauty. For instance, one of the ones we bought was Provencal in the South of France.

The living space in Les Oliviers by the Caudwell Collection
LUX: How’s the development going? Is there a scheduled completion date?
John Caudwell: In the South of France we’ve completed Parc du Cap – a luxury development with 88 1-4 bedroom apartments and penthouses, and Les Oliviers – 6 spacious apartments in a beautifully restored Art Deco building, both in Cap d’Antibes, and we’ve got other Caudwell Collection projects there as well, like Provencal. We’ve been working with the authorities to get Provencal to a point at which we believe it is developable – and after several significant challenges we’re now in a place to say work is fully underway to create 35-40 ultra high-end apartments there. We aim to launch in 2021-22. Over in London, with the Audley Square property, we’ve had to work very, very closely with Westminster council and the planners, and obviously everyone’s got their own angle but there’s been a real spirit of cooperation because everybody wants to see it happen. It’s good for the city because it turns an eyesore into a beautiful building, not to mention the jobs it creates through the building work.
Read more: Inside Lake Como’s luxury residence, Villa Giuseppina
LUX: And with the London developments, such as Audley Square, how did that come about?
John Caudwell: It came about as a result of us becoming aware of the site and contacting Nama, who were the people who held all the debt. You might know Nama as the Irish bank that took all the property debt? We ended up in a two-year negotiation with Nama on the site. It took a long time because there were a lot of fundamental problems with the site, there were a lot of risks at that time and the price they were asking for was too high. But eventually, whilst we were negotiating. we worked through some of the problems and did a whole range of due diligence exercises to try and assess and minimise the risk as well as reduce the price. Eventually, it got to a point where it was acceptable so we did the deal and then that was the start of all the work!

Les Oliviers was partly restored using local materials and products
LUX: The properties that you’re creating are very high-end, sophisticated, luxury – is there a plan to broaden the brand, the Caudwell Collection, beyond property?
John Caudwell: Well, we are already doing that partly, but depends on the success that we have and we do expect it to be extremely successful. But you know the situation in the UK at the moment is not so good with stamp duty, and the Brexit situation. I mean London is the powerhouse of the world, it’s a fantastic city and will remain a fantastic city – I am extremely positive about the future, but I am a bit concerned about the effect stamp duties have had on the market. I don’t disagree with it incidentally, I think it’s fair enough to raise all these huge sums of money from wealthy people who can afford very expensive properties, but it has damaged the property market. The non-doms, I don’t disagree with either, I don’t disagree with it from a moral point of view because I think the rich have to pay their appropriate share of the taxes, but it’s not good if you start losing very wealthy people who take their economic interests to other countries like Paris and New York and Monaco and so on. Those countries that welcome them, are then taking our livelihood away because those people, by being financially centric to London, also tend to then have a lot of their business interests in the UK and tend to be much more likely to have business centres in the UK.
Read more: Entrepreneur Adrian Cheng & leading architect James Corner are redesigning Hong Kong
And then of course Brexit as the next stage of that whereby I was very strongly pro-Brexit. I wanted a clean proper Brexit with a strong government and I said that when the Conservatives called the election, I said if there’s no other reason why the people vote Conservative, it needs to be to give the power to the party to negotiate a deal. And now where are we? Nearly two years down the line, we’ve got a very, very weak Conservative government with no majority, with a lot of back biting from within, with the house of Lords almost seeming to sabotage the position. I think, at the moment, it’s all very worrying because we needed a strong powerful Brexit or we needed to stay – we needed to either be properly in or properly out, not some horrible mishmash in the middle that doesn’t deliver the benefits. If we’re not careful we’re going to have all the pain of Brexit and limited benefits, which would be a fiasco. So, I am a bit concerned about that, it’s long answer to your question but the answer does relate to how far I see the Caudwell Collection going. And also, opportunities because opportunities like the Audley Square, that allow you to turn something that’s very, very ugly into a thing of beauty, or Provencal, which has been derelict for thirty years, but if we do what we’re planning to do there will become a most magnificent property, on par with some of the properties in Cannes. Those sorts of opportunities don’t come up every day and to be able to make those into a commercial success as well as an aesthetic success, is something that plays very much into my absolute ethos.

The original building façades of Les Oliviers were maintained during the development
LUX: Do you find this new business as consuming as Phones4u and your other previous companies? Or is it more of a side-line in terms of operating?
John Caudwell: Totally different. Phones4u was my life, my absolute life. Most people know of it because of the high street brand, but we were the world’s biggest in nearly every area in which we traded, which was accessories, hand set distribution, we even had our own in-house recruitment company with about 70 or 80 employees there, and we even recruited for other people. Same with security, we did our own security but then did it for other people, so we grew into what was a bit of an empire really, where several of my businesses were the biggest and best in the world. So, it was a complete and utter all-consuming thing, and also it was my entire wealth, so you know, fail at that and I would have been entirely broke, probably not totally broke, but I would have been broke.

An aerial view of the Parc du Cap development
Succeed at that and then the result is the result that I got. But it was also extremely stressful, every minute of every day was extremely stressful, and I could never live that life ever again, nor would I want to, so that’s gone, and I am glad it has, but they were very special years. It’s different now, these businesses I didn’t need to do because my life now is all about philanthropy. But when they came along, and I saw them, I thought well, that’s a really interesting challenge. It gives me the opportunity to create a thing of beauty, put my stamp onto London with a building that’s going to be beautiful and timeless and make money as well. It’s a unique situation and a lot more pleasurable. I’ve got a great team of people who are helping me to run all of this and it’s a much more relaxed situation. I’m nowhere near as dedicated to it in terms of my time and effort because I have people who do that, but also its not as stressful and threatening as the mobile phone business was, which was ferocious, every minute of the day. That doesn’t mean its easy – it isn’t, we’ve got to be smart, we’ve got to be clever. Lots of problems to address and solve and we’ve got to create the vision of beauty that we promised.

The view from a penthouse in Parc du Cap
LUX: How important is it for you that people talk about the Caudwell brand in relation to the properties you develop?
John Caudwell: The brand stands absolutely for quality. When people go to the Parc du Cap building, which is the one that I wouldn’t have built, but it is a beautiful, beautiful development, and most people who’ve visited it, say it feels quite pricey, and they understand why it is quite pricey, because the quality is exceptional for that coastline. And everybody says they’ve never seen another development of that quality which is quite nice to hear and that’s sort of part of the Caudwell collection brand. We got the same feedback with Les Oliviers it was the same feedback; it is a building that is really a fantastic quality throughout and is really desirable to live in, and that’s exactly what we’ll do with Provencal once we get started. We are creating these buildings of huge quality and recognisably of huge quality, it’s not just me saying it, but these properties stand the test of third parties too, whether they’re agents or buyers, everybody thinks they’re beautiful.
Read more: Caroline Scheufele on Chopard’s gold standard
LUX: There are parts of Les Oliviers that you restored, using local products and materials. Is restoration an important aspect of your developments?
John Caudwell: Our design approach with Les Oliviers was to carefully restore the original building façades and use some locally sourced materials including natural stone for the terraces and loggia floors, and Provencal limestone paving around the swimming pool. The quality of the finished product is exceptional – from the apartments fitted out with high tech features and contemporary yet classically inspired interiors through to the beautifully manicured Provencal style gardens. You can’t necessarily use local materials all the time and of course it’s a commercial venture, so I don’t put local materials as the priority but what I do put as the priority is that it must be as environmentally friendly as possible. For instance, with Audley Square, we’ve put geothermal in, and I’ve just put geothermal into my house. The whole point is to try cut down on pollution and energy loss.

The living room in one of the two bedroom apartments in Parc du Cap
LUX: Finally, can you tell us more about your philanthropic work and in particular, the Caudwell Children.
John Caudwell: That’s extremely exciting because we help children with 600 different illnesses. During the 18 years that we’ve been running, we’ve had more applications from parents with autistic children than any other category, in fact we’ve had so many applications that 50% of the work we do is with autistic children. We developed methods of intervention that have helped thousands and thousands of children and their families live a better life. Of course, autism is an extremely broad condition; it’s the families of autistic children that have difficulties managing and coping emotionally and physically and that’s where we’ve focussed our effort over the years.
There are around 700,000 people on the autism spectrum in the UK, so the task I gave to my chief executive was how to find more and more children and how to change the medical profession’s understanding of and attitude towards autism. We believe we can substantially help to improve the lives of autistic children and we’ve done it many, many times, but people who wish to be cynical could say that the autistic child would have carried on, on that developmental path anyway, so what you’ve done has made no difference because the child may have made that progress without you. So we’ve built this centre and are putting a big team of medical people in there to prove to the medical authorities that we can intervene in autism and that we can improve the lives of autistic children. When the centre opens in the next couple of months, we’ll still carry on the work for all the other children as well but the focus will be on autism. And if we can change the NICE guidelines to read differently, then doctors around the country, instead of diagnosing an autistic child and saying to the parents, ‘I’m sorry there’s absolutely nothing we can do, just go home and do the best you can with your child and keep your child safe and healthy’, they’ll be able to say, there is help you can get and this is what can be done and this is who you might go to and this is the way you can improve your child’s life.
To view the Caudwell Collection’s portfolio of luxury properties visit: caudwellcollection.com
For more information on Caudwell Children visit: caudwellchildren.com

Wendy Yu. Portrait by Jonathan Glynn-Smith
Wendy Yu – entrepreneur, investor, cultural ambassador, fashion devotee, and frequent flyer between Shanghai, Hong Kong, London and New York – is taking the word ‘global’ to a whole new level, as Elisa Anniss discovers when they meet
Instagram can be hugely revealing about the people who use it, though rarely will you get the fullest picture of any of them. With her 1,913 posts and the 94.1K followers of her Instagram account, @Wendyyu_official, it still paints only a partial picture of this remarkable young woman, who is the founder and CEO of Yu Capital, a major Chinese investor in fashion and technology, an entrepreneur and a philanthropist.
Nevertheless, snaps of Wendy Yu with Giambattista Valli, Thom Browne and Charlotte Olympia do reveal her stellar fashion credentials. There are the images of the Met Ball in New York and of a dinner for her friend Mary Katrantzou, co-hosted with Lord Rothschild at Waddesdon Manor. Instagram also tells us that she appears to be something of a collector of evening gowns. Indeed, the rare snap of her in trousers raises an obvious question. “I love both, to be honest,” she darts back, when challenged. “I’m very spontaneous. Sometimes I love things that are dreamy, crazy and imaginative. At other times I just like very simple things. I love to be a chameleon, it really depends on my mood.”
Follow LUX on Instagram: the.official.lux.magazine
This morning she’s flown in from Hong Kong. For the flight, she wore head-to-toe Alaïa with a yellow Mary Katrantzou fur. It’s typical of what she wears on planes – Alaïa or a kaftan from Oscar de la Renta paired with flat shoes. “All super comfy so I can sleep easily.” Last month she flew every two or three days. Shanghai is her main base, but Hong Kong, London and New York, are all places where Yu regularly spends time. “New York more now because next year we’re launching an exciting project there,” she ventures, but that’s all she’ll give on the details. Still, Shanghai is where she has a home and where her parents’ live – Yu is heir to her family’s business, the Mengtian Group, China’s leading wooden door manufacturer.
It takes sitting down and talking to this young entrepreneur and philanthropist to see that dressing up and accumulating possessions isn’t really what drives her. Her enquiring mind and the way she lights up, crackling with enthusiasm and talking nineteen to the dozen when discussing her many passions, leaves a lasting impression. It’s certainly something that Instagram is unable to convey. Fashion, disruptive technology, the arts, China and being a Sino- Western bridge connecting people, are just some of the subjects she tackles with energy.
“Wendy is passionate about London designers and entrepreneurs and has definitely made a positive impact by supporting some of the best talent out there. We need more people like her,” enthuses José Neves, the fashion-tech businessman who founded Farfetch, and husband of Daniela Cecilio Neves, in whose business Yu was an angel investor. Undoubtedly, it was Yu’s inquisitiveness that brought her to England in the first place. This involved spending time at school in Somerset, in the English countryside where she got a taste of the British boarding school system as well as meeting other, mostly non-Chinese pupils. Next, she went on to complete a degree in fashion management at the London College of Fashion with a stint in between interning at Vogue China. She has also completed executive business programmes at the universities of Cambridge and Oxford, interned for a family office in the Middle East and has spent time working for Mengtian. “Truth be told, while education is important, it’s not until you do internships and start working that you really learn about business,” she says.
Wendy Yu and Caroline Rush, Chief Executive of the British Fashion Council, co-hosted breakfast for Vogue China’s Editor-in-Chief Angelica Cheung
Today, Yu is the youngest member of the Fashion Trust, a British Fashion Council charity, and a founding member of the Victoria and Albert Museum’s Young Patrons’ Circle. Even though she herself doesn’t use the word ‘anglophile’, with her love of Harrods – “I still vividly remember the first time I went [there]. It really ignited my passion for fashion” – and her appreciation of British life beyond London – “I love the town of Taunton, and Devon is beautiful, too”– it’s a moniker that fits.
Read more: Geoffrey Kent on finding new places in a well-travelled world
In 2015, Yu founded the investment vehicle Yu Capital and in January 2018, Yu Capital became Yu Holdings. Yu Holdings is a platform created to unite the worlds of strategic investment, technology, philanthropy, arts and culture and to reinforce business and cultural ties between China and the rest of the world.
“The evolution of Yu Capital into Yu Holdings was a strategic decision to consolidate my investment activities with my cultural and fashion projects, all with the end goal of bridging the economic and cultural gap between China and the rest of the world, a mission that drives every decision Yu Holdings makes,” says Yu. The investment vehicle is divided into three main areas of interest: Yu Capital, Yu Fashion and Yu Culture. Yu Capital, the investment arm of Yu Holdings, is focused on strategic investment in global technology, lifestyle and fashion businesses that show high potential for growth in a global market.
Yu’s two technology investments are Didi Chuxing (for more information see end of article), the largest taxi-hailing firm in China, valued at US$35 billion and whose other investors include Apple, Alibaba and Tencent, and Tujia.com. This Chinese online marketplace and hospitality service enables people to lease or rent short-term lodging, something like Airbnb (see end of article).
“Because Didi and Tujia are both multi-billion-dollar companies, they have very big and powerful investors. I’m involved financially rather than strategically,” she notes. “I’m generally less involved with technology investments than with my fashion and lifestyle investments, where I look to add value and contribute to their development and growth.”

One of Yu Capital’s recent ventures, Mary Katrantzou, with her SS18 show
Earlier in 2017, Yu Capital made its first luxury fashion investment in the London-based designer brand Mary Katrantzou (see end of article) whose sought-after collections are sold in leading luxury stores around the globe. Yu confesses that before she makes the final decision on an investment she consults with her fortune master, who told her great things about Mary, prompting her to go ahead. “At the back of my mind there is always the question, is this relevant to the Chinese market?”
Read more: President of Monaco Boat Service Lia Riva on the family business
Whether she proceeds with a fashion investment or not also depends on the chemistry she has with a designer as well as the company’s future potential. “With Mary, I really like her as a person as well as a business woman. Her enthusiasm is infectious and she’s hugely talented.” She was also struck by Katrantzou’s background in architecture and opportunities that lay waiting in the whole lifestyle sector.
Yu believes that past collaborations with Adidas, Moncler and Topshop have already helped Mary Katrantzou capture the attention of Chinese consumers and that there is still greater opportunity there for Katrantzou’s core brand. “We are very open to the new emerging designers and the purchasing power in China is now very strong. However, one needs to select carefully which partners in China will be the best in the long term because they all want exclusivity.” Yu can help Katrantzou navigate these complexities. “I don’t have any agenda, I only want what’s best for Mary,” she says.
The investment in Mary Katrantzou followed two made in 2015, one in ASAP54, recently re-branded Fashion Concierge, and another in the sustainable accessories brand Bottletop. Yu was drawn to Fashion Concierge by the disruptive technology it displayed at the time of its launch, whereas with Bottletop it was the idea of social investment that appealed to her. “I liked their concept and approach to sustainability,” she says. As a pioneering fashion accessories brand (founded in 2012 by Oliver Wayman and Cameron Saul, the son of Mulberry founder Roger Saul), the brand revolves around the simple idea of re-cycling the ring pulls from drinks cans – hence the name. A novel, sustainable, chainmail-like material, often with an enamel finish in a range of colours, helps to make Bottletop products, which include totes, clutches, backpacks and belts, instantly identifiable. The company also funds the Bottletop Foundation, which supports young people in Brazil, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi and South Africa. “Wendy is a rare visionary and we have loved having her as part of the Bottletop family,” says Saul. “Wendy is also very strategic and has supported us with important introductions as we position the brand to launch in Asia.”
This is echoed by Daniela Cecilio Neves of Fashion Concierge: “I’ve greatly benefited from Wendy’s insights as a tech-savvy, fashion-loving individual, who can also provide me with a perspective on China,” she says.

Wendy Yu at the Women’s Opportunity Center in Rwanda
Ever since Yu took a trip to Rwanda with Brita Fernandez Schmidt, the UK executive director of the charity Women for Women International, social investment, and how similar principles could be applied to the less developed parts of China, have been at the forefront of Yu’s mind. “Brita invited me to see her work in Rwanda because that’s where they have the Women’s Opportunity Center. I’m very curious and I’ve always wanted to see different parts of the world. It was the most inspiring trip I’ve ever been on. I’m looking to potentially develop some culture-related projects with Women for Women, as Brita is keen to see rural parts of China. As a Chinese woman, I would like to explore how we could create support areas in China where there are still huge gender inequalities.”
This leads into the overarching ambition of Yu Culture, the purpose of which is to enrich China’s cultural landscape through development and exchange initiatives in film, art and media, and by working in special partnership with international cultural institutions on projects to be unveiled in 2018.
Yu is already closely involved in the Victoria and Albert Museum. “The V&A has been one of my favourite museums since my student days,” she enthuses. “They invited me to join and I said yes without hesitation.” Her role includes introducing friends from Asia as well as a young group of people from the international fashion and art world. “It’s a bridge, again,” she continues. “Introducing people comes very naturally to me. It’s win-win for everybody because they love the V&A and getting to know the industry community, and the museum loves to meet new art collectors.”
Her involvement is certainly appreciated by the museum. “As a Founding Member of the Young Patrons’ Circle, Wendy Yu has been an enthusiastic supporter of the Victoria and Albert Museum, not only contributing to the successful launch of this important initiative and its exciting programme, but also through her involvement with the Museum’s annual Summer Party and her passion and knowledge of the V&A’s fashion collection,” says a senior museum spokeswoman.
“I love to be the bridge between China and the rest of the world because I love both cultures and want to enhance the connection between the two,” continues Yu. The South China Morning Post recently described her as being both “a sounding board for British designers negotiating the labyrinthine ways of doing business in China” and China’s “unofficial ambassador for British fashion”.
Net-A-Porter, a company Yu admires because of its “great customer experience”, invited Yu to become one of its global ambassadors. In this new capacity, she is scheduled to take the former Prime Minister’s wife, Samantha Cameron, and her clothing brand Cefinn, which sells on Net-A-Porter, to China in 2018. It’s a collection she considers to be super wearable with a good price point. “I’ve been wearing her blouse with different outfits and wearing her skirts,” enthuses Yu. “I respect Samantha’s vision and I think Cefinn would be very relevant to Chinese professional ladies.”
According to Yu there are still major differences between the West and China, particularly in terms of technology. In China, she can go out carrying just a mobile phone. She explains that instead of a wallet, Chinese people use Alipay, a third-party mobile and online payment platform established in China in 2004 by the Alibaba group, or WeChat Pay, launched by Tencent.
Her insight into a world that the West is hungry to know more about, is just one of the reasons why she is so in demand in the fashion world. “Wendy’s business acumen and knowledge of the financial sector are invaluable assets to our British designers hence why her support and dedication to the BFC Fashion Trust are so invaluable,” says Caroline Rush CBE, chief executive of the British Fashion Council. Yu describes Rush as “a friend and a mentor” and is someone with whom she co-hosted a breakfast to welcome Angelica Cheung, the Vogue China editor-in-chief, to London. Yu’s involvement in the BFC Fashion Trust has also led to her meeting many designers and learning about the challenges that they face. “You find that a lot of designers are super-creative but they don’t really have that business sense. Nowadays, for a fashion brand to evolve, you have to have both creative vision and to understand the commercial world, exactly who the customers are and what they are looking for.”
Read more: Why we love Club Dauphin on Cap Ferrat right now
Huishan Zhang is a London-based designer in Yu’s friendship circle who is known for his classically feminine evening gowns and dresses that sell in his Mount Street flagship. Like Yu, Zhang was born in China, but left when he was still a teenager. “I’m great friends with Huishan Zhang,” Yu says. “He’s a lot of fun, we share a lot of friends and look to support each other as well, on both a personal and a business level.” According to Yu, he makes her made-to-measure dresses for her and she collects signed sketches of his designs. “Wendy has been a good friend to me,” says Zhang, who doesn’t manufacture in Italy but produces his clothes in his family’s factory in China. “She is an active entrepreneur and supporter of the fashion industry, honing in on new talent, along with great passion and a unique style.”

Portrait by Jonathan Glynn-Smith
It’s mid-afternoon and we’re coming to the end of our interview now and still there’s no sign of any jet lag or of her flagging post-photo shoot. Yu’s energy levels are high. But then they have to be, as she’s off to Lisbon next, speaking at Web Summit, which bills itself as “the largest tech conference in the world” and welcomes an extensive and diverse line up of speakers ranging from Al Gore to Suzy Menkes. Yu says she’s booked to talk on two panels, one with Caroline Rush and another with the CEO of Matchesfashion.com and Vestiairecollective.com. “It’s all come about very spontaneously and it’s a nice group of industry insiders.”
It won’t be Yu’s first foray into the speaker circuit. In June she appeared on the British Fashion Council’s Fashion Forum panel alongside a group including Yana Peel (CEO of the Serpentine Galleries) and the shoe designer Rupert Sanderson, discussing cultural and commercial partnerships in China. She has also given similar talks covering her investments and connecting with China, in Cambridge and at London Business School, as well as back in China. When asked if she ever gets nervous about speaking publicly she replies: “No, not really. Though I always prefer talking on a panel, it feels more natural. I wouldn’t say no to a glass of champagne if my nerves get the better of me!” And why not, I say.
LUX would like to thank 45 Park Lane in Mayfair, London, for the use of its exquisite Curzon Suite for the shoot of Wendy Yu by Jonathan Glynn-Smith. 45 Park Lane is the artistic sibling to The Dorchester, next door, and has a fabulous program of art events, its own curator, and its own artist in residence. dorchestercollection.com
For more information on Wendy Yu’s investment platform visit: yu-holdings.com
Mary Katrantzou
Mary Katrantzou, who won the £200,000 BFC/Vogue Designer Fashion Fund prize in 2015, is Yu Capital’s most recent investment. One of the heavy hitters at London Fashion Week, the Greece-born designer delights the audience each season with highly original ideas brought to life using elaborate embroidery and embellishment, a mix of textiles, prints and silhouettes and an inimitable signature that shouts Mary. The London-based ready-to-wear marque was established in 2008, after the designer graduated with an MA in Fashion from Central Saint Martins. She was soon dubbed The Queen of Print by the press, a tag that recognised the enormous influence of her work in the medium. In recent years, collaborations, including capsule ranges with Longchamp, Moncler, and Adidas Originals, have helped to broaden her appeal at home and abroad, and of course in China. Mary Katrantzou doesn’t have a bricks-and-mortar store, yet, but she does sell to leading luxury stores in many countries including Harrods, Harvey Nichols, Bergdorf Goodman, Saks Fifth Avenue and Le Bon Marché. “Wendy is an extraordinary person with a pragmatic and forward-looking vision, who is a close friend as well as an ambassador for the brand,” says Mary Katrantzou. “The most important thing for me is to be surrounded by people who understand my vision and support me in building a truly international lifestyle brand. It’s very exciting to enter our 10th anniversary with a board of incredible women advisors who are shaping the industry in their own right and will be helping us shape our future and reach our full potential.”
Tujia
The rental company has taken couch surfing to a whole new level with $300 million of investments announced in October 2017. Giving Airbnb a serious run for its money, and valued at $1.5 billion, Tujia was founded in 2011 under Tujia Online Information and Technology Company of Limited Liability. With 345 locations across China to choose from and at least 1,000 partnerships internationally, it boasts 650,000 listings and is tapping into a large affluent travelling class, revolutionizing the hospitality industry in China.
Didi Chuxing
The taxi-hailing app is China’s answer to Uber (in fact, it acquired Uber China in 2016) and is the largest such company in the world, with 200 million rides under its belt last year. The app was launched in 2012 and today has over 450m users across the Chinese continent, spanning 400 cities and a variety of services. From social ride-sharing to options including Didi Chauffeur, Didi Bus and Didi Car Rental and Hitch, its social ride-sharing branch, it has taken China by storm and has recently developed an English-language version of the app. It is also looking towards the future with groundbreaking investment into AI technology, with over $5.5 billion raised in 2017.
This article originally appeared in the LUX LOVE Issue, Spring 2018

Image by Oliver Schwendener
After years of exploring the remotest corners of the globe, Geoffrey Kent has perfected the art of being prepared. Here the Abercrombie & Kent Founder reveals his travel essentials – and what to avoid on your next trip

Young adventurer Geoffrey Kent
I’m never without my Louis Vuitton briefcase
Good hand luggage is vital. If you are travelling commercially, carry your need-to-have items with you and not in the hold. I always check my luggage as it comes out so fast these days but I’m never without my Louis Vuitton briefcase. It’s a Président Classeur from 1972 that’s been all over the world with me. I guess you could say it’s become my signature piece. I love that you can fling it in the back of a truck or helicopter luggage hold without it getting dented. No matter what I’ve done to it or where I’ve taken it – it always looks good.
Follow LUX on Instagram: the.official.lux.magazine
In a pinch, I’ve used it as weights for my daily workout when staying in a tent in the middle of nowhere. Fully packed, it weighs about 11kg. I’ve also used it to get out of many a hole – figuratively and literally. In Tanzania when my Land Cruiser got stuck on a dirt track, I put my case down in the mud, placed the jack on top and jacked the vehicle out. It’s indestructible. Little did I know, when I bought it nearly 50 years ago, that it would still be going strong half a century later. Talk about a future heirloom…
Or my Iridium satellite phone
Louis Pasteur said that “chance favours the prepared”, and once – in 1975 – I spent a night in jail in Juba, Sudan. The Southern Sudanese army were holding some of my clients hostage and, against all advice, I had flown in to rescue them. I sat in that stale, dank cell wondering how on earth I’d fix the situation when I didn’t even have a phone… All ended well, but I’ll never forget that night.
Read more: The ultimate mid-week escape at The Royal Crescent hotel, Bath
Nowadays I also carry my iPhone. Google Maps has been a game changer in terms of navigating the world. On my first ever solo journey, I carried a large, folding Shell map. Now all this information is available at the touch of a screen, making even the farthest corners of Earth more accessible.
I pack shoes that work for any occasion
For a good grounding, Merrell’s ‘Vibram Traction’ boots are the perfect blend of casual cool and clever high-performance tech. Extraordinarily light, they are equally at home in the bush and on a mountainside. The rubber sole provides stability and durability. Having grown up running barefoot wild around the Aberdares in Kenya, shoes are a bit of a nuisance, but Merrell’s trainers have been designed for barefoot running so are the perfect holiday shoe for me. I also pack Hugo Boss and Gucci pairs for smart events when away too.

Touch-screen gloves from Geoffrey Kent’s Safari Collection
I like to stay connected – even in the most extreme climates
When journeying to colder climes, my Geoffrey Kent Safari touch-screen gloves are invaluable. My favourite app is Instagram. I do it religiously and hate missing out on a photo opportunity when fumbling to take off gloves. Made from a mix of wool and cashmere, these have conductive pads on the forefinger and thumb to allow you to use your device without removing them.
I try to leave the smallest impact possible
On a less material note, a philanthropic outlook is vital. How can you positively impact lives and livelihoods in the communities where you travel? Examining how we can contribute to animal conservation will ensure longevity of those populations. For example, point blank refuse to partake in elephant riding, painting or any activity in which the animals are forced to ‘perform’ in any way. These activities are not natural, and the training required is detrimental to this species’ wellbeing. Travelling with conscience is the only way we can insure a sustainable future.
Read more: 6 reasons to buy a Richard Mille McLaren watch

Geoffrey Kent and his wife Otavia
I love to travel with a companion
My wife Otavia shares my sense of adventure and desire to explore. She often accompanies me on the Inspiring Expeditions I lead. We’re off to Corsica next, then will be circling the globe by private jet, before ending the year with the Emperor penguins at the South Pole.
Geoffrey Kent has just launched the Geoffrey Kent Safari Collection, a range of timeless, high-performance, luxury travel apparel and luggage for today’s adventurer. Visit www.geoffreykentsafari.com for further information.

Dr Johnny Hon
Johnny Hon, founder of venture capital and investment company Global Group, is on a mission to lower cultural and trade barriers between east and west to encourage commerce, charity and cultural exchange. The entrepreneur and philanthropist, based in London and Hong Kong, speaks to LUX Editor-at-Large Gauhar Kapparova

LUX Editor-at-Large, Gauhar
Kapparova
LUX: The Global Group seems to have diverse interests and ambitious plans.
Johnny Hon: I founded the Global Group in 1997 whilst completing my PhD at Cambridge University. It has since grown to become a leading venture capital, investment and strategic consultancy with offices in London and Hong Kong. Over the past 20 years, the Global Group has evolved from financing high-yield technology companies to expand into private equity, angel investment and financial services. The company’s diverse interests and areas of expertise range from fine art to FinTech, biotechnology to entertainment and leisure. The future of the Global Group is exciting – we’re a rapidly growing company that responds to opportunities, rather than limiting ourselves to specific sectors. We are always looking for exciting, interesting opportunities, whether that’s a start-up in the UK or supporting the growing appetite for excellent quality wine in China.
LUX: You catalyse and facilitate trade between Europe and China. This seems to be important to you at what must be an essential time to be doing it.
Johnny Hon: We live in an increasingly global era and this is changing the face of modern business. The Global Group has always worked with European companies looking to enter the Asian market, as well as Chinese clients and high net-worth individuals with aspirations in the European market. I believe now, more than ever, it’s essential to encourage trade and mutual engagement between Europe and China and in particular to usher in a new golden era of Sino-UK relations.
In my opinion Brexit can open up vast potential as it will provide overseas investors with more opportunities than ever to enter the market. We have our European office in London, and I think it will always be the financial heart of Europe. I encourage Chinese clients to invest in the UK’s businesses and future, and vice versa, and feel optimistic about the future of global business.

Johnny Hon at the charity première of the stage show 42nd Steet with HRH The Duchess of Cambridge
LUX: You have a broad portfolio of business, philanthropic and diplomatic interests. Please tell us more – it seems you are in effect an ambassador between east and west at a very high level?
Johnny Hon: The main mission of the Global Group is, as our motto says, ‘Bridging the New Frontiers’. We work to remove barriers between the East and the West, and I am passionate about reflecting this in my personal and business interests.
I am British-educated but was born in Hong Kong, and I’m deeply proud of my roots and Chinese heritage. I have always felt like I represent both cultures and I have tried hard to act as an ambassador – a gateway – ever since I set up my company. The Global Group challenges expectations and concerns about doing business in China, and I also embody this role in my diplomatic work.
I am the Honorary Consul for Grenada in Hong Kong and the country’s Ambassador-at-Large. I take huge pride in the private consultancy and advisory work I do with state leaders, prime ministers and presidents from countries around the world.

Johnny Hon’s broad range of philanthropic and diplomatic work includes charitable fund raising
Philanthropy is a vital part of my work and an endless source of motivation and inspiration for the Global Group. One position that fills me with particular pride is my role as the first ever Diamond Benefactor of the Duke of Edinburgh’s International Award. I am responsible for growing the scheme throughout the AsiaPacific region and introducing Chinese students and young people to such exciting life skills as teamwork, enterprise and leadership.
I’m also a Founder Benefactor of London based think tank Asia House and Vice President of the 48 Group Club, which works to raise awareness of Chinese business and innovation in the UK and promote positive relations between the two countries.
In all areas of my life – business, diplomacy, philanthropy and personal – I take great pride and pleasure in my ambassadorial role.
LUX: Does the West have much to learn from China, and vice versa?
Johnny Hon: We can all learn and benefit from a global outlook. China is now a hub of technological advancements and entrepreneurial spirit. The West can learn from its productivity levels, dedication to innovation and broad acceptance of technology, especially regarding the fourth industrial revolution.
The West, and the UK in particular, is inspiring in the approach it takes to investing in future talent and it is the home of some of the world’s greatest educational institutions. It is also an outstanding provider of services, especially in the financial and legal sectors.
From East to West, I am passionate about education and how it is already changing the business landscape. Right now, over 300 million people in China are learning English and the UK has the world’s second largest population of Chinese students studying overseas. I think we should all look to China and how it is encouraging, supporting and inspiring a global outlook for the next generation.
LUX: Tell us more about your philanthropy and your plans in that area.
Johnny Hon: Philanthropy and social responsibility is at the core of the Global Group. It bolsters my sense of purpose and motivates me to work even harder.
I have always wanted to give back. When I was reading for my PhD at Cambridge, I realised that I would be able to have more impact as a businessman than a doctor, and this started my philanthropic career.

Amongst many philanthropic roles, Johnny Hon is the Vice President of the 48 Group Club
We’ve now donated to over 160 charities worldwide and my projects have ranged from setting up Oxford and Cambridge University scholarship schemes to sponsoring the first London production of the China National Beijing Opera Company at Sadler’s Wells through the Hon Foundation for Music and the Performing Arts.
It is particularly rewarding to be able to combine my passion for the arts with my interests in raising awareness of Eastern culture in the UK, supporting the Global Group’s mission to bridge the gap between the East and West.
LUX: Please tell us about other areas you are developing in your business that are exciting you right now.
Johnny Hon: Sitting at the helm of a rapidly expanding company that is growing in numbers, clients, countries of operation, and team members, is hugely exciting in itself.
Looking at investment opportunities and areas, right now, there is a fascinating trend for Chinese investors to look to British heritage companies. China has a growing consumer society with an increased disposable income and appetite for British luxury goods such as whisky and smoked salmon. There’s a huge market there for UK companies to work with China, and vice versa, to develop this and other opportunities.
This year, we are building on the sustainable side of the Global Group, with a focus on our shared global future. We are focusing on technology that sets out to tackle challenges posed by issues such as population growth and its environmental impact, including green technology, agricultural technology and biotech, for example.
Investing in something that could improve life quality and expectancy means that I have the potential to make a real impact and change the lives of many millions of people for the better, which is both exciting and awe-inspiring.

Kate Upton at the 2017 amfAR Gala Cannes
Charity art auctions are taking off around the world, and for the best and worst of reasons, says Simon de Pury, himself the world’s leading philanthropic auctioneer

Simon de Pury
In times past, the main philanthropic efforts in the art world used to be confined to the US, for a couple of reasons. Firstly, there is fiscal encouragement for individuals to make charitable donations in the US, which is not the case in Europe. And more importantly it is an integral part of the entrepreneurial educational philosophy in the US, that if you are successful, you give back.
Any successful person in any area in the US is expected to have one or two causes to which they contribute some of the fortune they have made. But over the past 10 years, things have changed. More and more wealth has been created around the world, and the art market has consequently become more global. This means I have witnessed efforts in philanthropy around the world increasing dramatically.
Follow LUX on Instagram: the.official.lux.magazine
It is very gratifying to see, and in many cases to be involved with, cultural institutions that organise regular fundraising events. We also see increasing numbers of organisations of friends of museums, whose main task is to raise funds for philanthropic and charitable causes. In some cases, these are to benefit the institutions themselves; and in others, funds are raised for important causes that are not adequately funded through governments.
Perhaps the ultimate art philanthropist is Maja Hoffmann, who has devoted so much energy to the new LUMA Foundation in Arles; designed by Frank Gehry, it is going to become a cultural art centre of major importance. She also funded the Fondation Vincent van Gogh Arles; and she is a donor to MoMA and the New Museum in New York, and the Kunsthalle in Zurich. She supports these institutions not just in financial terms, but also by putting together sophisticated programs. She is a shining example.

The amfAR 2017 Gala in Cannes
Then there is the growing area of non-cultural philanthropy, one in which the art world is becoming increasingly involved. It’s not a recent development (although it has been growing exponentially recently) . The art world was the first to mobilise in the early days of the AIDS epidemic, when Thomas Ammann, an art-dealer friend of Elizabeth Taylor and Audrey Hepburn, set up amfAR, which has raised great amounts of money over the years.
What is striking about the art world is that some artists have themselves made significant donations. Damien Hirst donated a beautiful golden mammoth which Len Blavatnik bought for $16m at the amfAR auction in Cannes in 2014. It’s now at the Faena hotel on Miami Beach and something of an Instagram magnet. It also happens to be one of best works in the Damien Hirst oeuvre. Hirst is the most generous artist I know; he has donated many millions of dollars’ worth of art to various charities over the years. Tracey Emin is also immensely generous, as is Chuck Close, who never holds back in supporting causes close to his heart. There are many others, too; artists these days are solicited on a daily basis to donate works to various causes.

Leonardo DiCaprio and Madonna at the 4th Annual Saint-Tropez Gala organised by the Leonardo DiCaprio Foundation in 2017
There is one lingering anomaly, at a time when we should all be highly concerned about the future of the planet: the fact that only three per cent of global charitable donations go to environmental causes. Leonardo DiCaprio is leading the way in devoting time and energy to raising awareness of the poor state of the oceans and other environmental issues, and I have had the honour of being auctioneer at the four large charity auctions he has organised in St-Tropez over the past four years.
Read more: One-of-a-kind designs by talented artisans at Baku Corner

David Beckham arriving at the 2017 amfAR Gala
What is significant about these auctions is that they include works by artists such as Jeff Koons, Urs Fischer and George Condo, many of whom donate very substantial works. In 2016, of the 20-odd works on sale during the live auction, 15 were donated and 12 of them set new auction records. This shows that people are not simply buying art at these auctions as a charitable act – they are buying top works, which makes it sustainable and gives it extra purpose. Leonardo manages, through his status, not only to obtain top donations, but also to bring in potential purchasers from all over the world. In that tent in St-Tropez on the gala evening, there is a greater concentration of money than at the big auctions in New York.
What is increasingly extraordinary about these events is how global the audience is now. High net-worth individuals are coming from all over the world, with more and more attending from Russia, the former eastern bloc, the Middle East, China, Korea, Japan, Malaysia, Indonesia, Latin America and all over Africa. It has really become a global effort.
All of this also raises awareness, and once awareness spreads it becomes easier to raise funds. Offices that look after HNIs all now have specialists in philanthropy to advise their clients how they can help. People are getting drawn in for different reasons. Some people pay for the artworks because they just want the artwork. But increasingly individuals want to take responsibility because governments are not. One of the reasons philanthropy was initially more widespread in the US is that most institutions there depend on private donations, there being no public funding. In Europe, public budgets used to be much bigger, but with cuts, individuals have had to step in.
You can also see this with the instant mobilisation that takes place when something happens, for example the recent refugee crisis. Some artists are galvanized into action by such crises – Ai Weiwei has made a movie and marched on the streets of London together with Anish Kapoor. It’s the future.
Simon de Pury is an art auctioneer and collector and the founder of de Pury de Pury. Read more of his columns for LUX here.
FROM EARTHQUAKES TO UPRISINGS, FOR ONE PRIVATE JET COMPANY THE SKIES ARE NO LONGER THE SOLE DOMAIN OF ROCK STARS AND HOLLYWOOD A-LISTERS. GUY FIORITA REPORTS
Turn on the news any day of the week and, unfortunately, there is probably a story about a human tragedy taking place somewhere in the world. Usually by the time we first hear about it, relief is already on the way. We see images of it arriving by the planeload to some far-flung airstrip. Ever stop and wonder who is behind those jumbo jets full of food and blankets? Not many would guess that it’s the same company that’s flying the hottest new boy band in ultra-luxury from one stop to another on a world tour but, from spoiling VIPs to flying relief missions, for the last 40 years Chapman Freeborn has been doing both.
Launched in 1973, Chapman Freeborn is the world’s leading jet charter company with offices in 25 countries. They have flown their share of jetsetters, royalty, oligarchs and stars and they’ve learned to provide a luxurious experience better than anyone else, but according to Alex Berry, Group Sales and Marketing Director, there is another side to the business that is a lot less glamorous but much more rewarding. “From flying humanitarian aid into areas in need, to moving people displaced by war, there hasn’t been a major international incident in the last 30 years that we were not involved in.”
When tragedy strikes, like an earthquake in Haiti or famine in Sudan, aid organizations need to move food, blankets, workers and much more, and they need to do it fast. “The airlines won’t fly on credit. Not even for organisations like the UN or Red Cross. So you need to have someone with the capacity and financial capabilities to make this work and make it work fast. Since we are privately owned and financially strong, we can meet the needs of the agency by mobilizing people and equipment without any delay.”
Some cynics say flights like these merely amount to making money out of other people’s misery. It is a claim Berry has heard before. “Do we make money out of evacuating people from war zones or bringing in relief to the needy? Yes we do, however we understand the importance of these missions and we make sure that everything is carried out as quickly, efficiently and professionally as possible. Often there are lives on the line. It is a huge responsibility and we take it very seriously.”
The Haitian earthquake of 2010 is a perfect example of Chapman Freeborn putting their experience and resources to work for a good cause. After the devastating quake, relief material came pouring in from around the world but the airport had no offloading equipment to handle it all. “The first thing we did was fly in the proper gear and we immediately unloaded 10 planes. They could then fly back out to bring in more material. The Haiti tragedy happened on a Boxing Day. Our entire staff came in and worked throughout the holidays. Most of them ended up even sleeping in the office. It was tiring but very rewarding work.”
Chapman Freeborn has a product called REACT (Rescue, Evacuation and Aid Charter Team) that monitors international news sources and then, as its name suggests, reacts as quickly as possible when an aid organisation needs their help. During the Arab Spring REACT responded to crisis situations in Egypt, Libya, Tunisia and Bahrain handling over 100 evacuation flights, flying over 20,000 passengers to safety. “Having 35 offices in 25 different countries around the world means we can deploy people from local offices to be on the ground right away. We were the first aircraft into Fukushima, Japan. We flew in a German search and rescue team with dogs and 13 tons of technical equipment from Frankfurt to Tokyo on a chartered B767 aircraft.”
In October, 2011 when St. Anthony Central Hospital in Denver closed an old facility and donated the surplus medical equipment to Hanoi’s Bach Mai Hospital, Chapman Freeborn organised the air transportation of over 50 tons of medical equipment. “The delivery was particularly poignant as it arrived on the 40th anniversary of the Bach Mai Hospital bombing in 1972 which claimed the lives of 28 hospital staff. It was very inspiring,” says Berry. And, as it turns out, just part of the job.
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Archives
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- November 2015
- September 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- March 2015
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- September 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
Categories
- Adventure Travel Issue
- Aesthete Issue
- Architecture
- Art & Design
- Art & Photography
- Art collectors
- Autumn 19
- Autumn/Winter 2020/2021
- Autumn/Winter Issue
- Bespoke Issue
- Business
- Cars
- Cars & Collectibles
- Case Study
- Celebrities
- Culture
- Culture Issue
- Design Issue
- Dining Issue
- Earth Issue
- Family Issue
- Fashion & Jewellery
- Features
- Food
- Future Luxury Issue
- Health
- Hedonism Issue
- Image Issue
- Italy Issue
- Latest Stories
- Leaders & Philanthropists
- Leaders Slider
- Love Issue
- Luxury Travel Issue
- New Luxury Issue
- Online Exclusive Slider
- Opinion
- Spring 2020
- Summer 19 Issue
- Summer 2020
- Summer 2021
- Sustainability
- Taste Issue
- The Beauty Issue
- Travel
- Uncategorized
- Water Issue
- Winter 19 Issue
Popular Posts
Categories
- Adventure Travel Issue
- Aesthete Issue
- Architecture
- Art & Design
- Art & Photography
- Art collectors
- Autumn 19
- Autumn/Winter 2020/2021
- Autumn/Winter Issue
- Bespoke Issue
- Business
- Cars
- Cars & Collectibles
- Case Study
- Celebrities
- Culture
- Culture Issue
- Design Issue
- Dining Issue
- Earth Issue
- Family Issue
- Fashion & Jewellery
- Features
- Food
- Future Luxury Issue
- Health
- Hedonism Issue
- Image Issue
- Italy Issue
- Latest Stories
- Leaders & Philanthropists
- Leaders Slider
- Love Issue
- Luxury Travel Issue
- New Luxury Issue
- Online Exclusive Slider
- Opinion
- Spring 2020
- Summer 19 Issue
- Summer 2020
- Summer 2021
- Sustainability
- Taste Issue
- The Beauty Issue
- Travel
- Uncategorized
- Water Issue
- Winter 19 Issue










































































