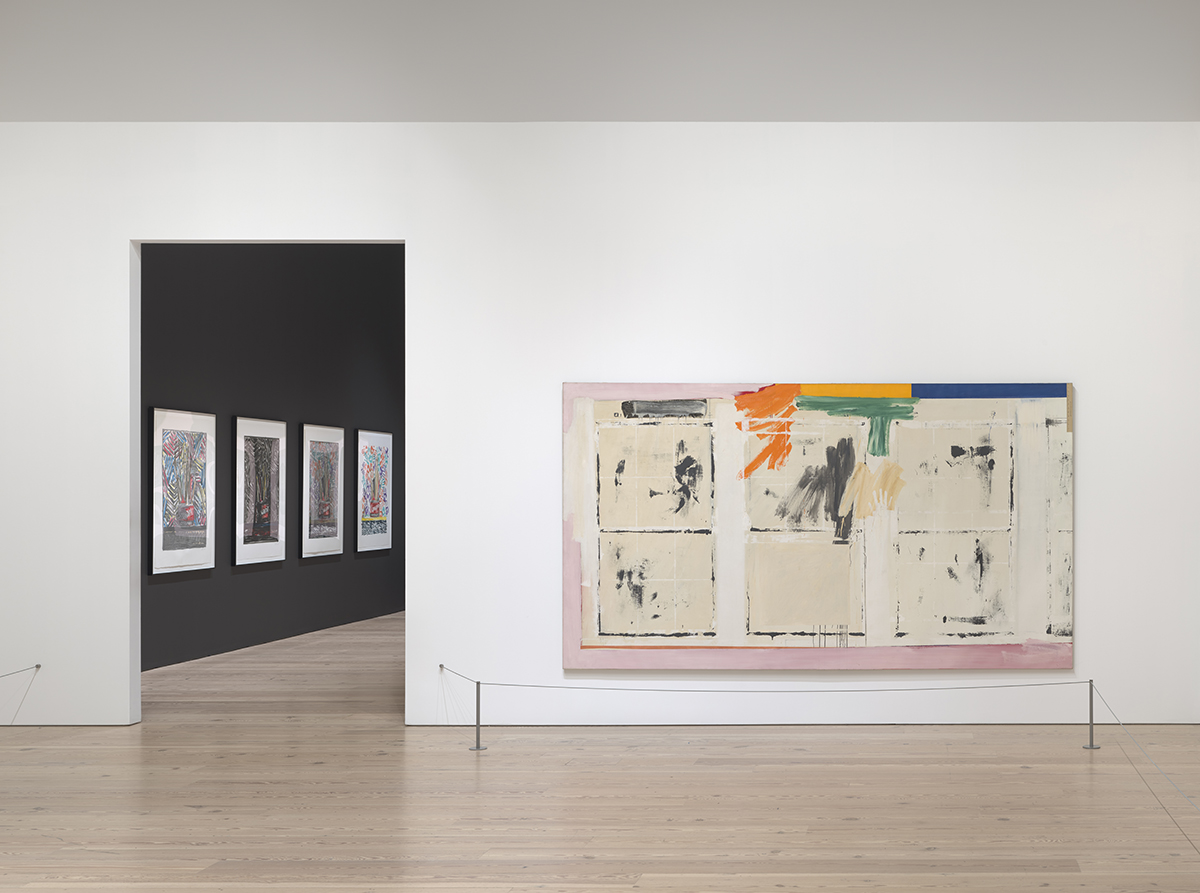

Installation view of Jasper Johns: Mind/Mirror (Whitney Museum of American Art, New York, September 29, 2021-February 13, 2022). From left to right: Savarin, 1982; Savarin, 1982; Savarin, 1982; Savarin, 1982; Studio II, 1966. Photograph by Ron Amstutz
In our ongoing online monthly series, LUX’s editors, contributors, and friends pick their must-see exhibitions from around the globe
Sophie Neuendorf, Vice President of artnet & LUX Contributing Editor
This month, Hauser & Wirth presents glimpse, British artist Phyllida Barlow’s first solo exhibition in Los Angeles, opening on 17 February (until 8 May 2022) to coincide with Frieze LA. The show will include new large-scale works assembled on site and made in response to the gallery’s physical adaptation of the historic Globe Mills, a collection of late 19th and early 20th century buildings. It’s sure to be a knock-out and as an added bonus, the gallery has an excellent on-site restaurant named after one of its founders: Manuela.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
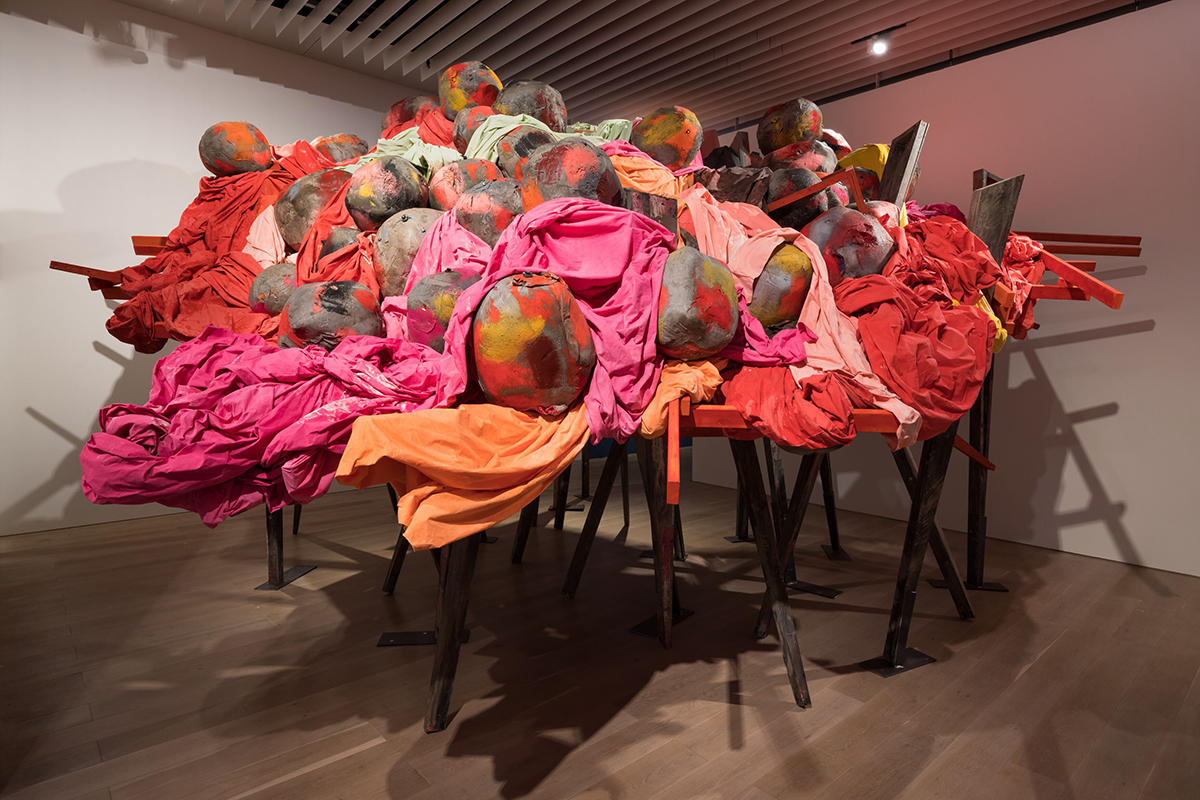

Phyllida Barlow, Undercover 2, 2020. Installation view, ‘Another Energy: Power to Continue Challenging – 16 Women Artists from around the World,’ Mori Art Museum, Tokyo, 2021. © Phyllida Barlow. Courtesy the artist and Mori Art Museum, Tokyo Photo: Furukawa Yuya
While you’re in LA, I also recommend stopping by Esther Kim Varet’s gallery Various Small Fires. The gallery launched in 2012 with the aim of fighting back against the traditional gallery system that allowed for already-big Western names to get even bigger. As a gallerist and dealer, Varet likes to keep it small: she only represents around 20 artists, fostering their growth right from the early-stages of their careers. As such, the shows here are always a great place to discover new talent before they take off. The current group show, for example, includes eleven artists curated by Todd Bockley of Bockley Gallery (on until 20 February 2022).
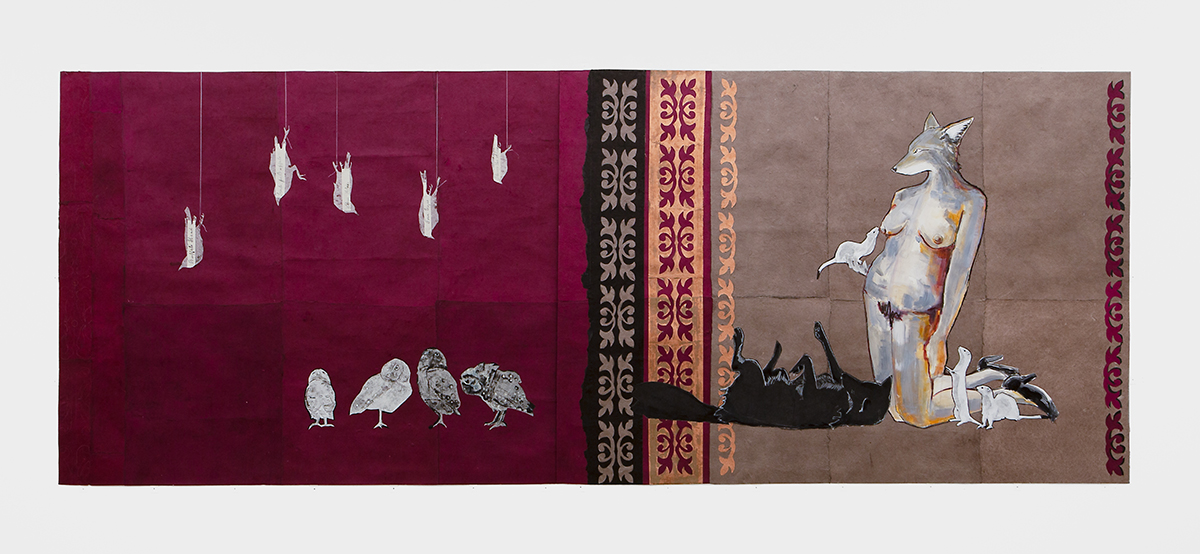

Julie Buffalohead, The Nourished, 2019. Courtesy of the Artist, Various Small Fires, Los Angeles/Dallas/Seoul and Bockley Gallery
Sutapa Biswas, Artist
Three powerful, beautiful and moving exhibitions which are ‘must sees’ over this next month (in addition to my own solo show at the BALTIC Centre for Contemporary Art, Gateshead of course) are Lubaina Himid’s exhibition at Tate Modern in London (on until 3 July 2022), Shigeko Kubota Liquid Realities at MoMA, New York (on until 13 February 2022) and Jennifer Packer’s The Eye Is Not Satisfied With Seeing at The Whitney, New York (on until 17 April 2022). I had the good fortune of seeing Lubaina’s exhibition, and the Serpentine’s iteration of Packer’s show, but I was devastated that the recent outbreak of the omicron Covid variant resulted in my having to cancel a scheduled visit to Kubota’s exhibition – I’m still dreaming of seeing it and hope this exhibition travels!
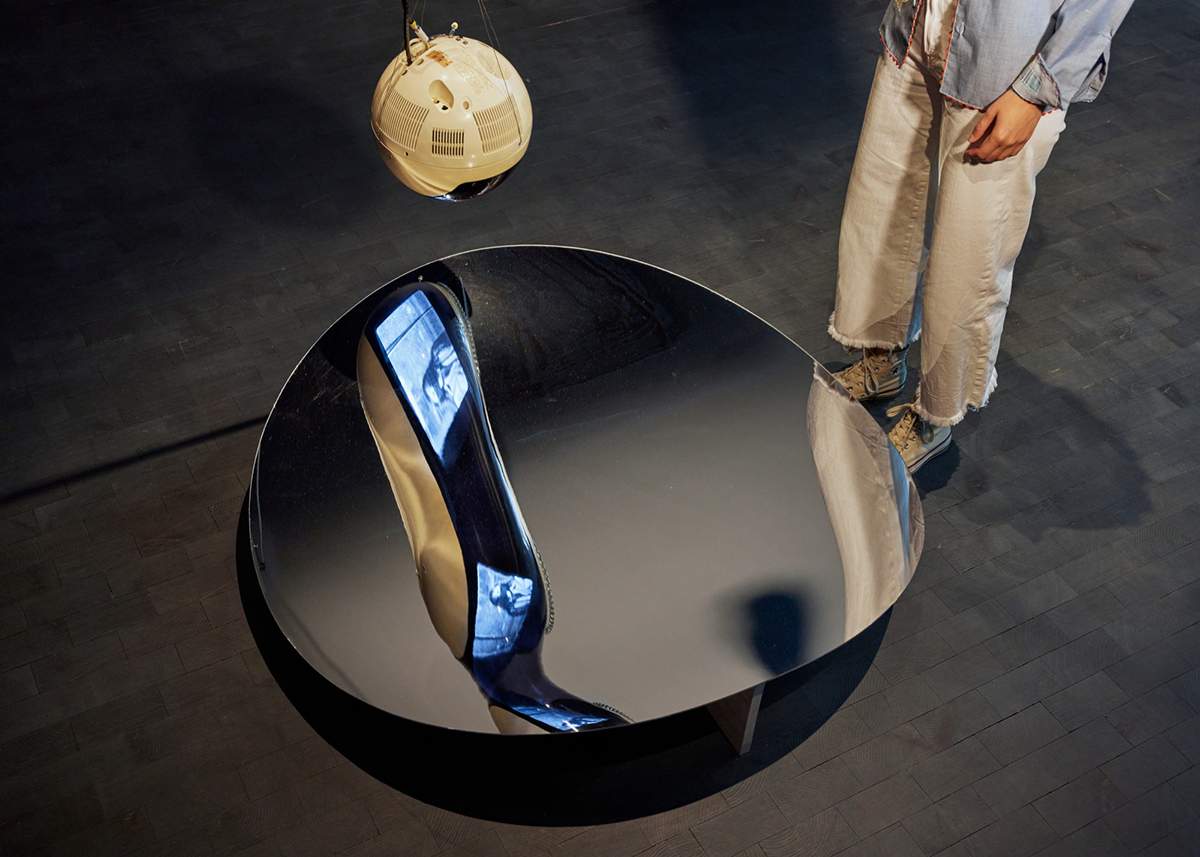

Shigeko Kubota, Video Haiku–Hanging Piece, 1981. Courtesy Shigeko Kubota Video Art Foundation. Artwork © 2021 Estate of Shigeko Kubota / Licensed by VAGA at Artists Rights Society (ARS), NY. Digital image © 2021 The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Photo by Denis Doorly
All three exhibitions bring together something vitally important in terms of our engagement with the subjects of their works in relation to the context, to form (the aesthetic) and to the nuances of meaning. I’m drawn to how each of these artists explore the intersections between art, history, form and our everyday realties and hopes. I love the confidence with which each of these artist’s works speaks through their works and what I learn as a viewer through my experience / encounter with their works. Moreover, I love how these artists’ works are haunting, opening thought in unexpected ways. Though the medium within which each of these artists work are so different, there is a language that connects them which relates to ‘the seeing’ and ‘the being’. Perhaps, for me, this ghosting of sorts is in part articulated through Kubota work titled Video Haiku – Hanging Piece, 1981. Prior to MoMA’s show I had not seen this work previously, but even on encountering it as a reproduction, I did a double-take. As a piece, it resonates deeply both formally and conceptually in terms of my own work as an artist. Such is the power and beauty of these women’s art.

Lubaina Himid , Ball on Shipboard, 2018. Courtesy of Rennie Collection, Vancouver © Lubaina Himid
Darius Sanai, LUX Editor-in-Chief
The two shows I want to see most in February are shows I know I am not going to get to. First there is Mind/Mirror, the Whitney’s retrospective of Jasper Johns, in association with the Philadelphia Museum of Art (on until 13 February 2022). It’s the most comprehensive retrospective of Johns’ work ever staged and likely to be a once-in-a-lifetime experience for most of us. He has long fascinated me for his reflections of the dramatic ructions in American society immediately after WW2, when within a few years, women in the western world gained arguably their biggest single step change in emancipation, segregation was officially abolished, and teenagers were invented. Along with Kurt Schwitters and Roy Lichtenstein, I think he is an artist whose importance will increase dramatically over time. If you’re lucky enough to be on the East Coast – go!
Read more: Sophie Neuendorf on Koons, Kitsch & the Evolving Art Market
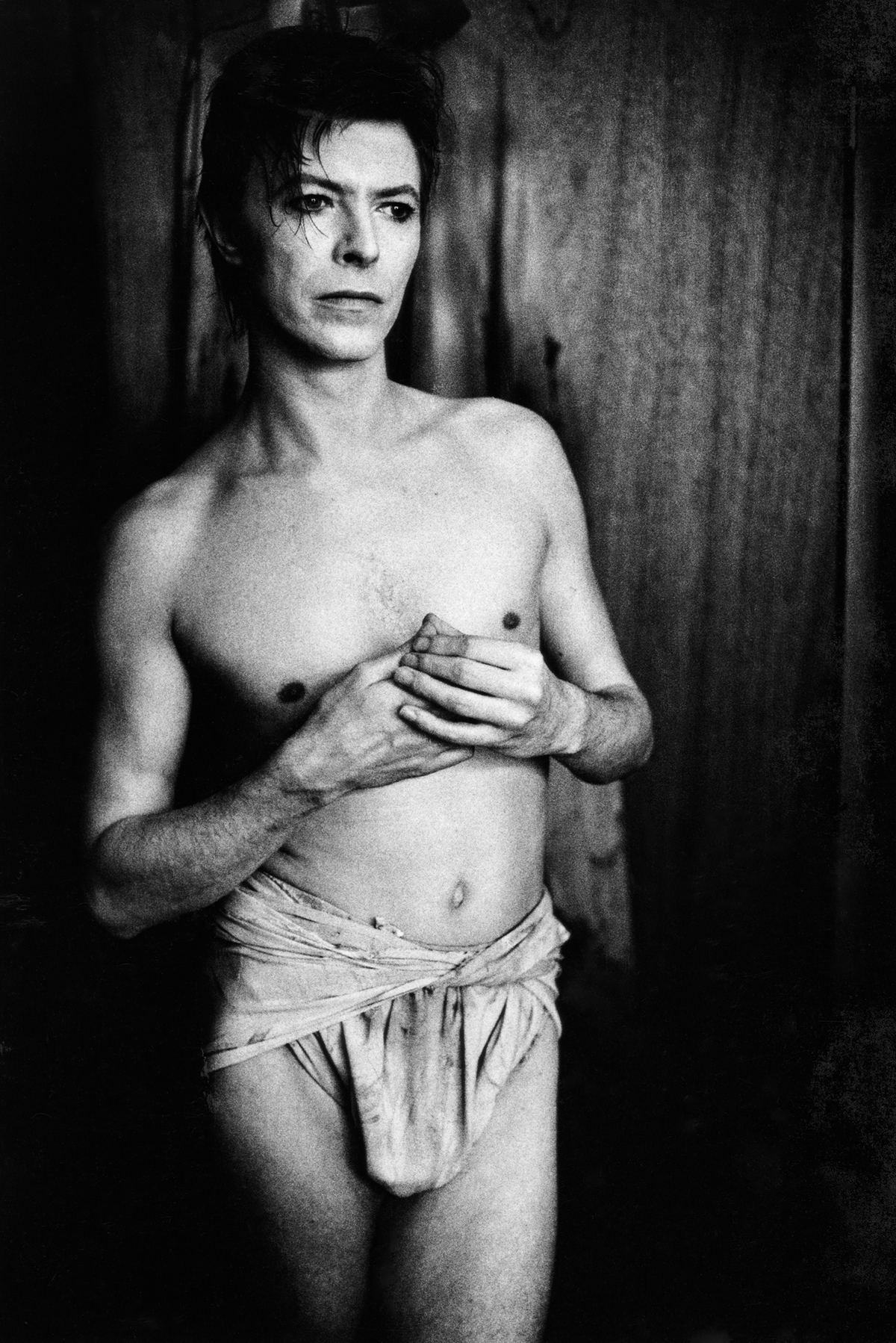
Anton Corbijn, David Bowie, Chicago, 1980. Copyright Anton Corbijn
The other show is at the other end of the scale in terms of size, but not interest. Anton Corbijn first caught my eye when I was a child and my sisters worked for NME, the pre-eminent post punk newspaper. I didn’t have much interest in the bands featured in the paper at that stage, but Corbijn’s photography, artful, moody, powerful, and always monochrome, was memorable. As an outsider, I was also always fascinated by the idea of this Dutch guy being a mover and shaker on the British 1980s music scene. He moved onto photograph movie stars, supermodels and designers, including David Bowie, Naomi Campbell and Virgil Abloh. Now uber-curator and LUX contributor Simon de Pury has curated a show, viewed by appointment at The Hague, Amsterdam (which I’m not going to make) and online at de-pury.com. Speaking to Simon last week, I told him his next move in the pop world should include the works of Pennie Smith, who created the black-and-white imagery in the book The Clash: Before And After, a kind of epic, humorous Canterbury Tales of the punk band’s first US tour. Watch this space.
Read more: Legendary photographer Iran Issa-Khan on ‘The Forces of Nature’
Tarka Russell, Director Timothy Taylor Gallery
When in Los Angeles, I never miss a visit to David Kordansky Gallery. During Frieze LA, he has Jonas Wood showing a collection of new paintings and works on paper (on until 5 March 2022). Another unforgettable trip is the The Getty museum where you are immersed in treasures.

Jonas Wood, Future Zoo, 2021. Photo by Marten Elder, courtesy of the artist and David Kordansky Gallery
Loulou Siem, Artist
This month, Pal Project, Pierre and Alexandre Lorquin’s art space in Paris, is showing Paragone by Mateo Revillo (on until 12 March 2022). I had a preview just before the opening and it is electric. Revillo has painted lines in beeswax and pigment on tile shaped plaster boards and hung them like diamonds – lines that run away and towards each other, going somewhere and nowhere and wrapping the space in unseen tape that asks: what happens outside of the edge? Live snails crawl up the walls, creating yellowish, unconfident loops on the once pristine gallery surface. Meanwhile, the wonky lines in the paintings feel fast, like static, and seem to challenge the somnolent snails. Snails that tease the limits of the paintings: awkwardly sexy?
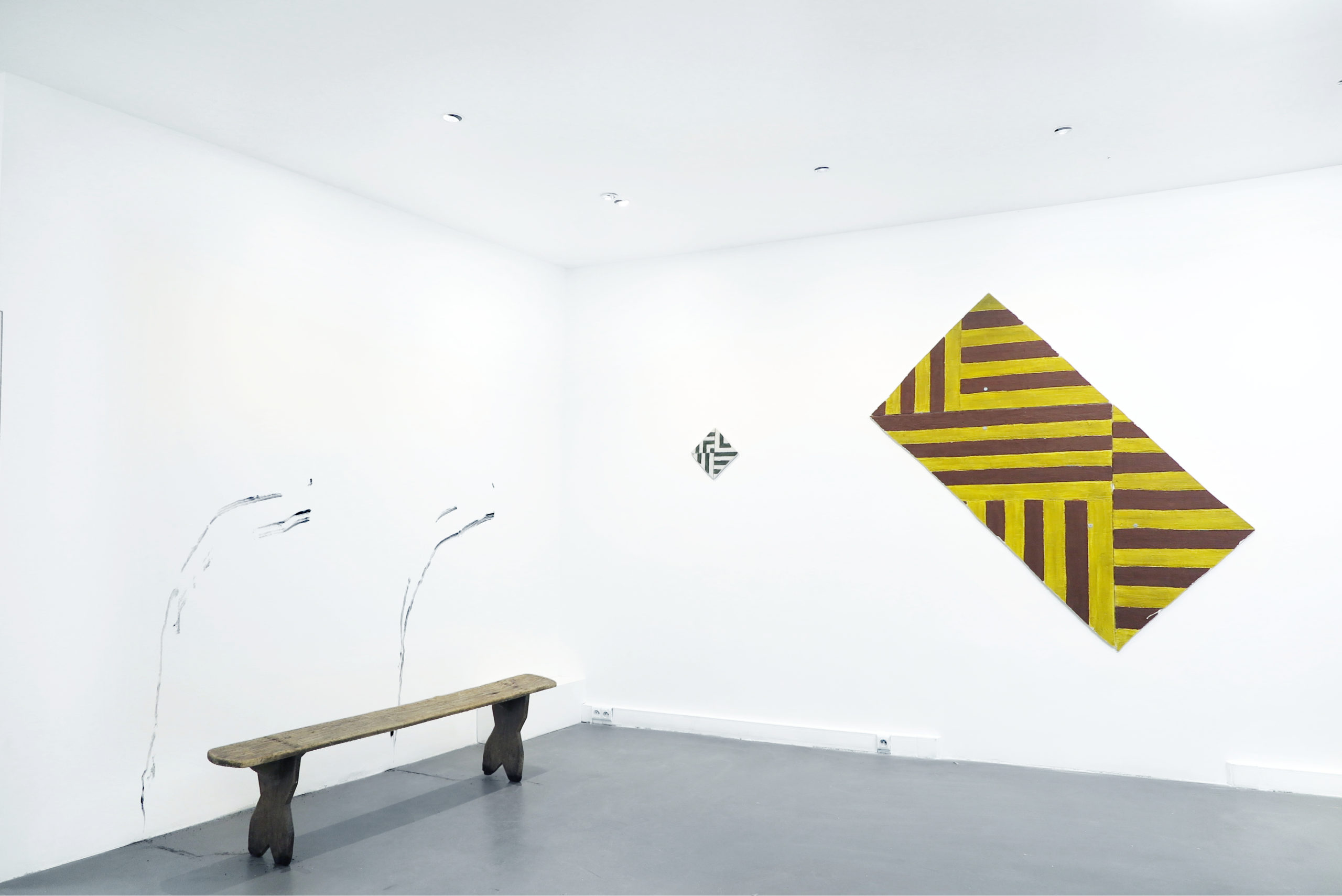

Installation view of Paragone by Mateo Revillo. Courtesy of Pal Project, Paris
I normally think of tiles as existing in multiples, made up for architecture, but here each is given jewel-like space, and do not need a collective to communicate. In fact, the materials in the show are industrial, not typically decorative. The plaster board is part of the wall itself, the bench that has been burned has doodled soot down the wall at its fall and the relatively small church of wedged coal bricks is solid and uncomplicated. The paintings feel monumental to me in their abstraction. In some moments, paint has flaked off the edges of the plaster, reminiscent of some Mediterranean antiquity, except these tiles were always meant to be perfectly imperfect. If you’re in Paris this month or at any point the future, I highly recommend stopping by: I think there could be a lot of exciting things coming out of this space.














 1. Of all the things you might collect, you chose ‘tat’. Why?
1. Of all the things you might collect, you chose ‘tat’. Why?
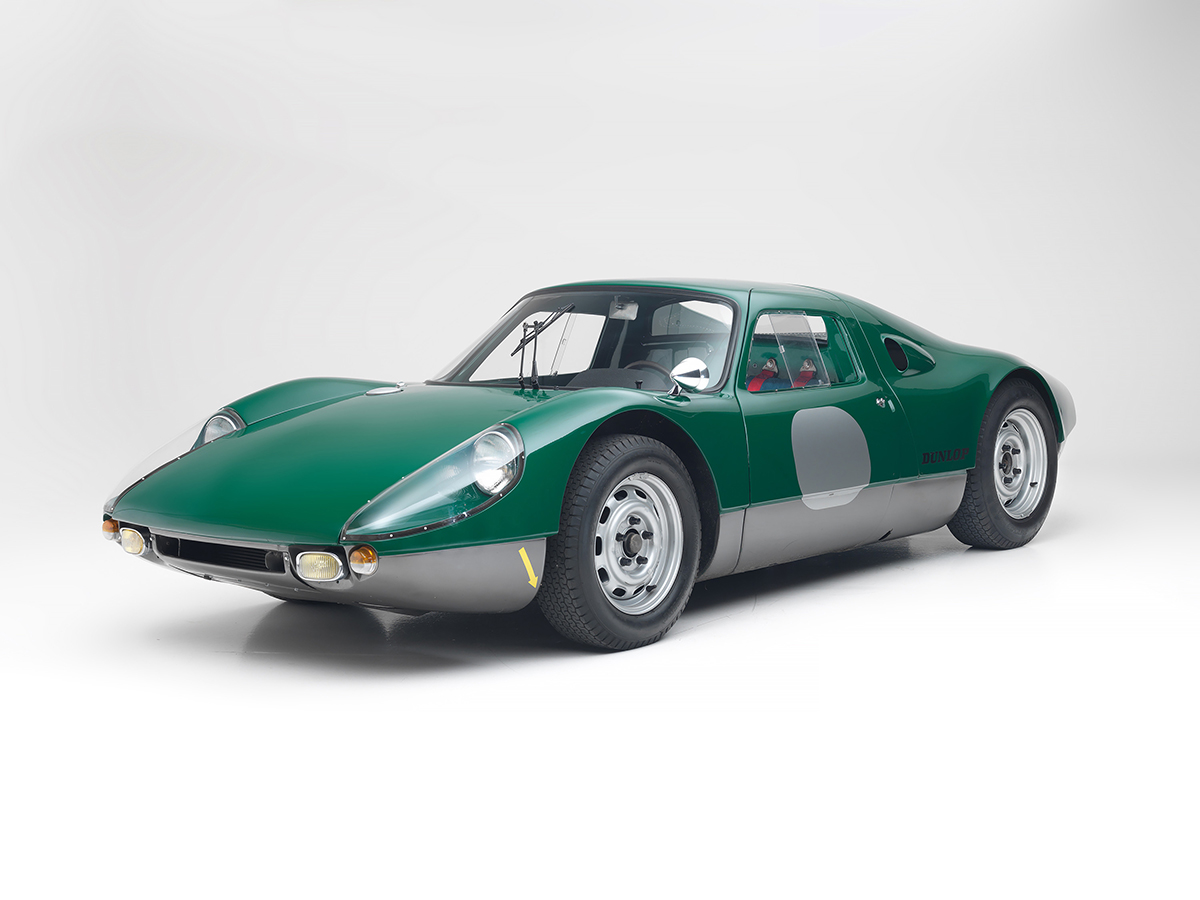
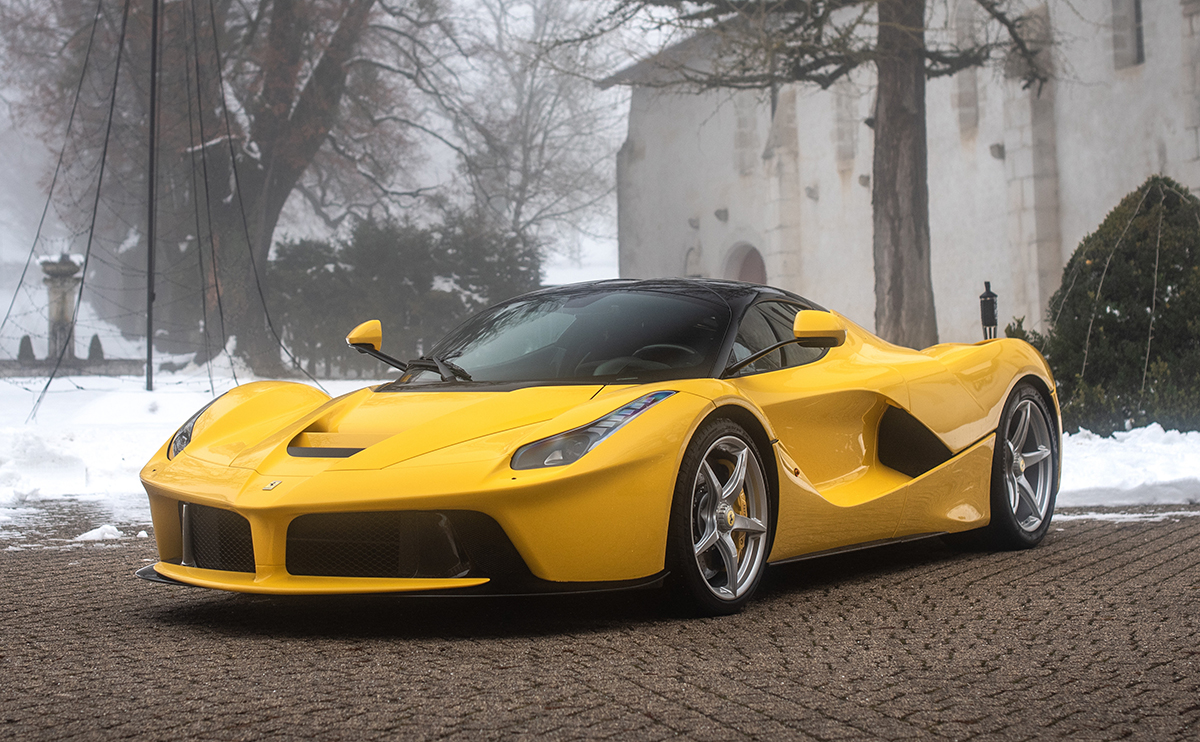
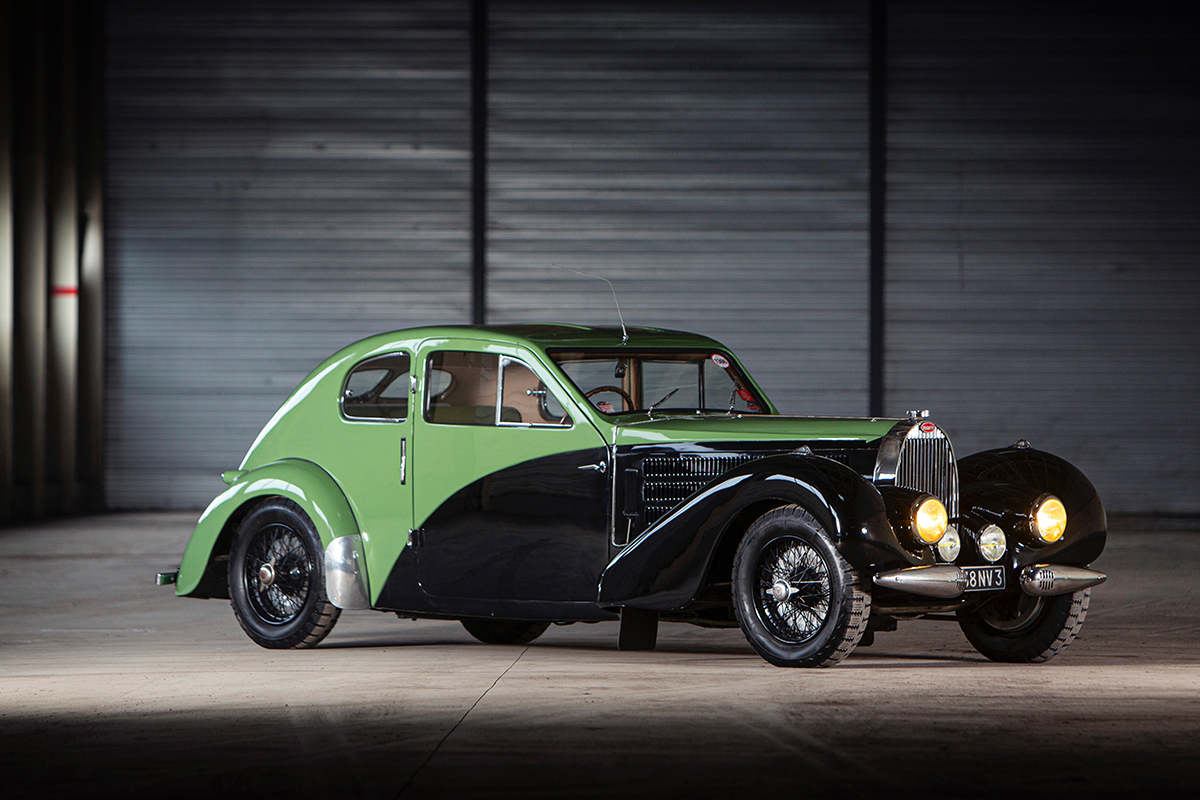
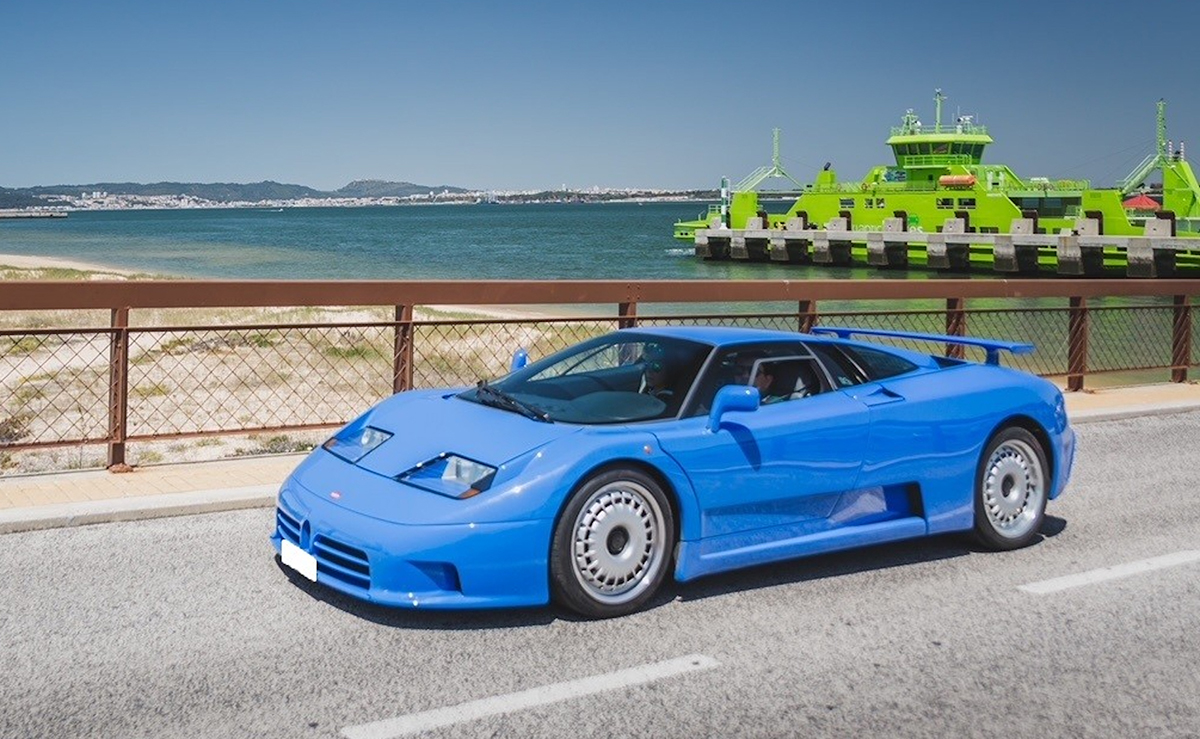
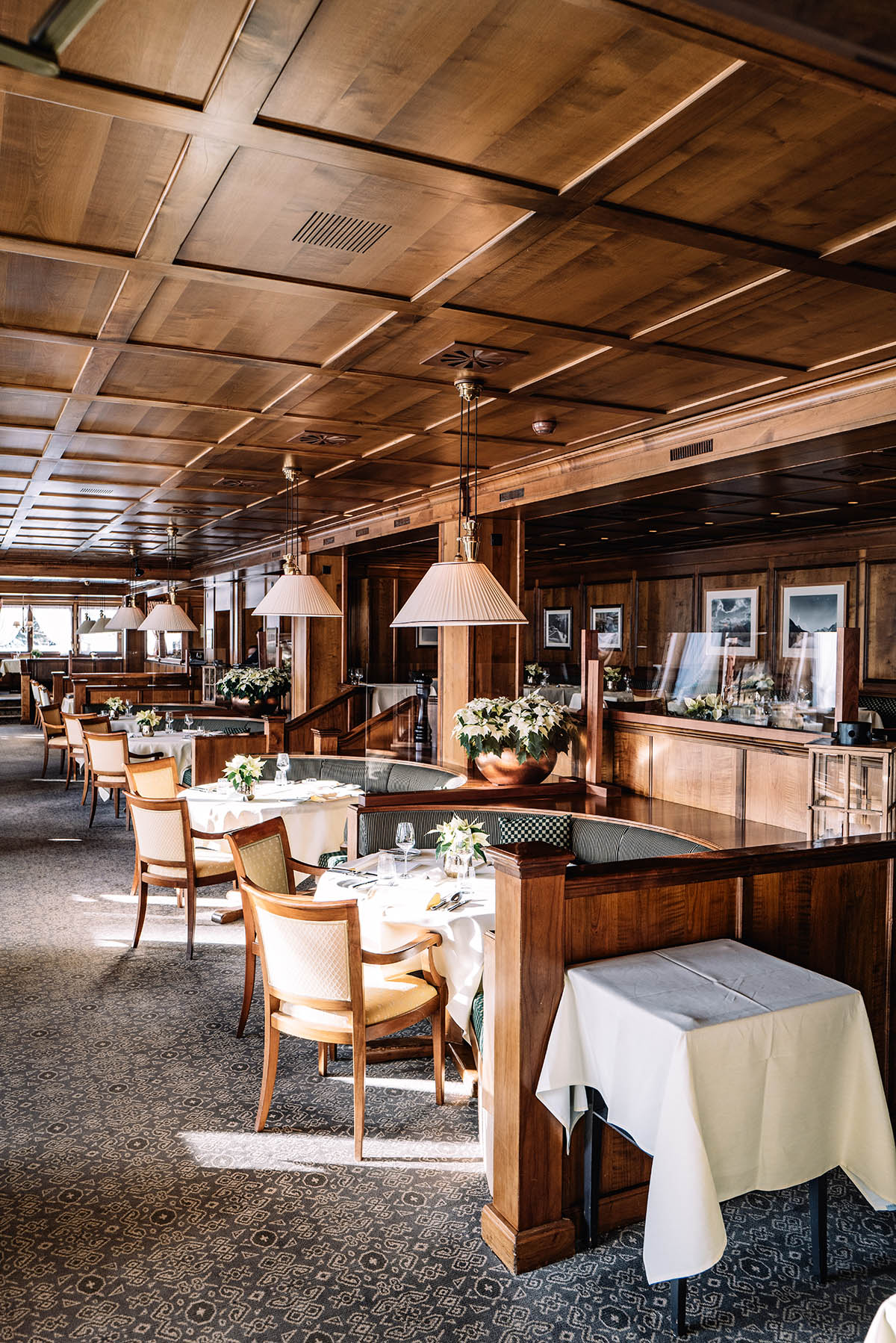
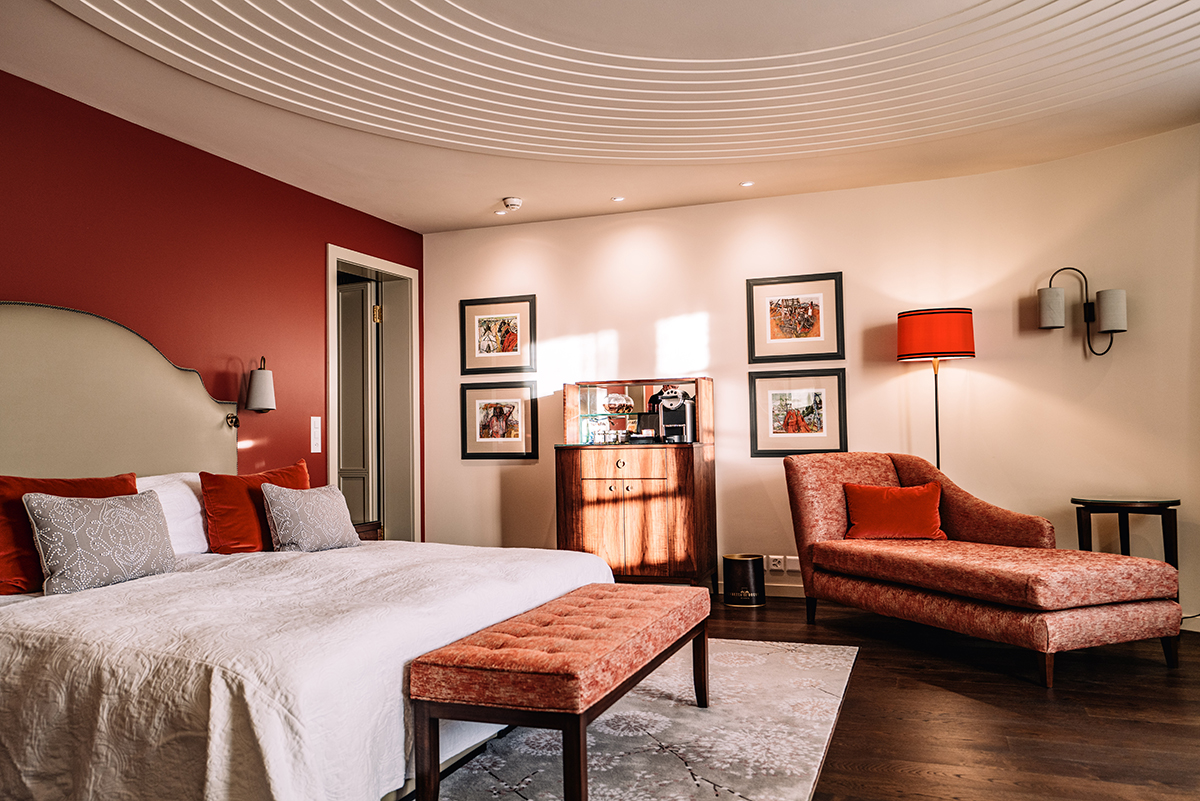
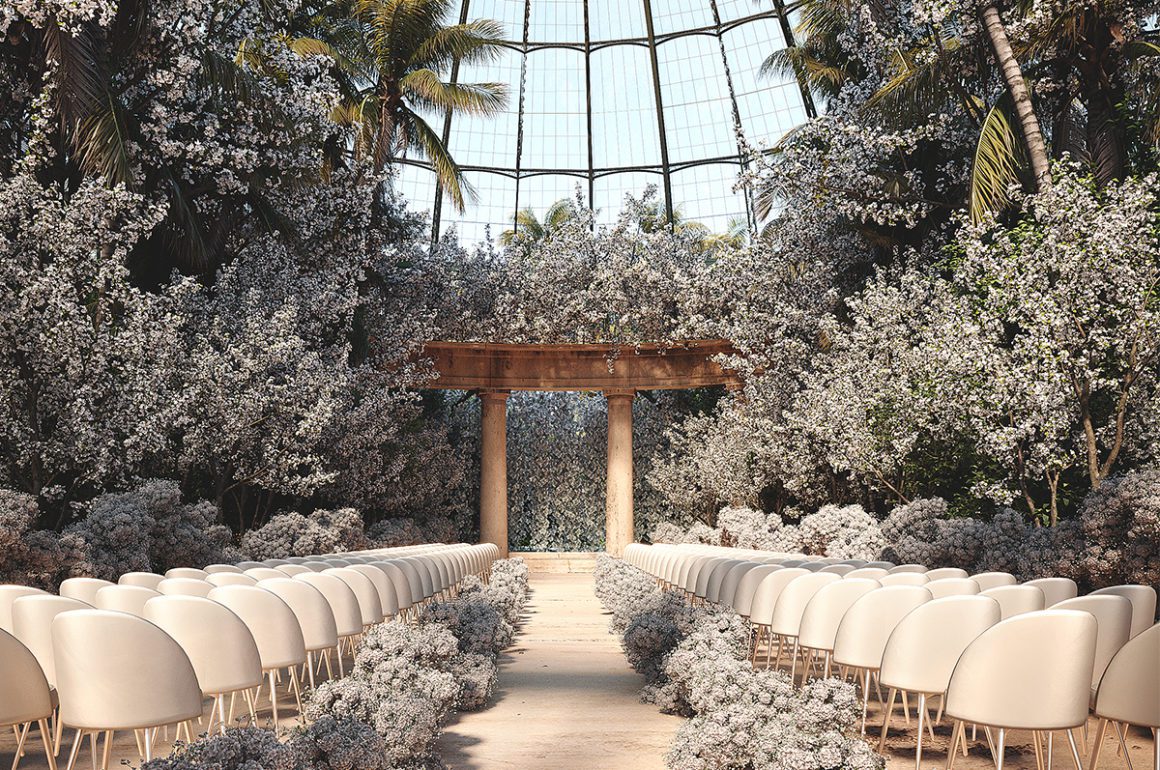
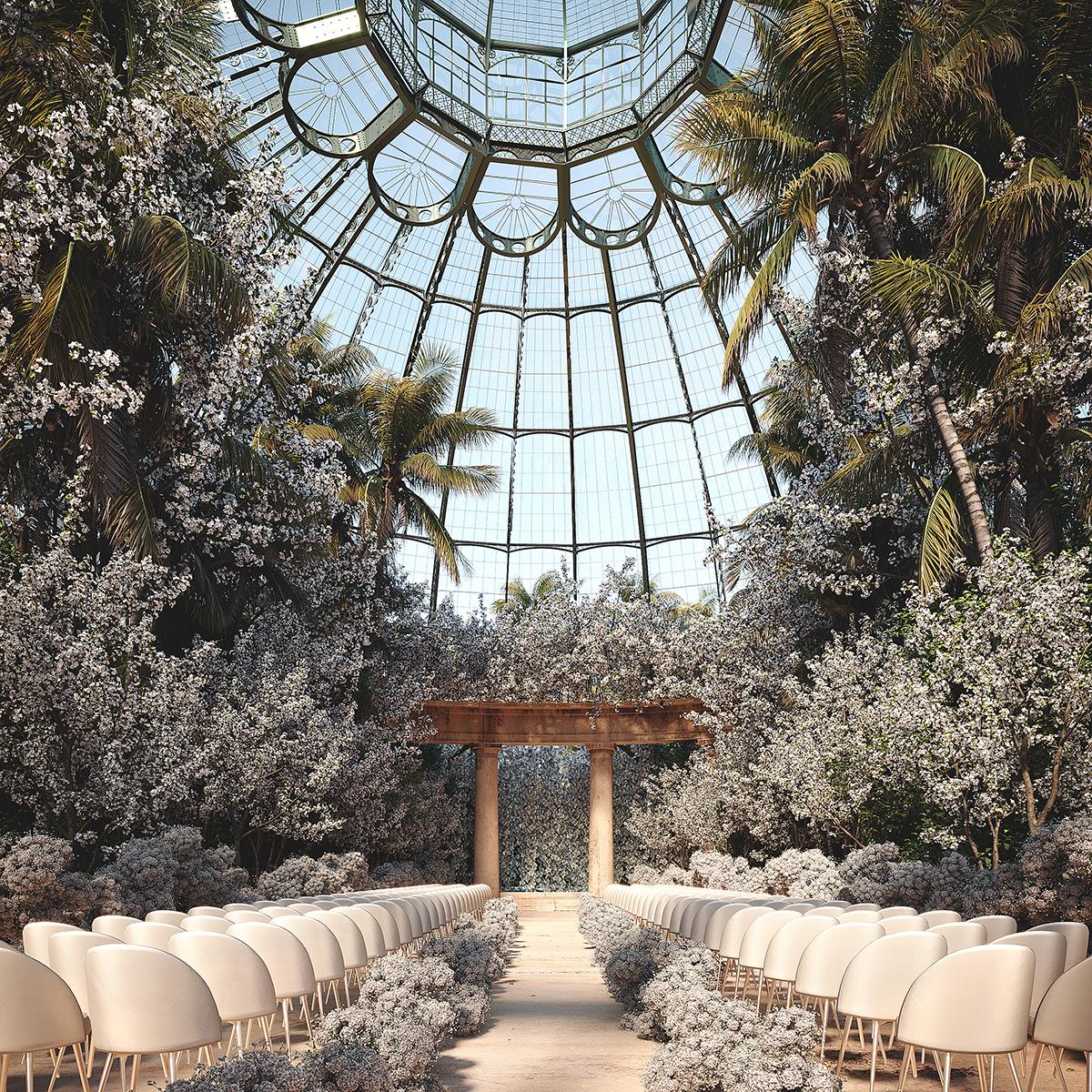
















 If we can say one thing about Covid, it is that it has pushed us to become more aware of our social life and the things we spend time on. Of course, as restrictions lift around the world, there is bound to be some mindless ‘panic partying’ for a while. After all, we were locked down for a long time, and any event feels exciting, now that we are finally free to socialise again!
If we can say one thing about Covid, it is that it has pushed us to become more aware of our social life and the things we spend time on. Of course, as restrictions lift around the world, there is bound to be some mindless ‘panic partying’ for a while. After all, we were locked down for a long time, and any event feels exciting, now that we are finally free to socialise again!



















Recent Comments