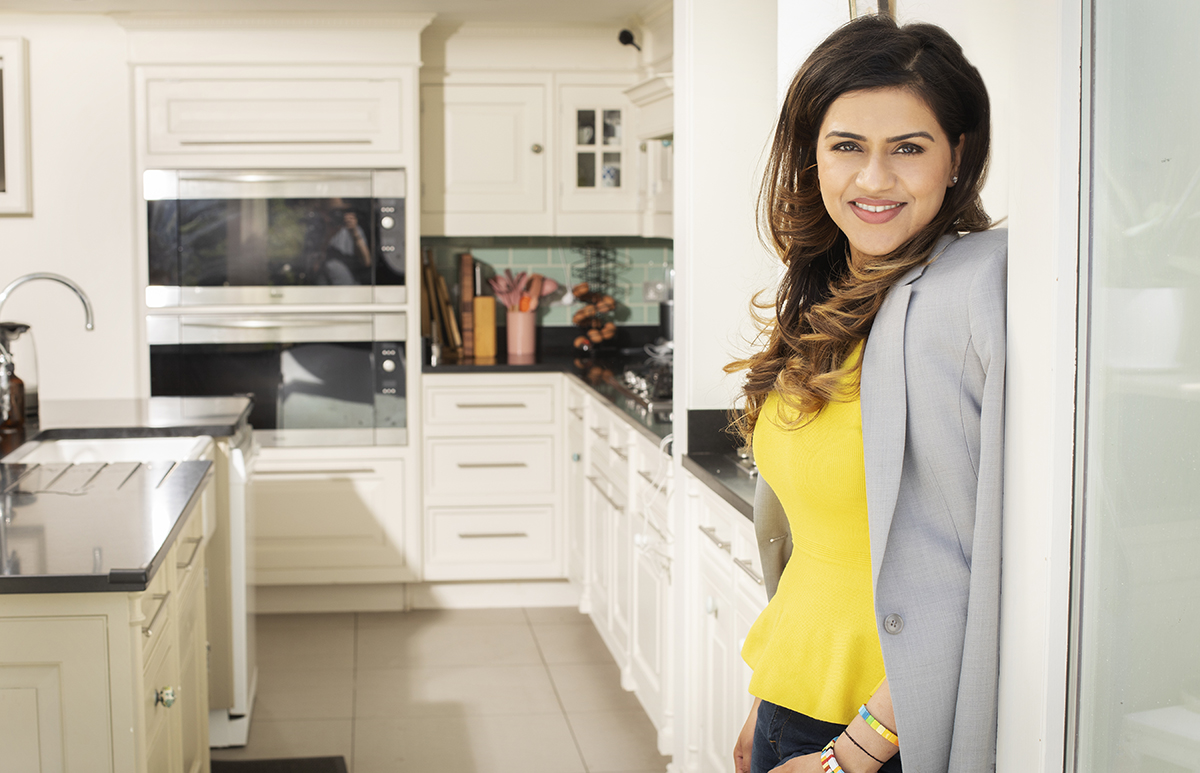
Sakshi Chhabra Mittal is the founder and CEO of FoodHak, a startup revolutionising the food industry by combining science, tech and traditional Ayurvedic principles to make healthier meals more accessible to all. Here Sakshi, speaks to Samantha Welsh about starting an innovating company and the potential for food science
LUX: What were your first entrepreneurial steps?
Sakshi Chhabra Mittal: I started working with doctors while in a full time job, to create a health-focussed line of food that was anti-inflammatory, low glycaemic index, gluten-free, dairy-free and free from refined sugars. Their patients heard about this and asked to subscribe. This pushed me to do a soft launch from my home kitchen; intended to be one week, it stretched to over four months with strong demand (purely word of mouth) and nearly 100% retention. I then found a kitchen near my office, woke every day at 5am to start operations with a part-time chef, kitchen assistant and an operations team. We learned a lot, most importantly, if you are building a business in the D2C space, your product becomes your life!
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
LUX: How did this evolve into a tech specialism?
SM: While I was studying for my MBA at Wharton in US, I was fascinated how tech can help scale science and business innovation. After graduating, I joined an early-stage tech VC where I invested in Babylon, Deliveroo and Darktrace, and was then invited to join SoftBank in Silicon Valley where I used my biotech training to invest in companies innovating in oncology, immunology, data science.
LUX: What brought about the pivot to food science?
SM: I had studied diseases professionally but personally I developed a rare liver breakdown during my first pregnancy. Known as OC, Obstetric Cholestasis recurs in subsequent pregnancies in more than 90% of cases. There is no known cause or cure but as our bodies are machines, science can offer answers, so I did clinical research into food types, changed my diet and managed to avoid OC recurring. I had found a gap in the market! Food science can help us potentially reduce chronic disease, relieve government healthcare budgets, live more sustainably, foster education in nutrition.
LUX: Clinical evidence links poor gut health with inflammation and disease; how does FoodHak’s proprietary tech bespoke complementary dietary solutions?
SM: We have built proprietary data models, taking all published clinical research on food, and making ingredient-disease links. This is our personalisation engine. We are launching personalisation features on our website, where people select meals according to their health goals, for example, to aid in adjusting cholesterol, blood pressure, immunity. We are also developing a personalised AI recipe generator App.
LUX: Tech or taste, what comes first?
SM: TASTE! Food is an experience, you have to get the taste right, everything else like lifestyle changes and customer retention follow on.
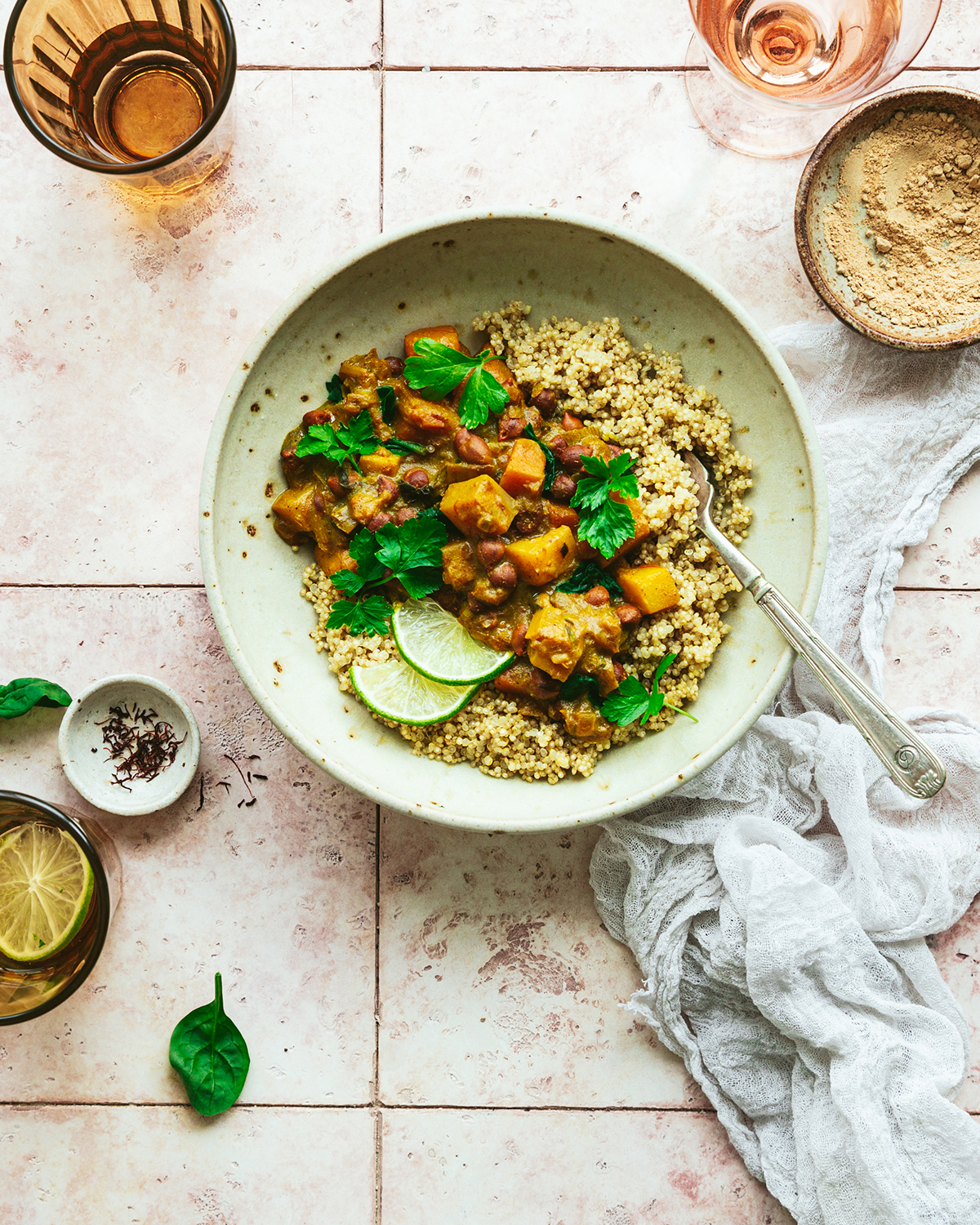

LUX: How does FoodHak fit within the fast-growing plant-based nutrition market and what is your USP?
SM: We are a first mover in the ‘food as medicine’ space. We bring clinical research to the table via delicious dishes that can help people live a long, disease-free life. Tech companies tell you what you should and shouldn’t eat based on data sets but none completes the loop and personalises food. Our proprietary data models create bespoke recipes, our AI recipe generator varies and extends choices. The market opportunity is the vast population suffering allergies, inflammation, sugar-related issues etc. FoodHak’s dishes are plant-based using around 30 varieties with superfoods. We focus on a low glycaemic index, being gluten free, dairy free, free from refined sugars, we use science and tech, and we deliver bespoked gourmet meals to your door!
LUX: How do you achieve operational efficiencies with this model?
SM: We use sophisticated food packaging technology where we heat seal food in pouches. This gives us a naturally longer shelf life on fresh food and helps us with our zero-food waste policy. Our customers enjoy the extra flexibility in the shelf life as well. This enables us to run large-scale batches in food manufacturing, which reduces workshifts, encourages less frequent deliveries, and so saves on operational costs.
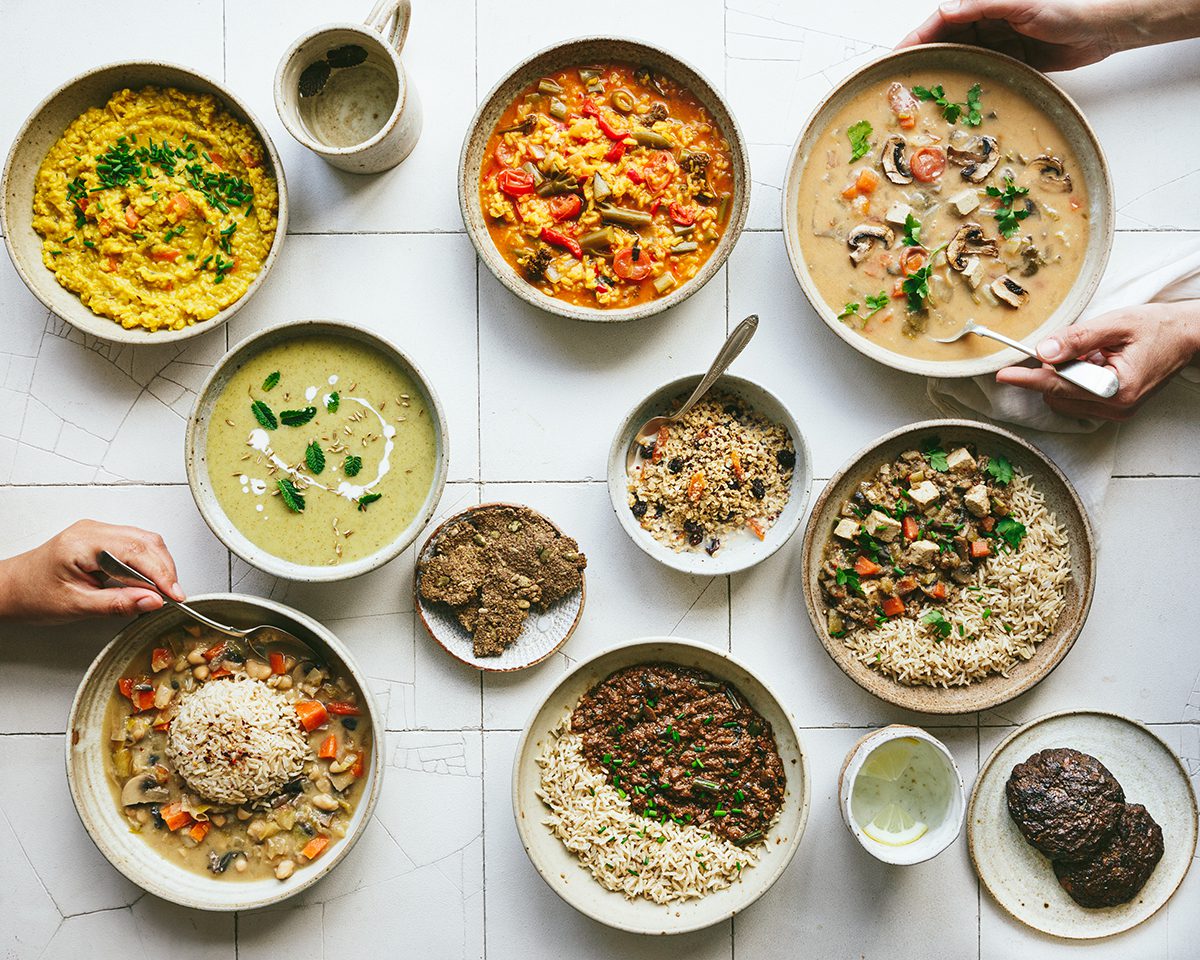

LUX: How has working in diverse industries influenced your leadership style?
SM: We make a deliberate effort to interview women to join the company. I learnt from working in finance that if you don’t seek out women to join the company you will never have an equal opportunities workforce. Over 50% of our employees are women. I am also proud that virtually 100% of our workforce is diverse, including minorities and people from developing nations. Diversity of opinion around the table is critical to making the right decisions.
LUX: Has Covid changed corporate culture at FoodHak?
SM: I believe to build a strong culture and values from day 1 in a start-up is impossible with people working from home (WFH). The feeling of connection and ownership comes when you sit with your team and see them problem-solve in their respective areas. You see your product being made and packaged with love. You see the values exhibited by the senior leadership on a day-to-day basis. There is no reason to be WFH unless you really need to. It’s also important that each employee at FoodHak has equity from Day 1. They have a sense of ownership over the business, the product they are making, they want to come into work and give it their best shot to make the company succeed. We believe that the early employees have sacrificed so much to help build the product and they should be growing their wealth as the company grows.
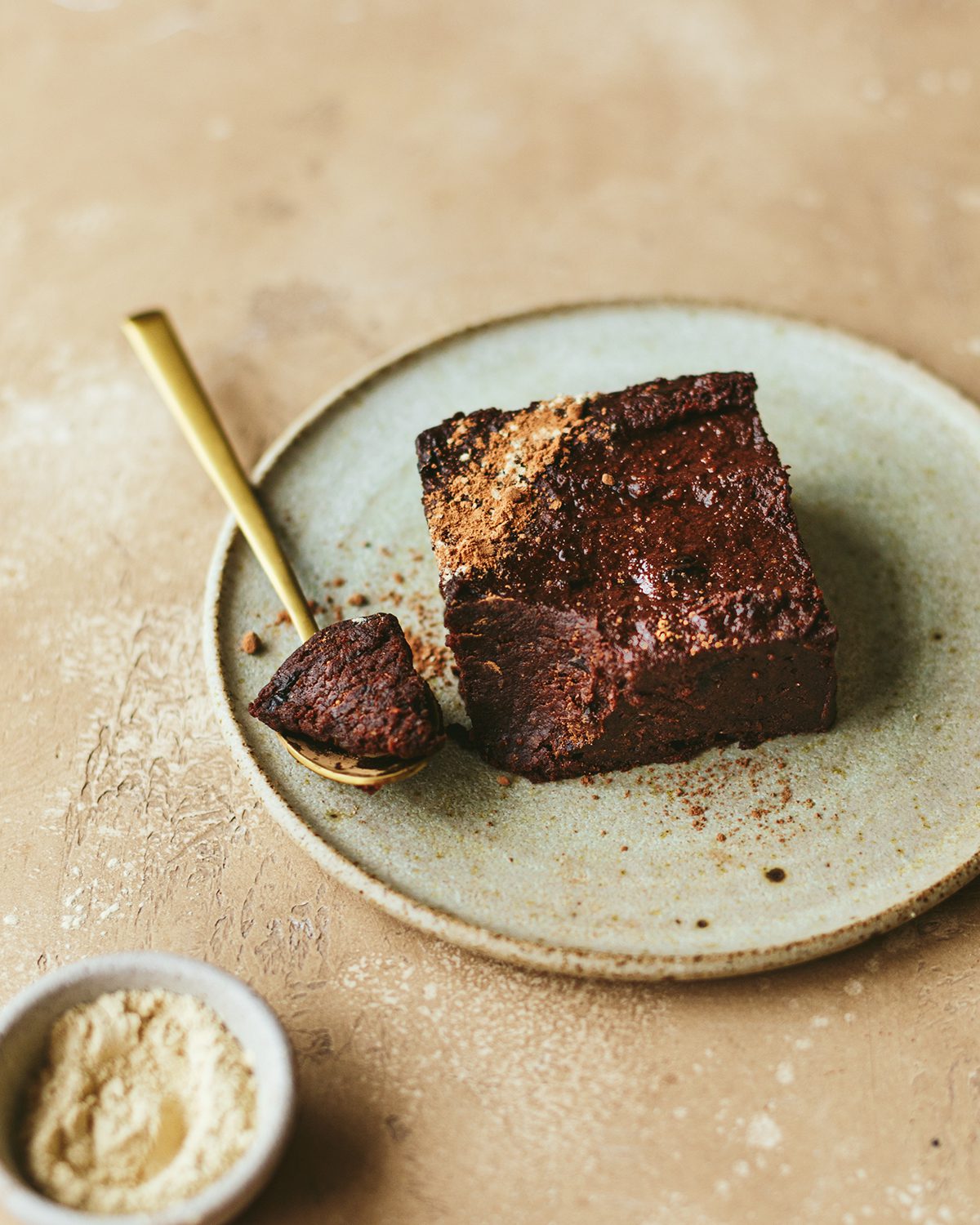

LUX: How successful have you been in attracting investment?
SM: We went out to raise $5M but were oversubscribed and ended up extending the round. It became clear that our proposition is strong, the product is differentiated, and the time is now to lead the future development of food, which is not into fake meats or other processed alternatives. It is real food powered by science and tech. We have one of the best cap tables (possibly) in Europe, with Venture Capital firms like First Minute Capital, Urania Ventures, strategics like Holland and Barrett, and influential business angels like CEO of the Vision Fund, CEO of Palo Alto Networks, Jim Mellon, Jeremy Collar, Mervyn Davies, Lydia Jett and others!
Read more: Chef Rasmus Kofoed: The Vegetable King
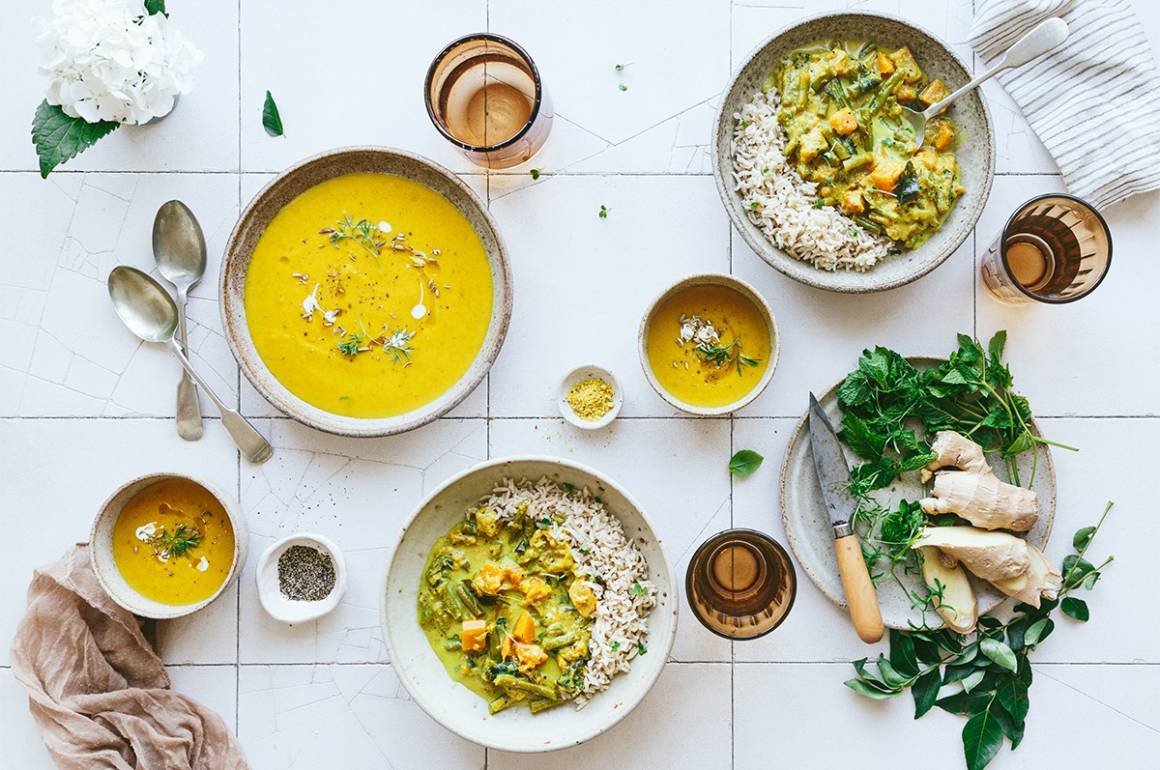
LUX: How do you see tech continue to drive FoodHak’s success forward?
SM: We can use this tech to create any food in any category really quickly, while continuously adding variety on a weekly / monthly basis. We can also use ingredient swaps to create personalised recipes at scale. So, think of us as the new age, health-focussed, food conglomerate that’s powered by science and tech!
Find our more: foodhak.com
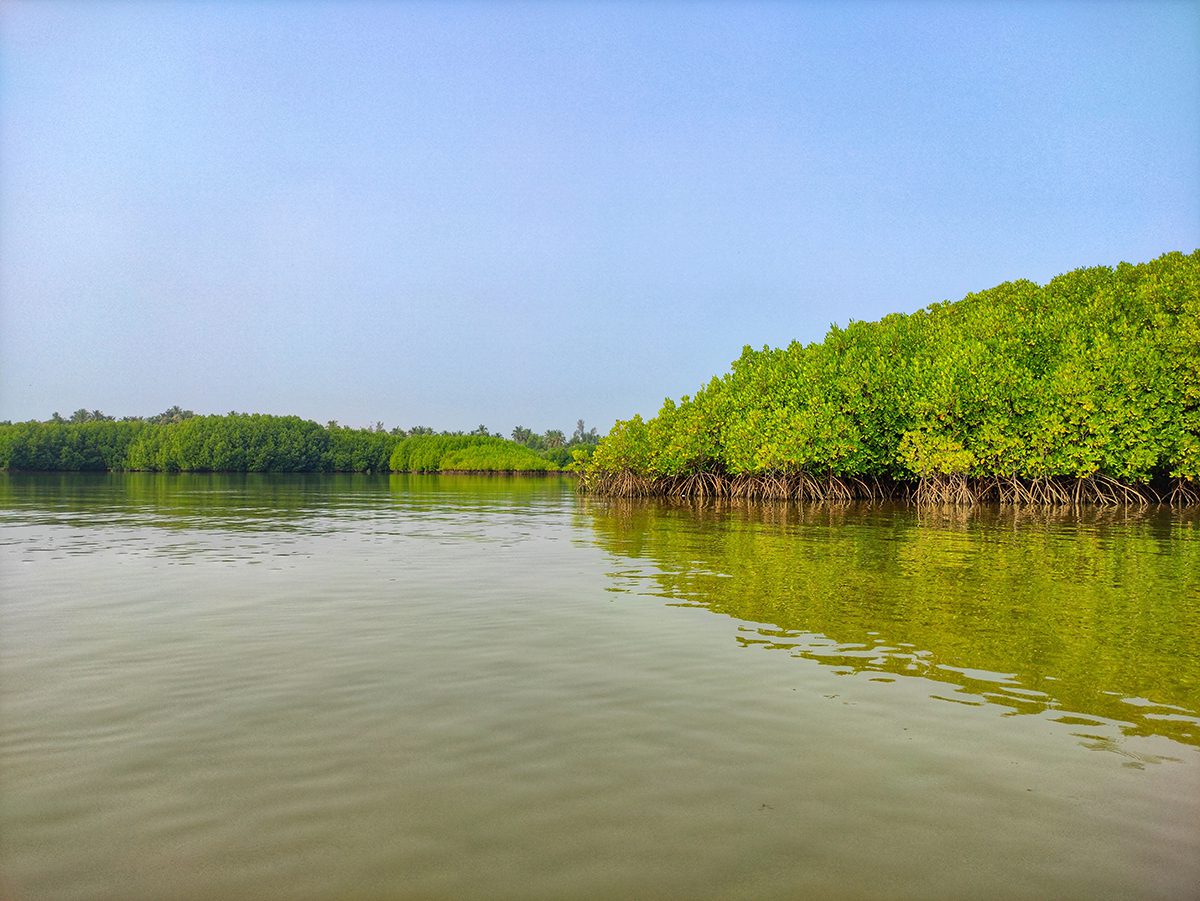















 Can we put a price tag on nature? Valuing the carbon services of plants and animals is essential to bridging the gap between finance and conservation, says Professor Connel Fullenkamp, the leading academic working at the intersection of science and economics. Here, Fullenkamp speaks to LUX about the importance of engaging capital markets in biodiversity financing, and why necessity is the mother of invention
Can we put a price tag on nature? Valuing the carbon services of plants and animals is essential to bridging the gap between finance and conservation, says Professor Connel Fullenkamp, the leading academic working at the intersection of science and economics. Here, Fullenkamp speaks to LUX about the importance of engaging capital markets in biodiversity financing, and why necessity is the mother of invention
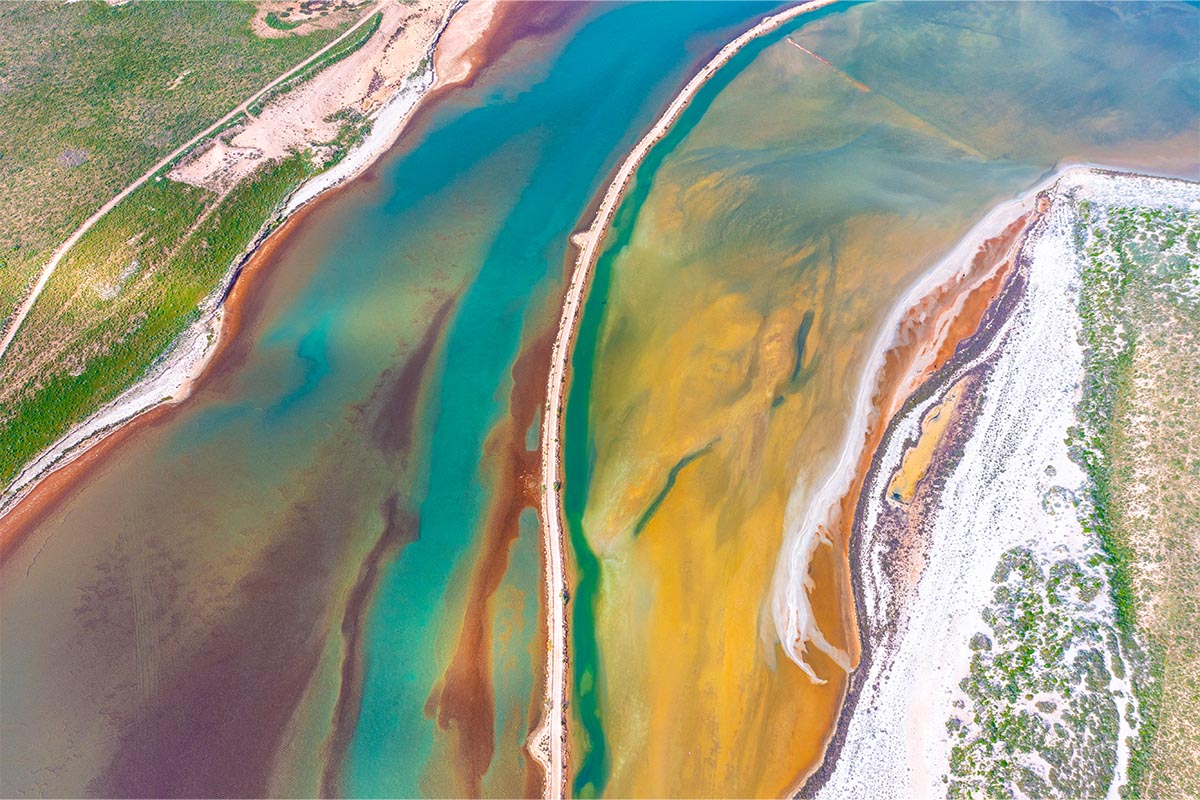
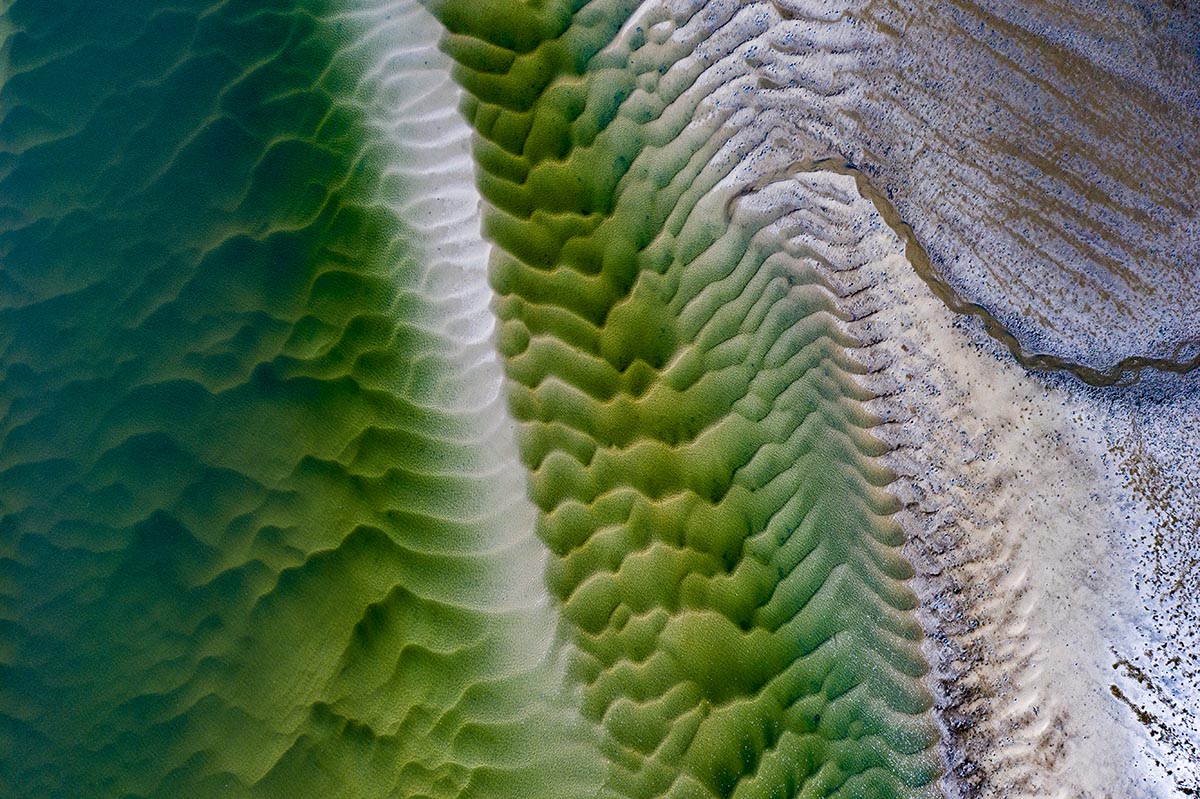
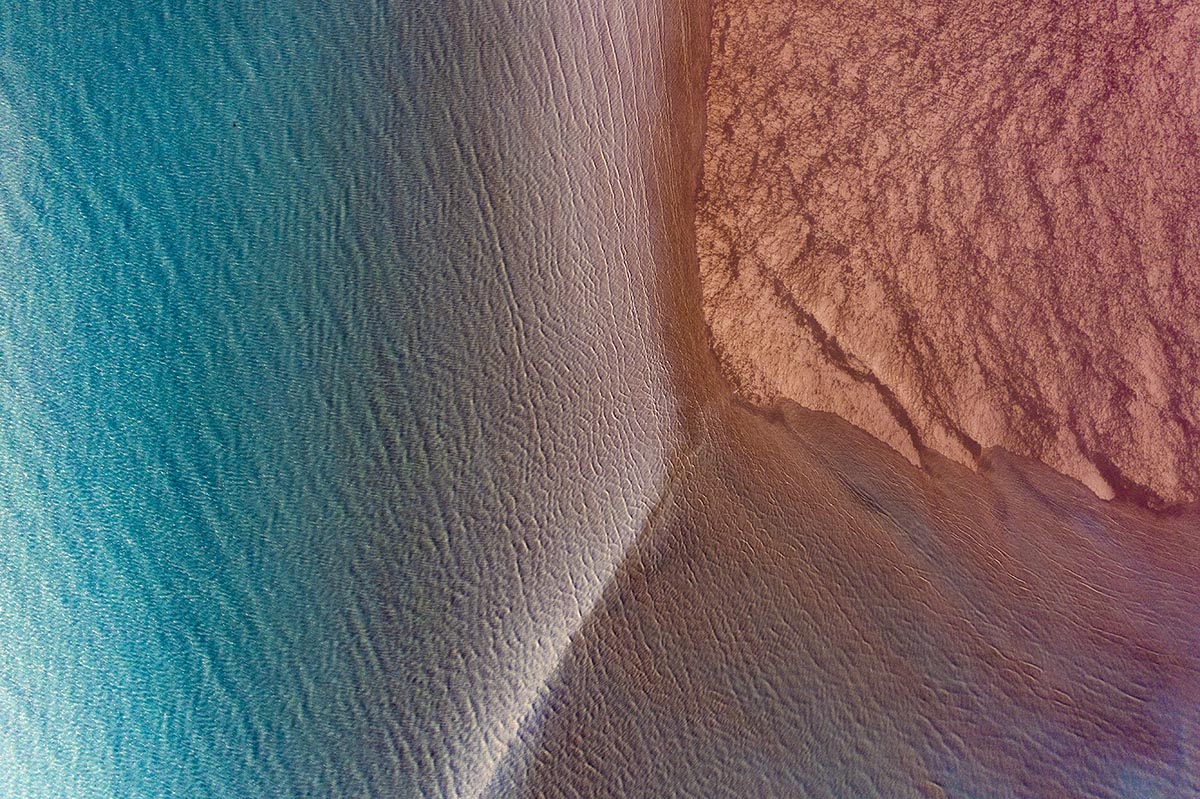
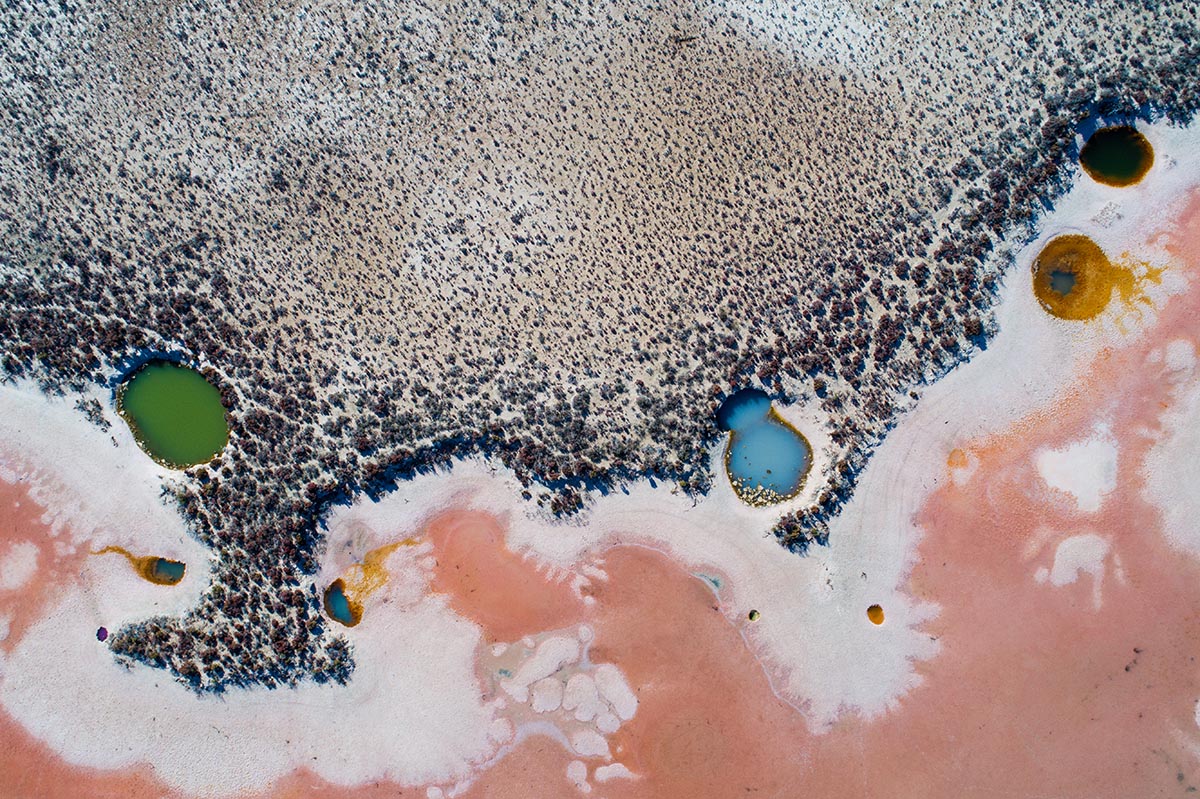
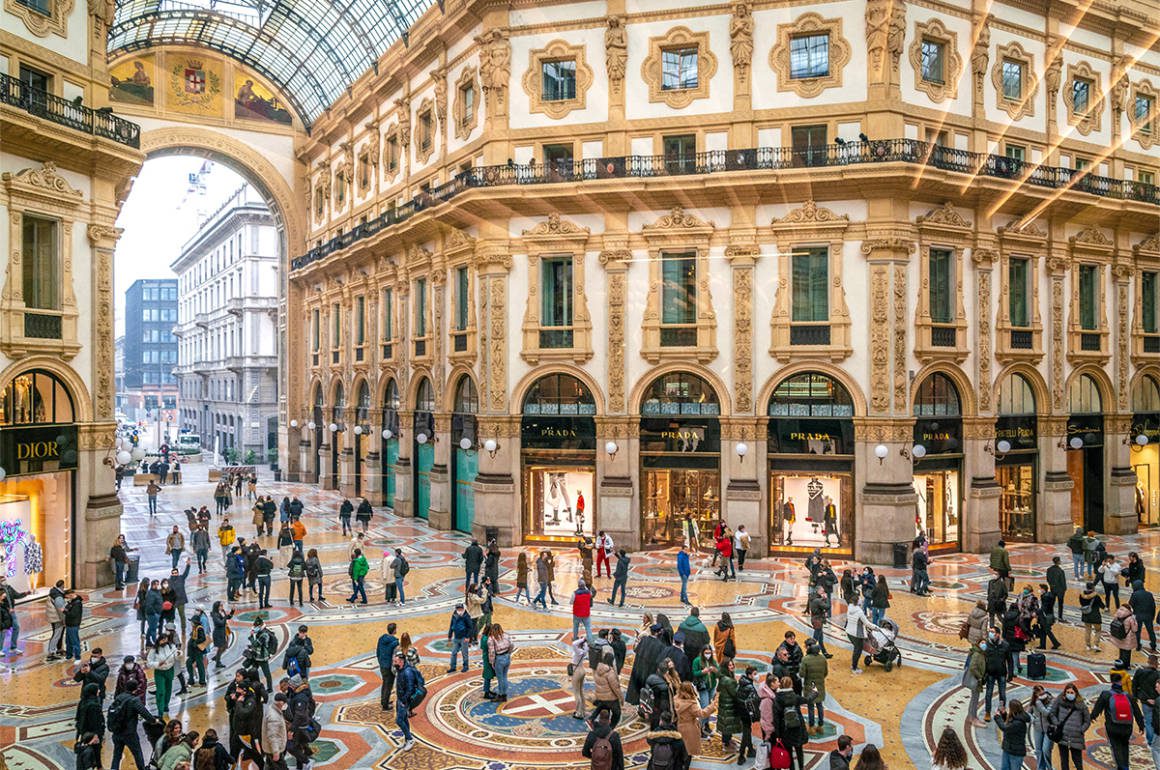
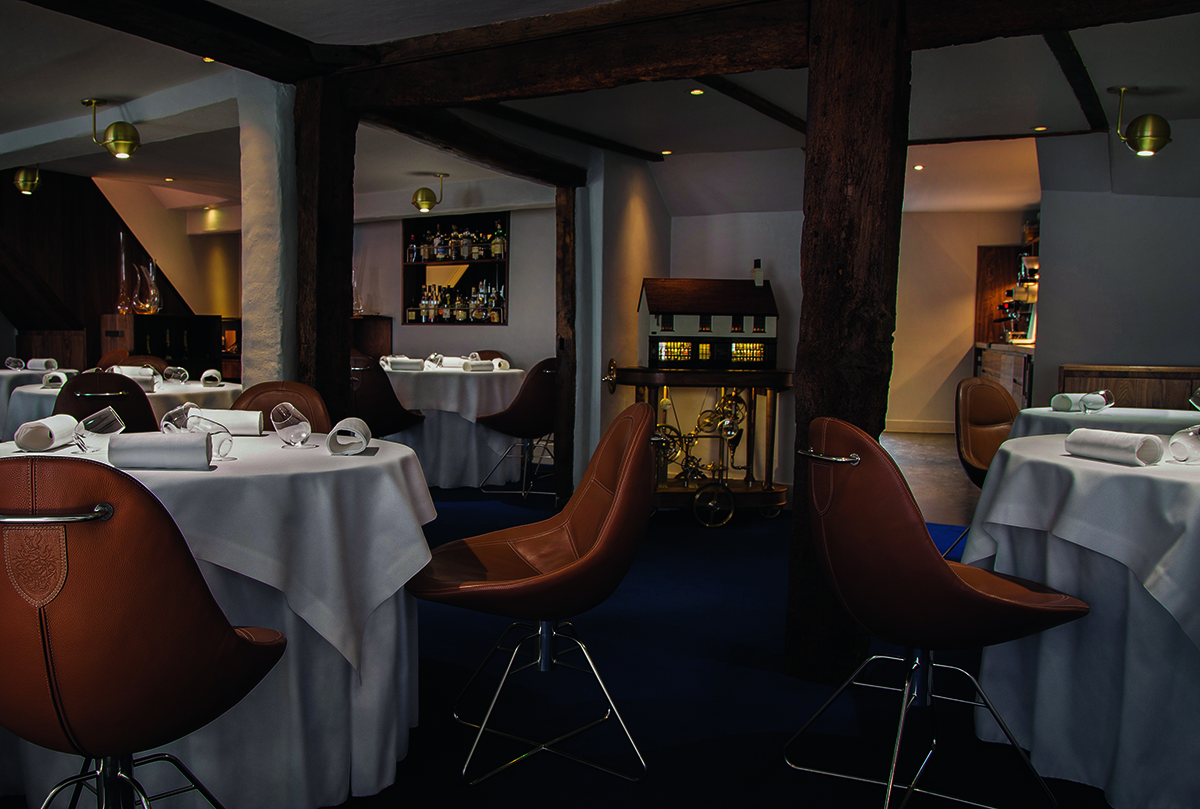
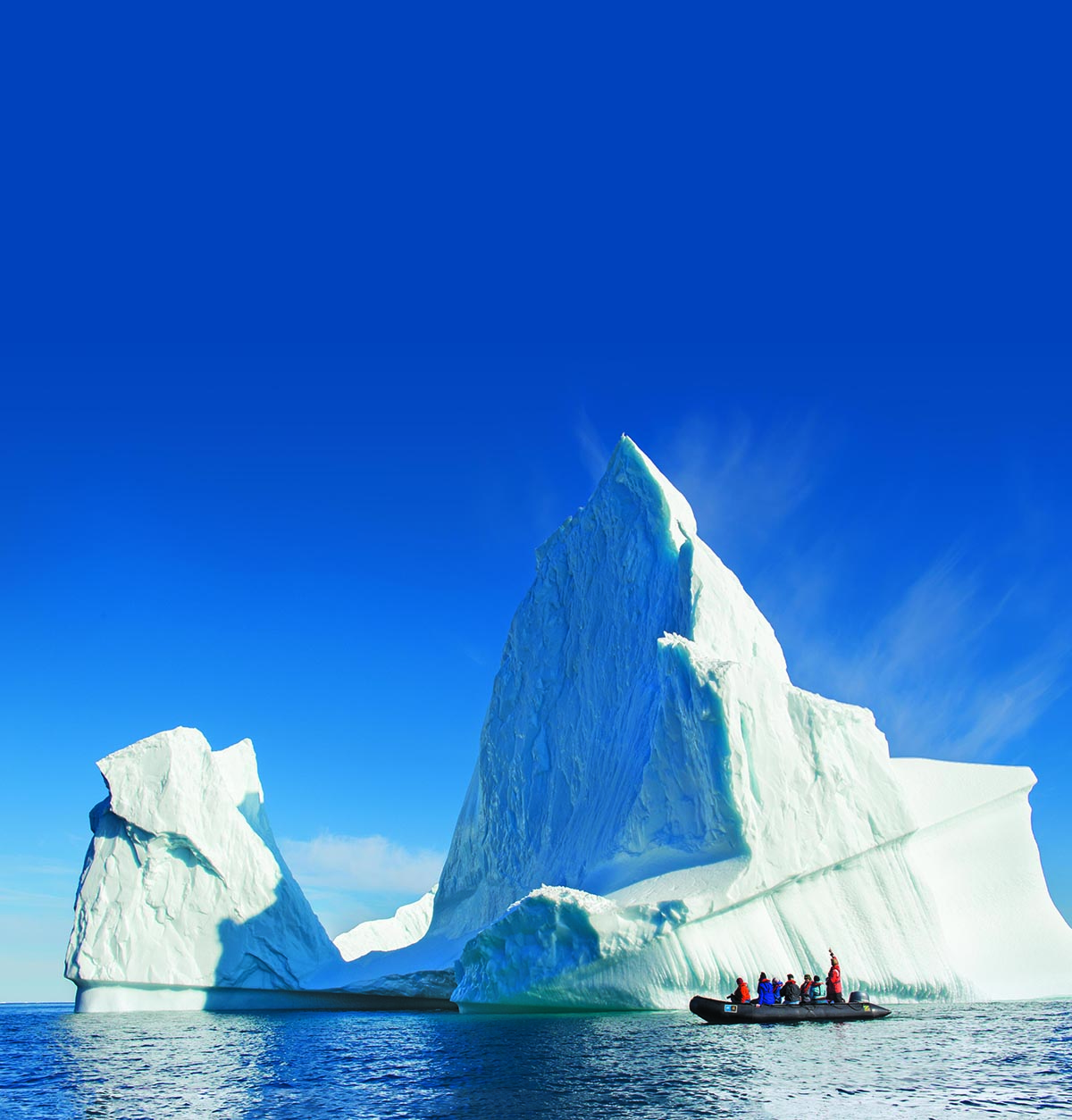
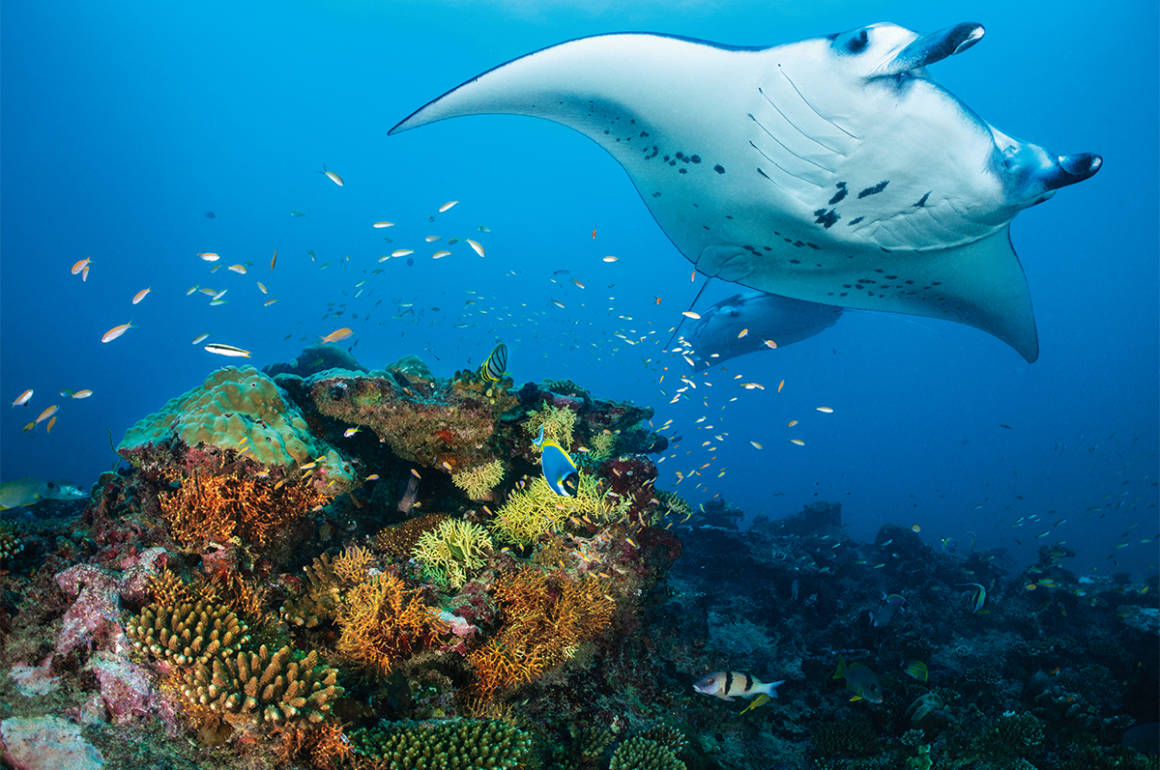
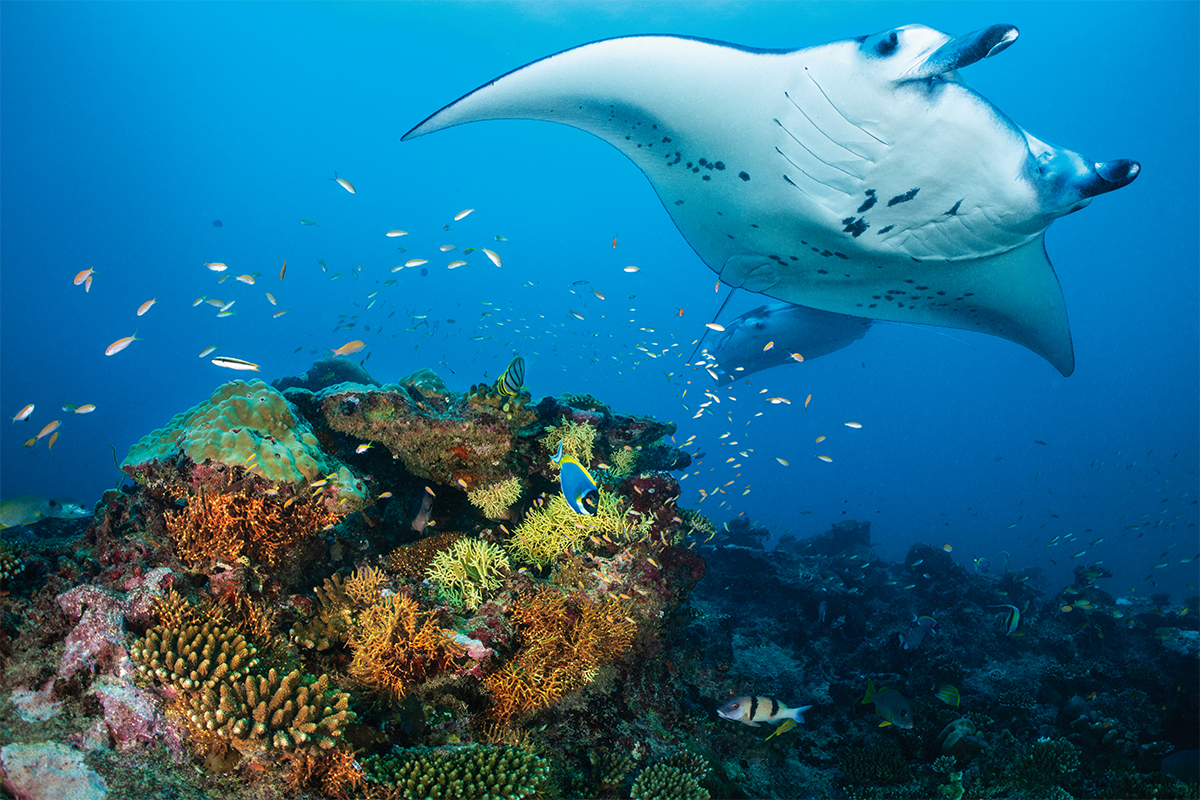
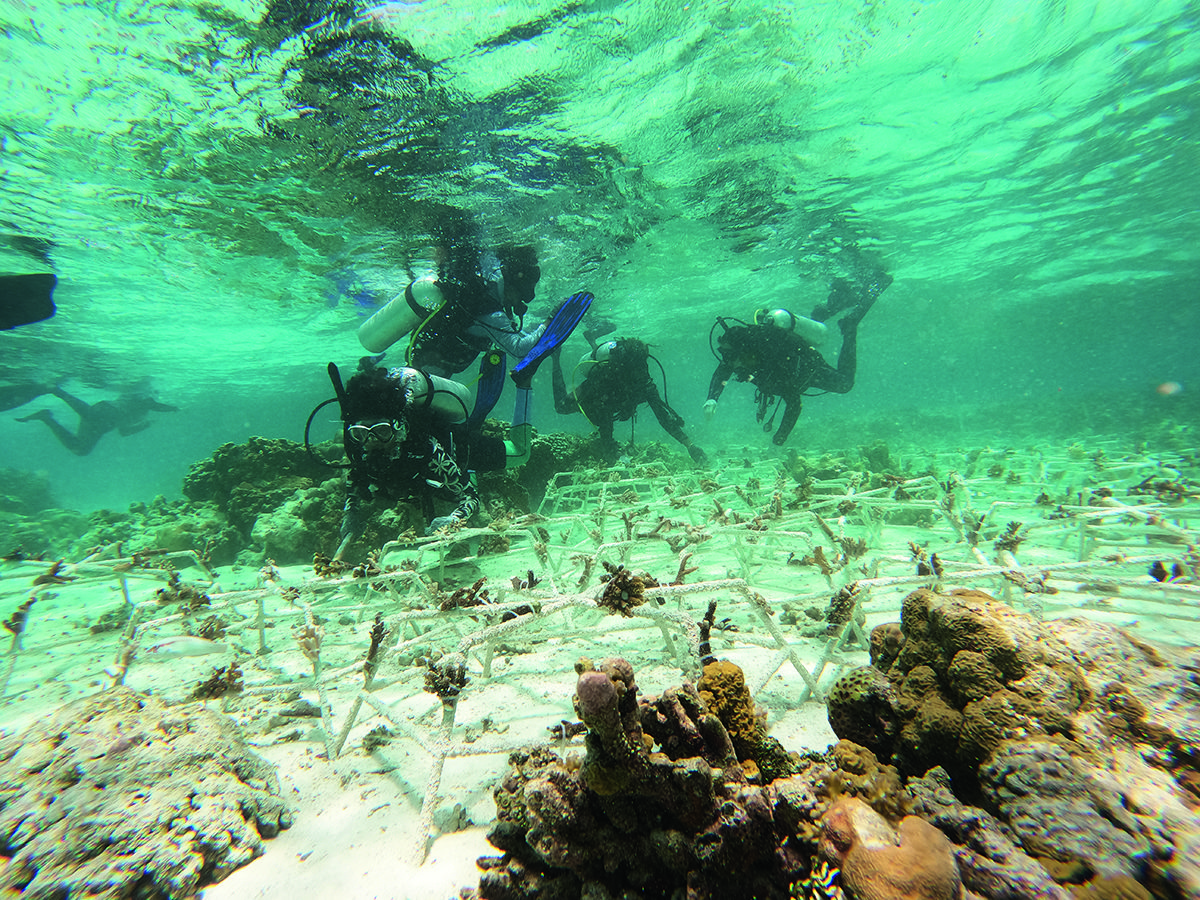
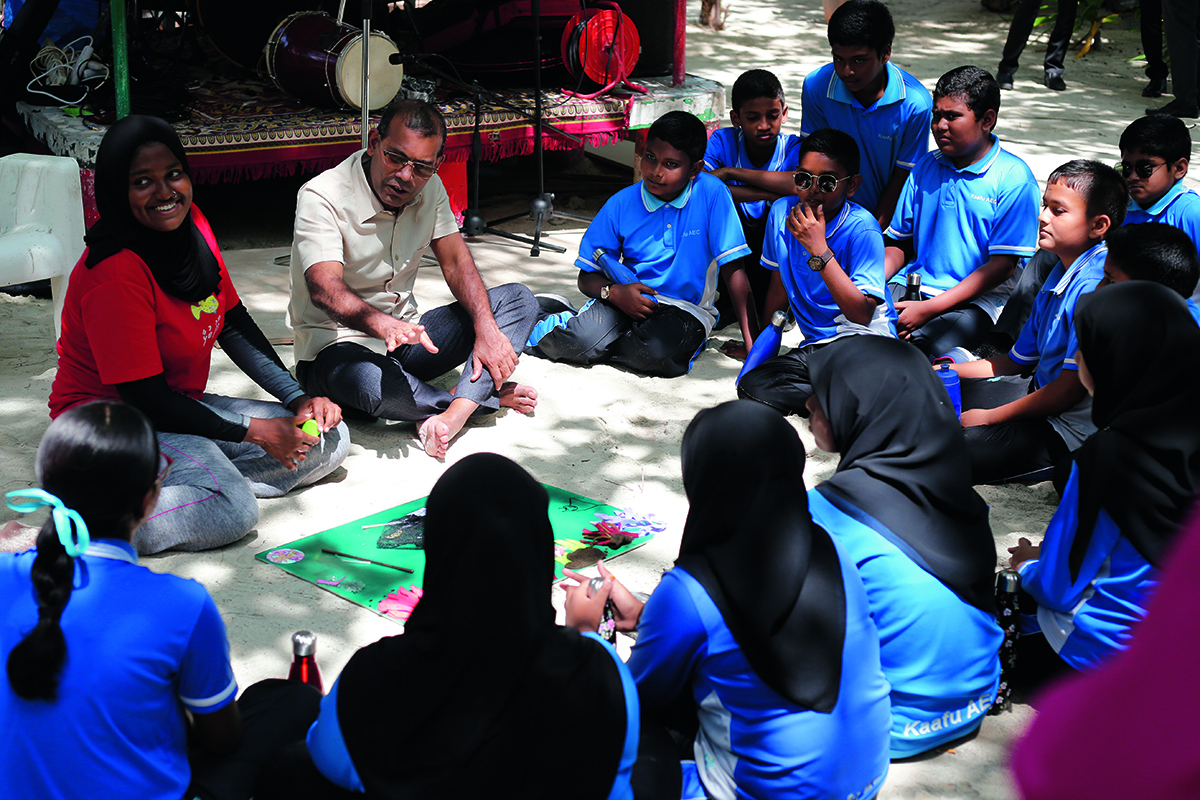
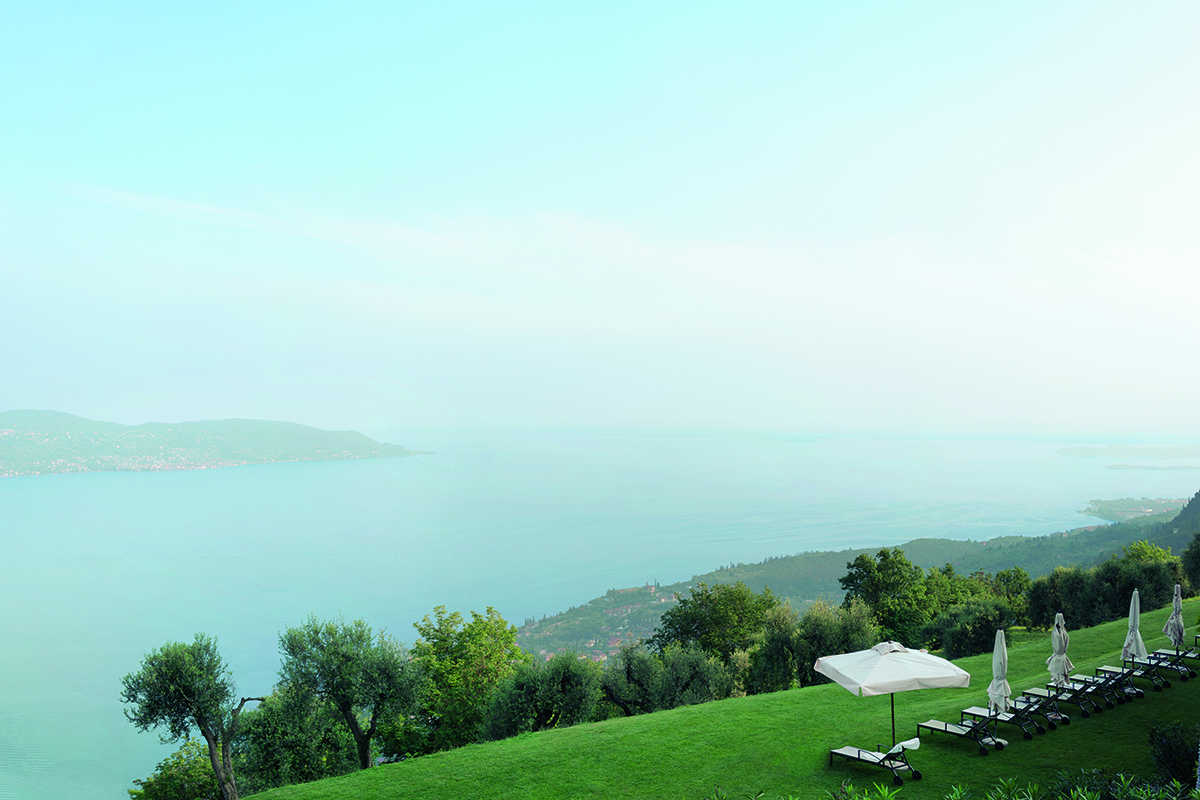
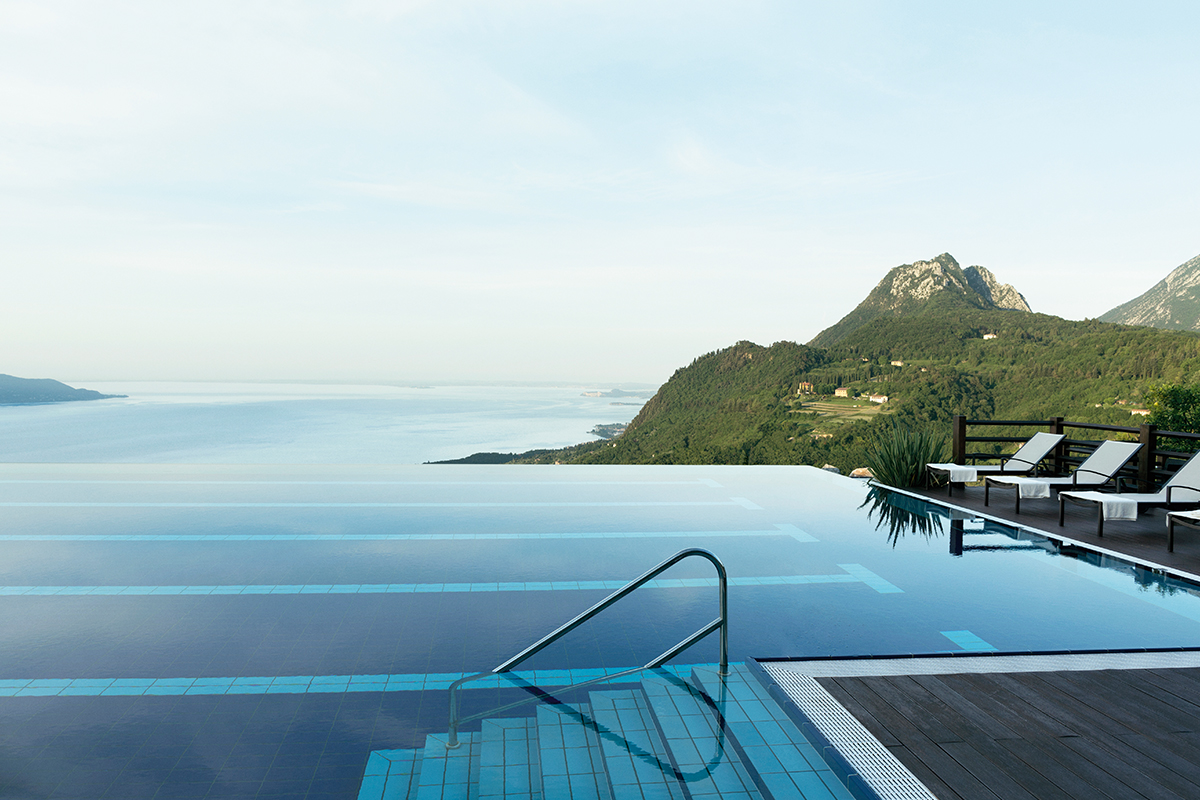
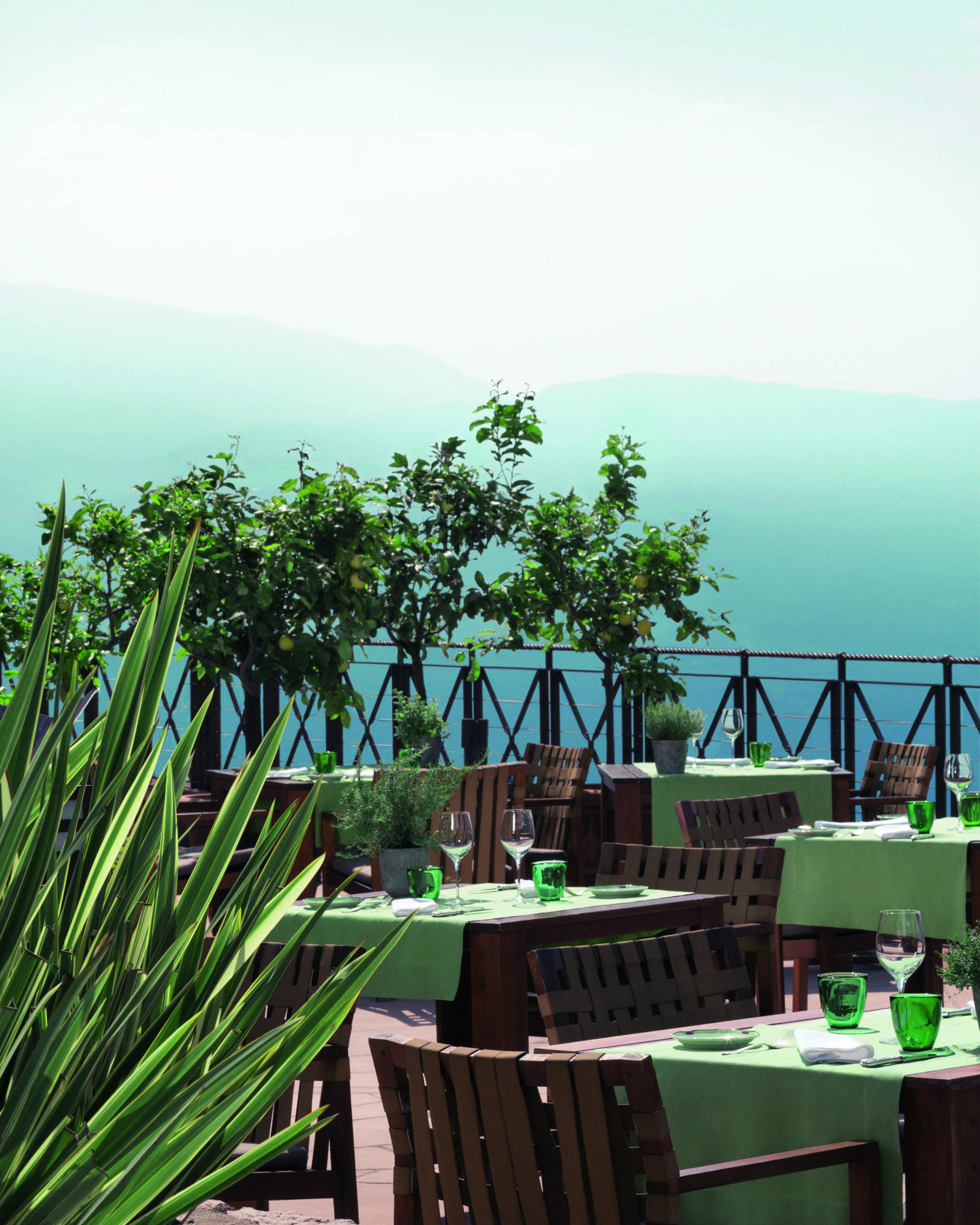
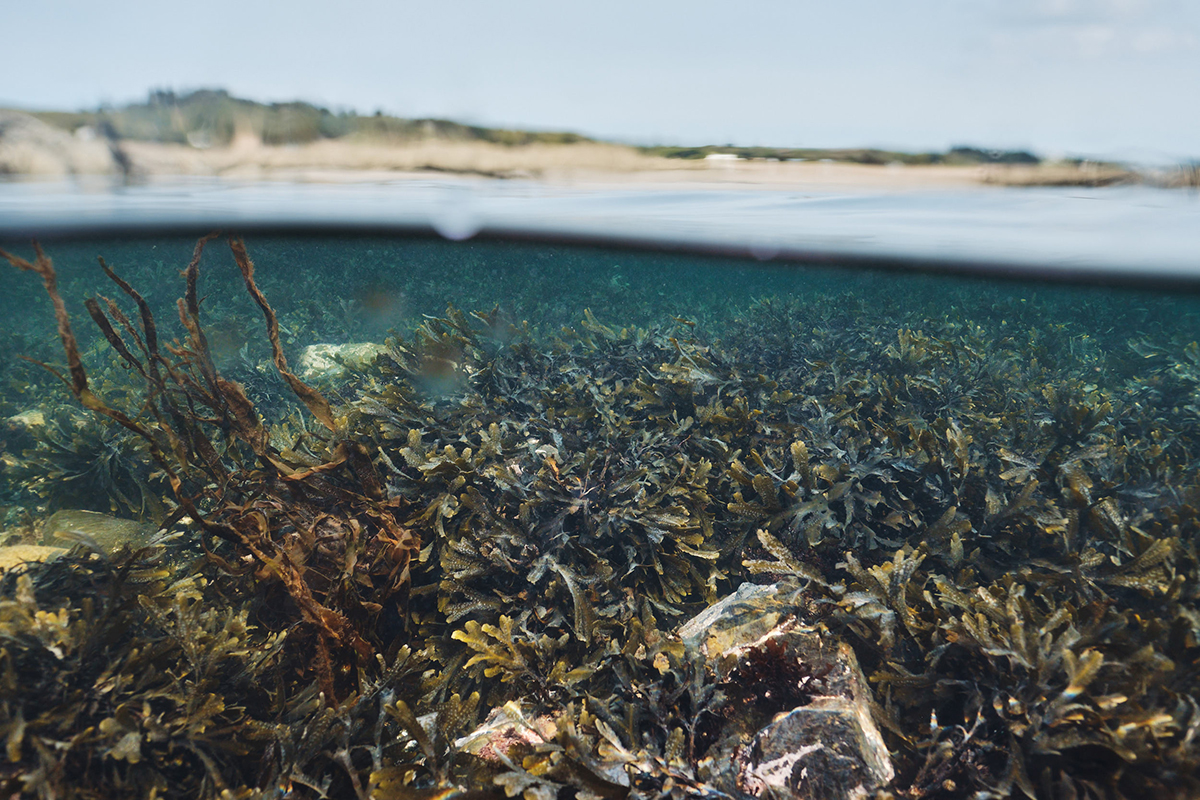
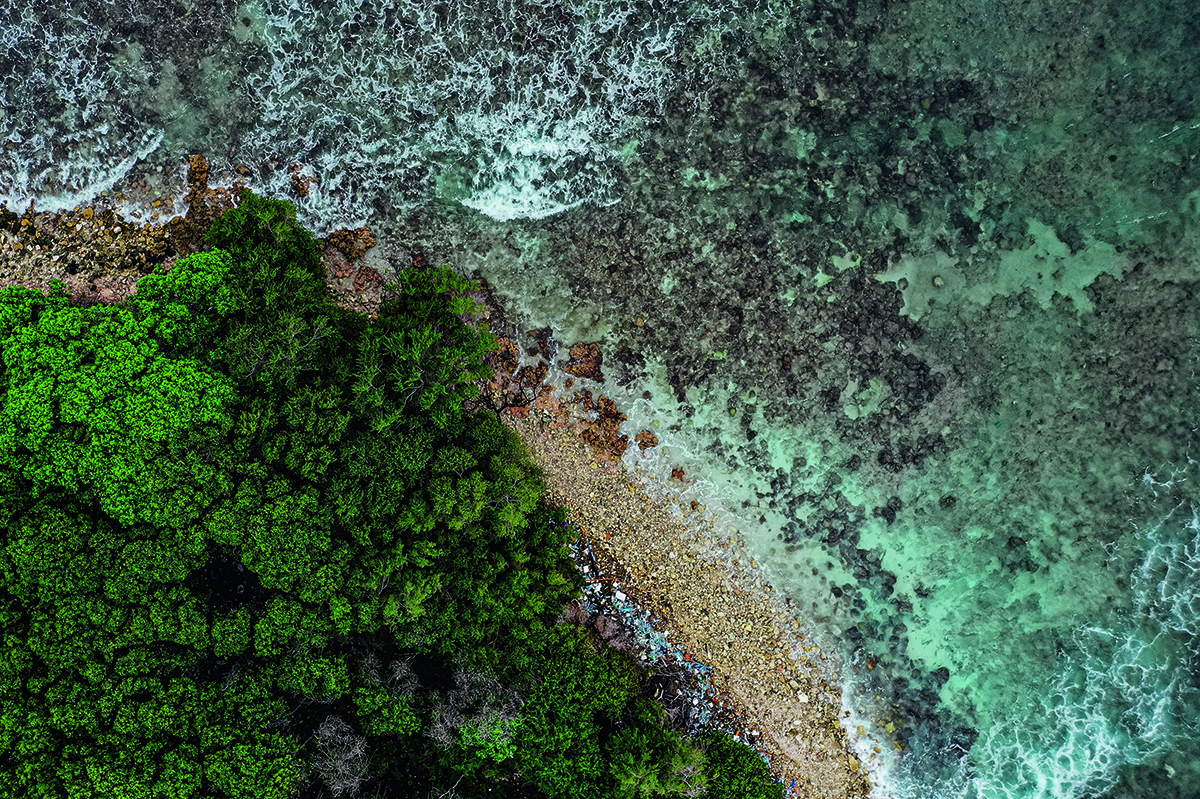
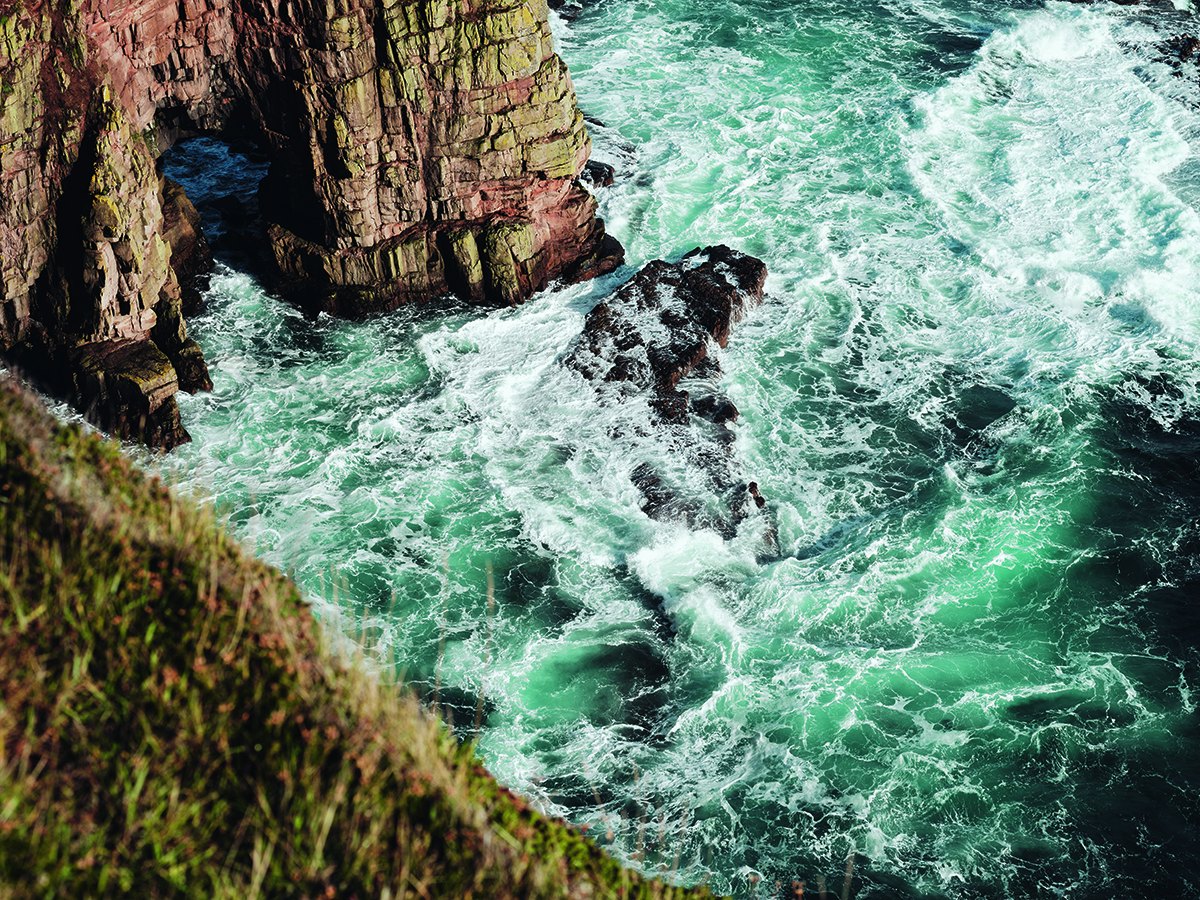
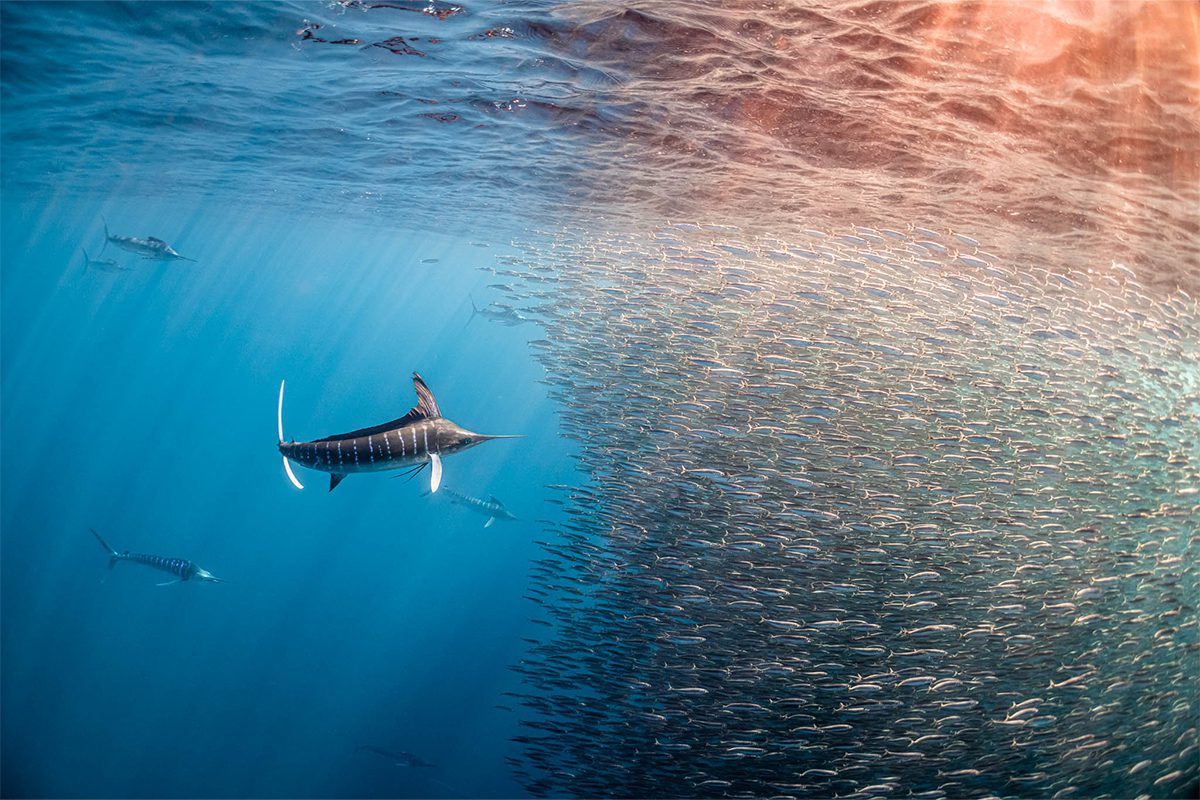
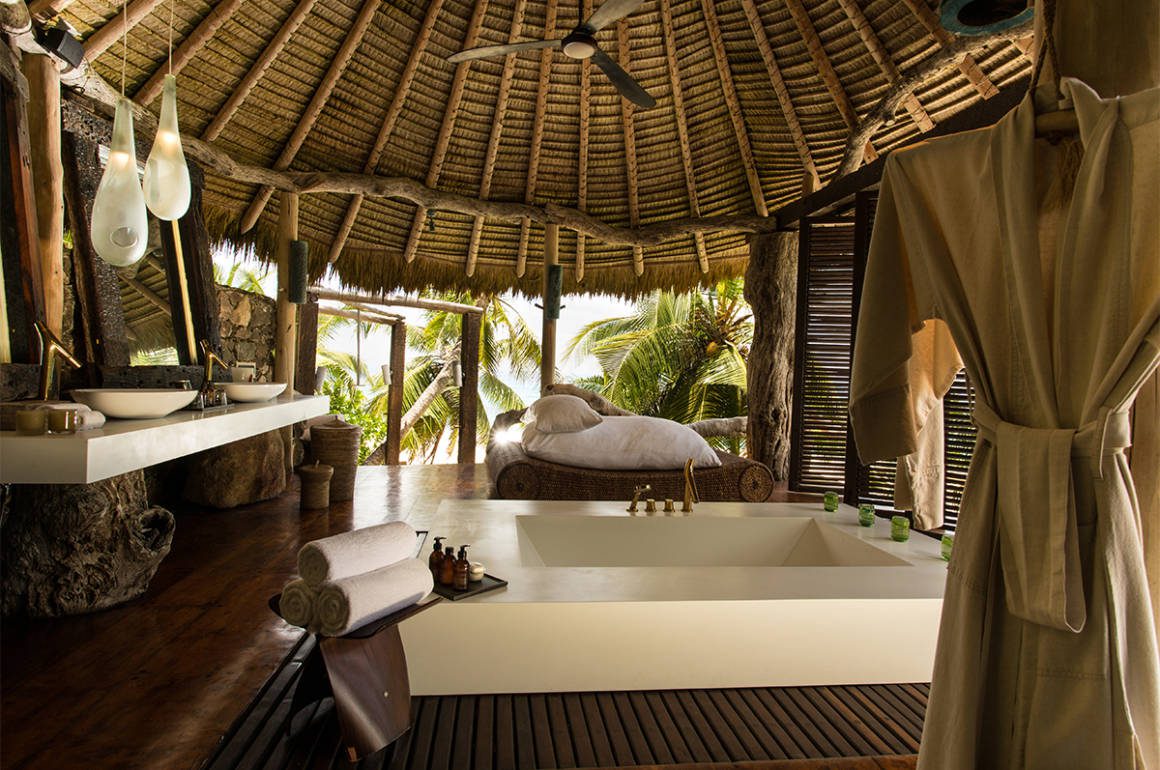
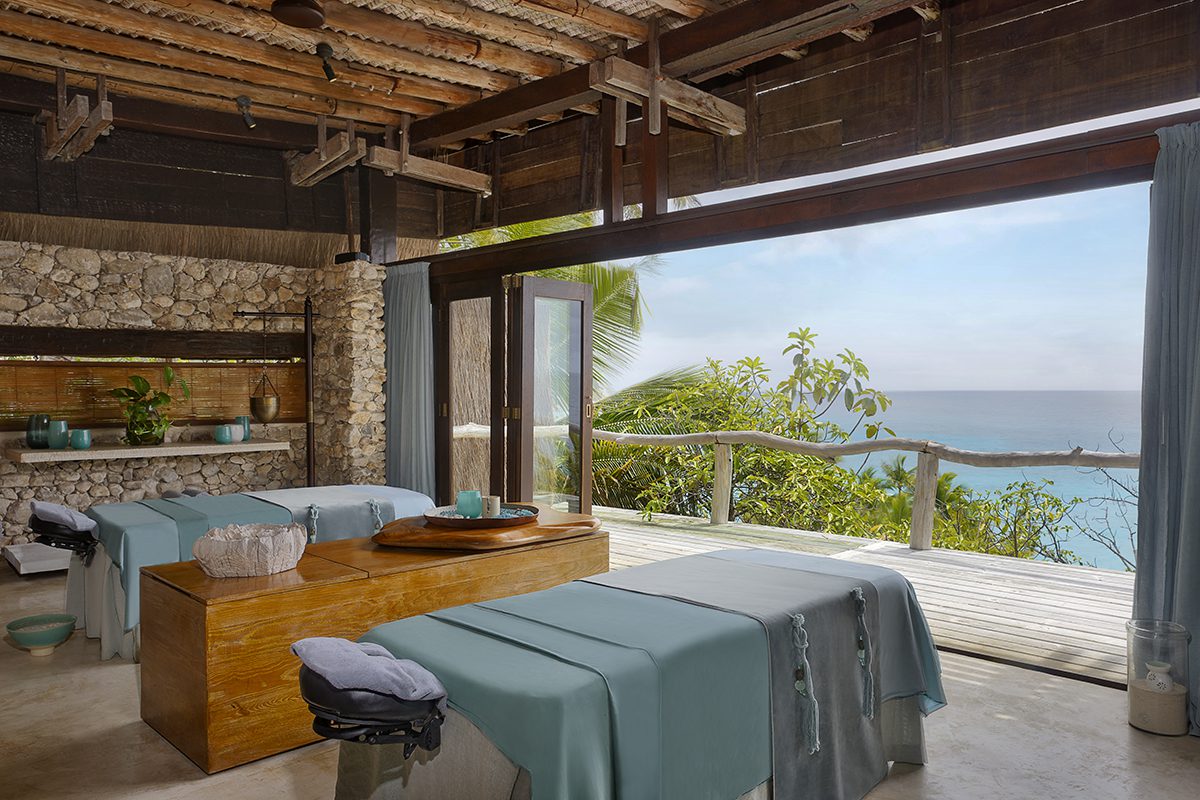





































































































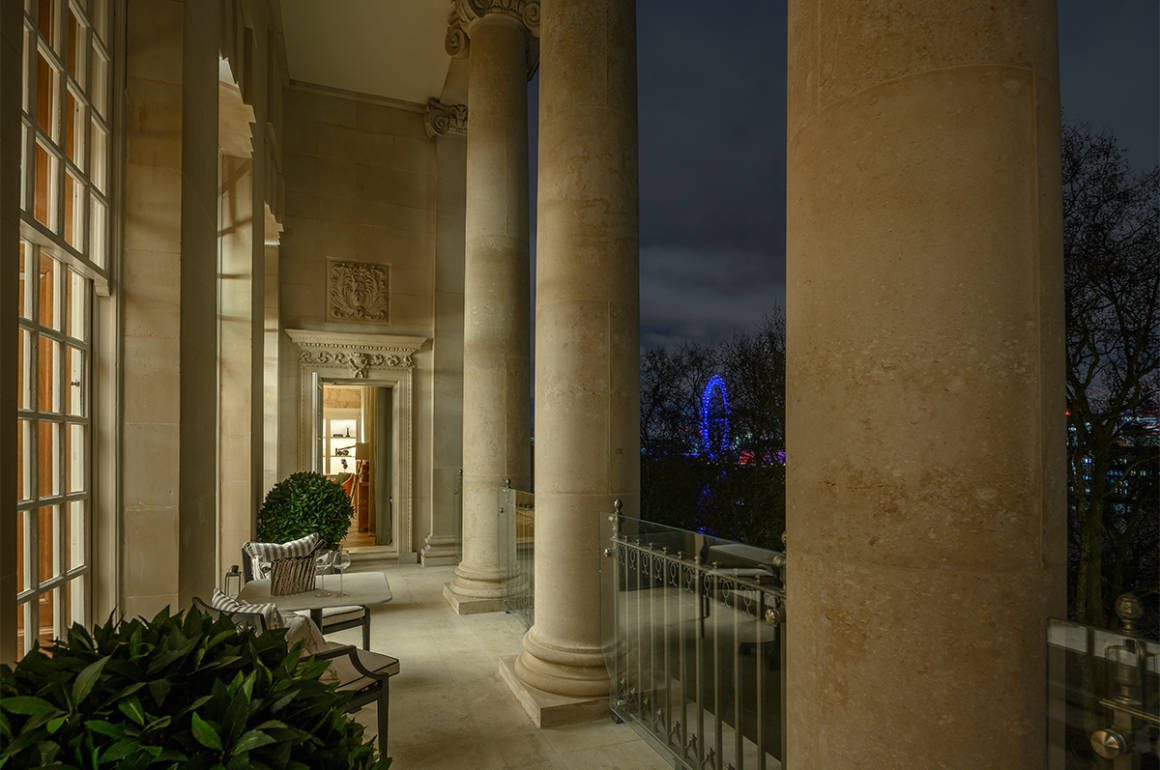
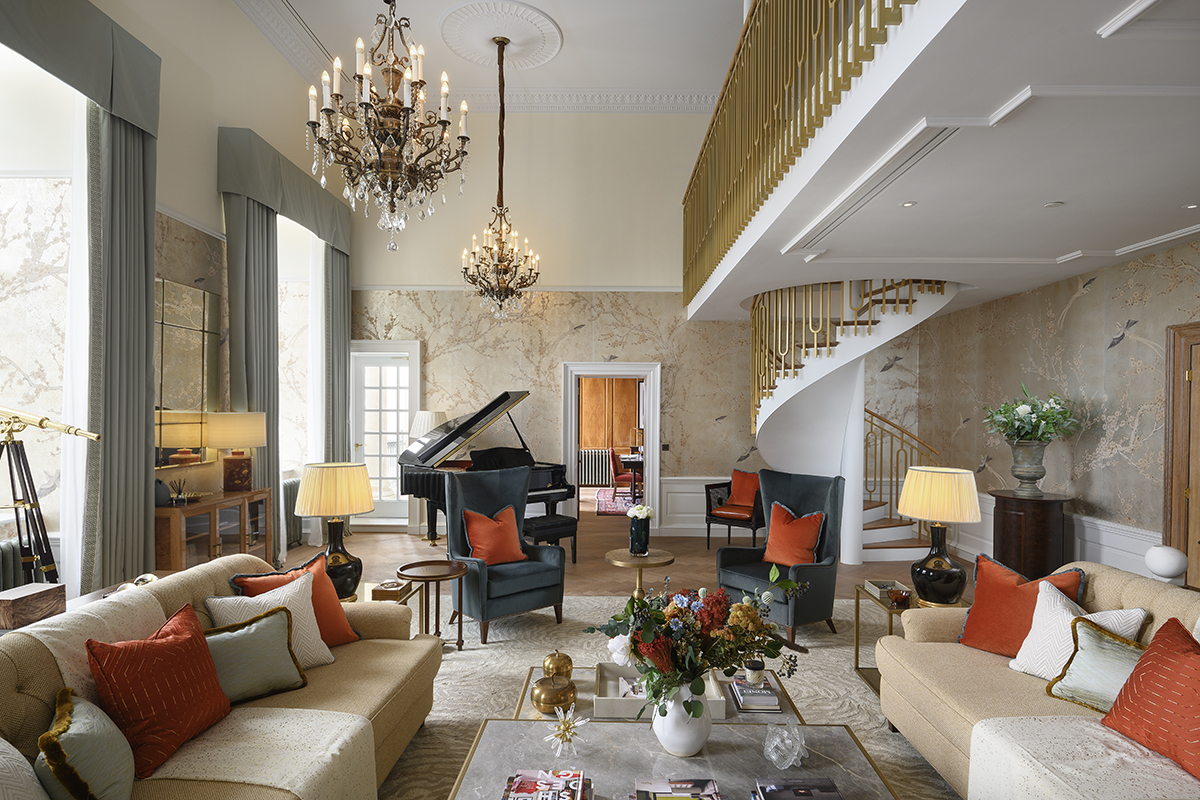
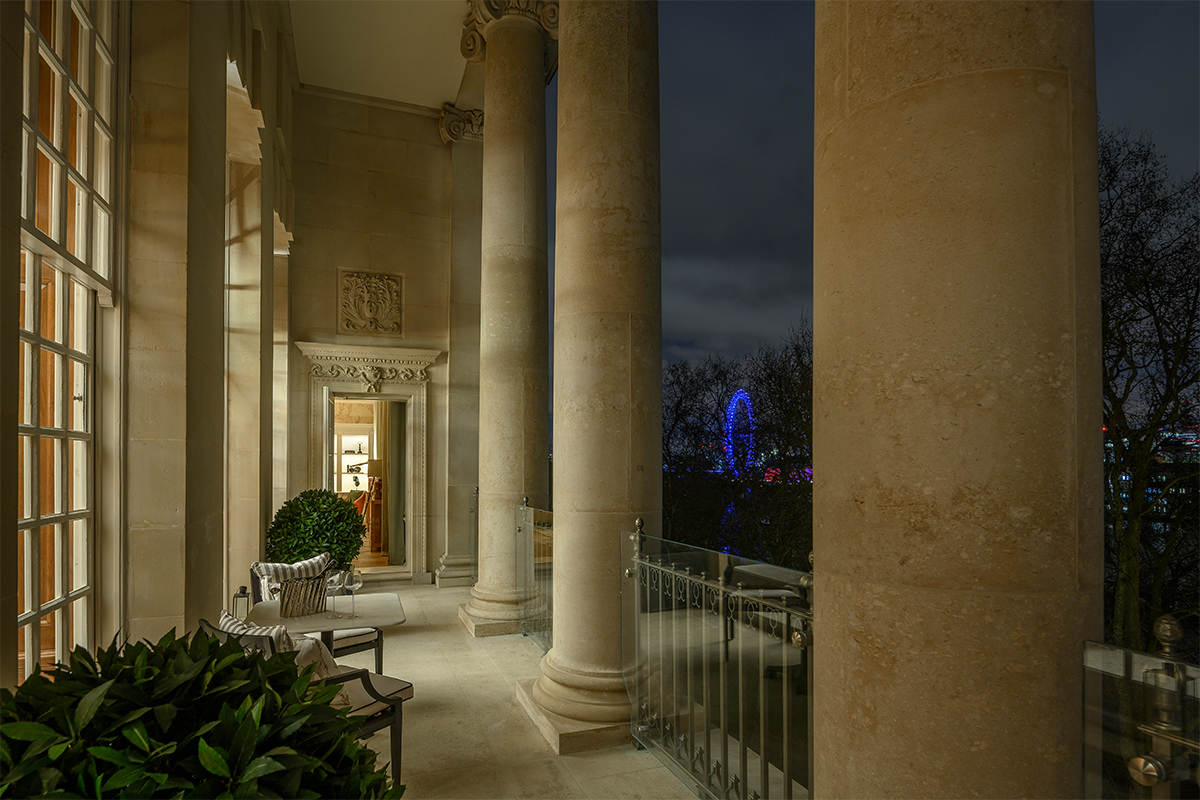
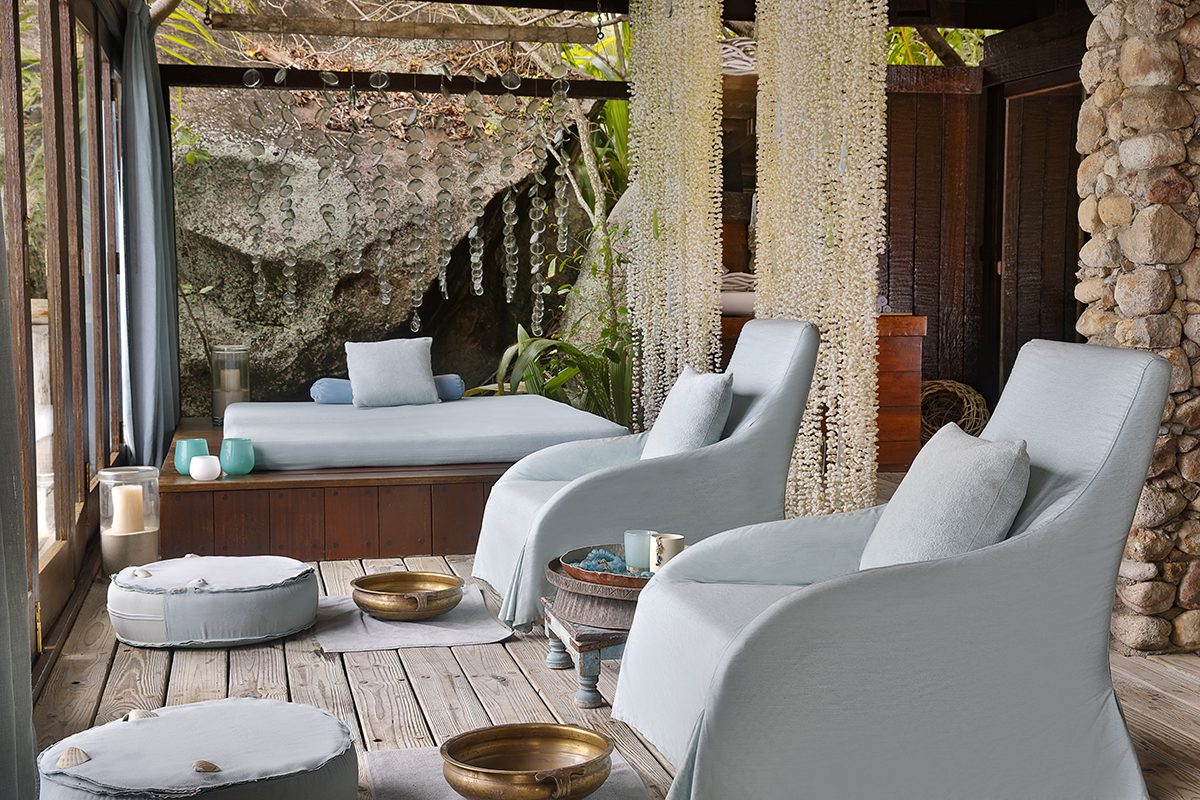
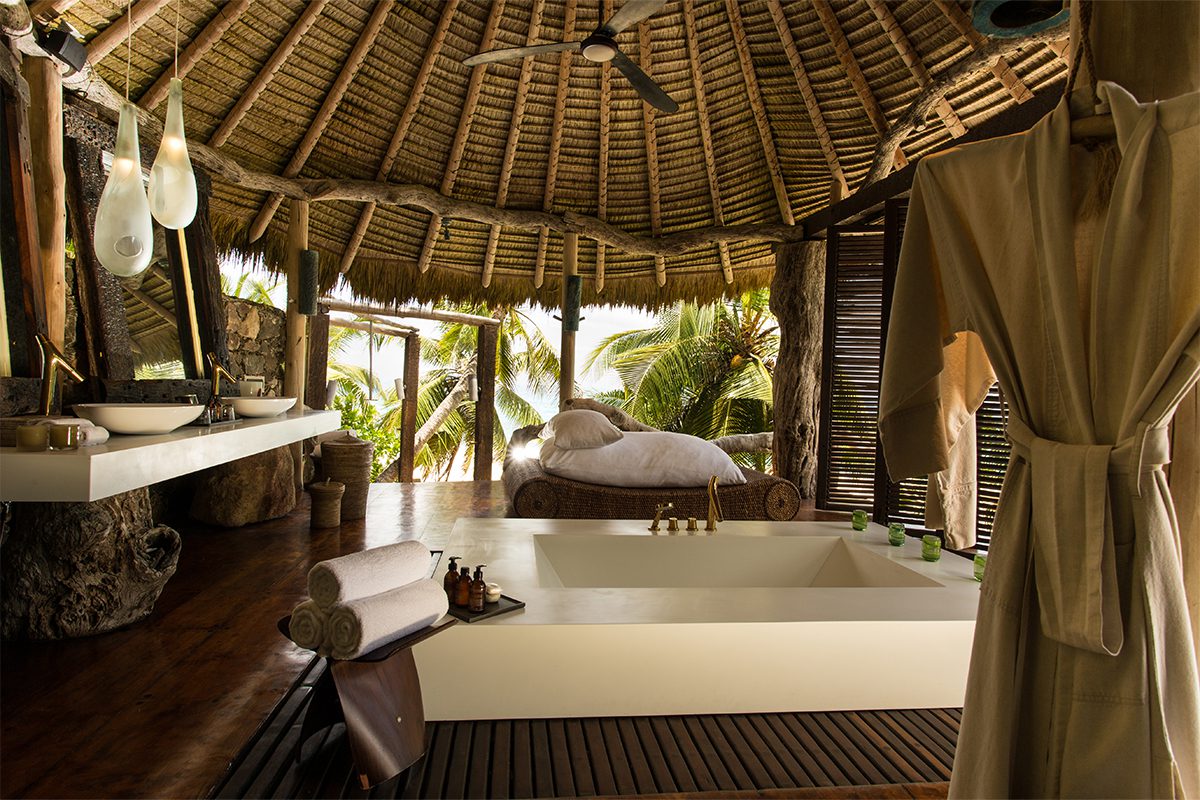
 Clinique La Prairie has established itself as a leading name in longevity research, offering wellness programmes for over ninety years. For its inaugural escape far away from its traditional Alps and Lake Geneva landscape, the brand has set base on North Island Resort in the Seychelles to create a complete Clinique La Prairie experience
Clinique La Prairie has established itself as a leading name in longevity research, offering wellness programmes for over ninety years. For its inaugural escape far away from its traditional Alps and Lake Geneva landscape, the brand has set base on North Island Resort in the Seychelles to create a complete Clinique La Prairie experience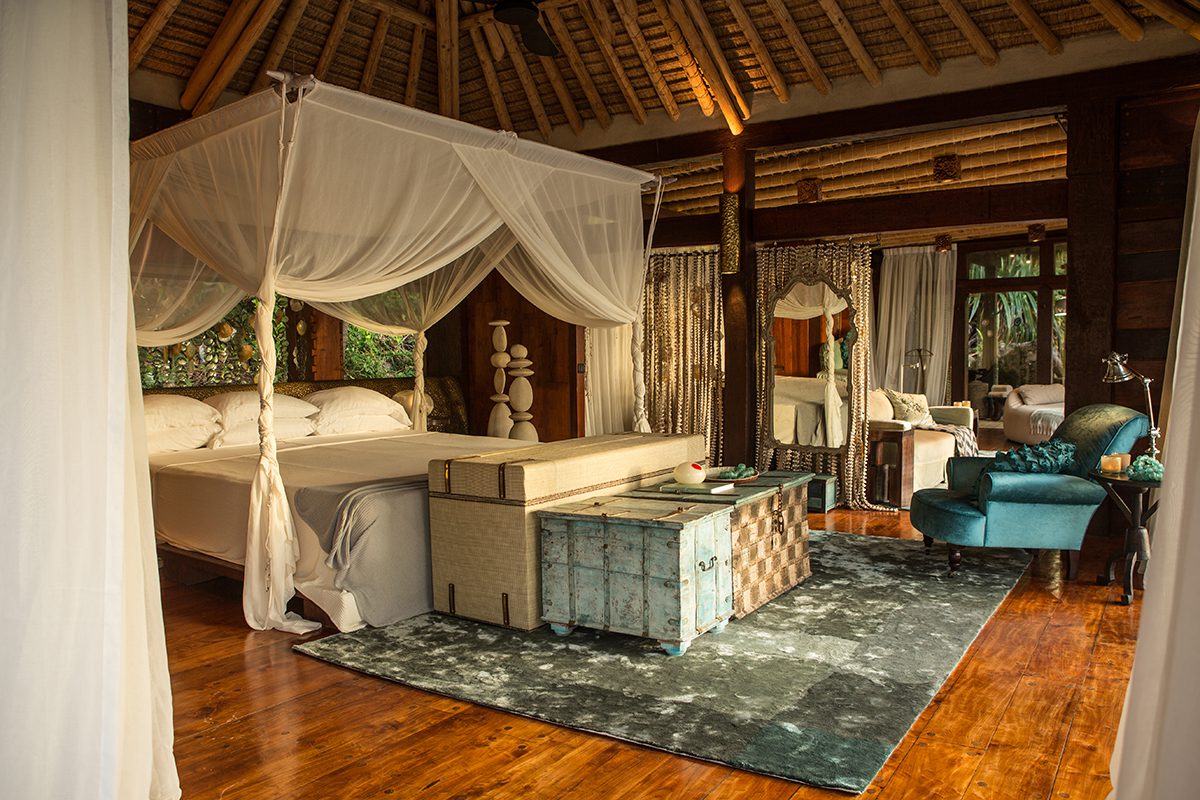








Recent Comments